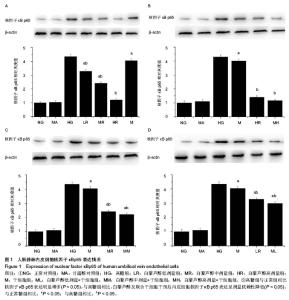
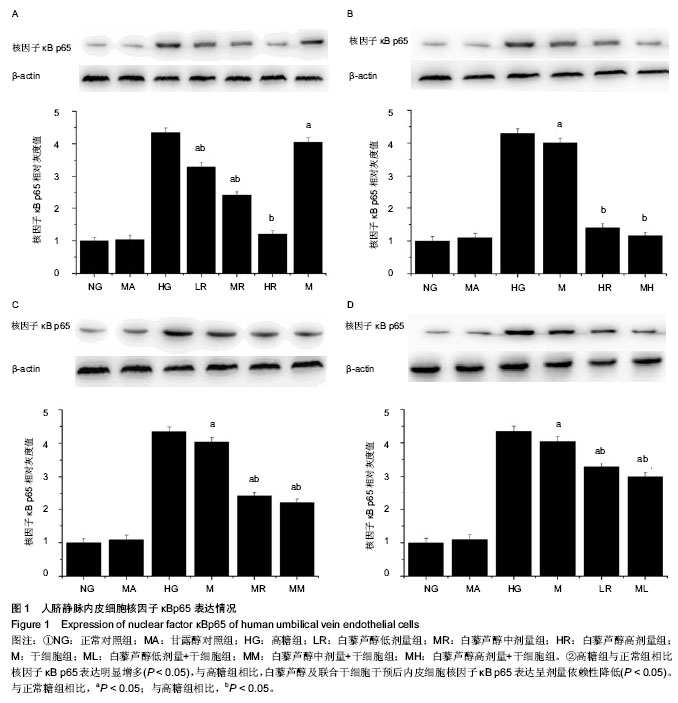
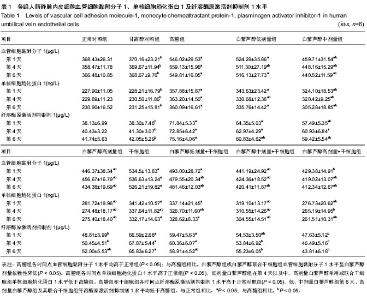
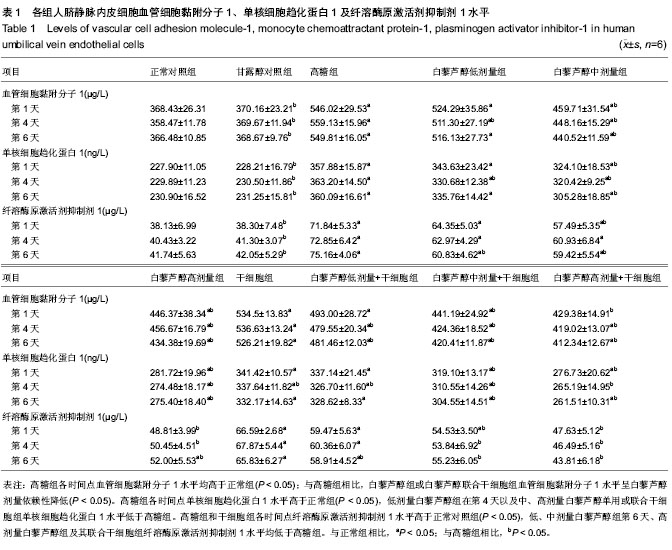
| [1] Potenza MA, Gagliardi S, Nacci C,et al. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes: from mechanisms to therapeutic targets. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(1):94-112.
[2] 曹烨,关新强,徐志懿,等.白藜卢醇对心血管保护作用的研究进展[J].医学综述,2013,19(23):4231-4237.
[3] Xu Q, Hao X, Yang Q, et al. Resveratrol prevents hyperglycemia-induced endothelial dysfunction via activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;388(2):389-394.
[4] Crisostomo PR, Abarbanell AM, Wang M, et al.Embryonic stem cells attenuate myocardial dysfunction and inflammation after surgical global ischemia via paracrine actions. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008;295: H1726–H1735.
[5] Crisostomo PR, Wang M, Markel TA, et al. Stem cell mechanisms and paracrine effects: potential in cardiac surgery. Shock. 2007;28: 375–383.
[6] Weil BR, Abarbanell AM, Herrmann JL, et al.High glucose concentration in cell culture medium does not acutely affect human mesenchymal stem cell growth factor production or proliferation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009; 296(6):R1735-1743.
[7] 林雪波,周波,孙芳,等.蛋白激酶Cβ2-活性氧交互环介导高糖致内皮细胞损伤记忆效应[J].中华内科杂志,2010,49(3):239-244.
[8] Brownlee M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature.2001; 414(6865):813–820.
[9] Tanaka N, Yonekura H, Yamagishi S, et al.The receptor for advanced glycation end products is induced by the glycation products themselves and tumor necrosis factor-alpha through nuclear factor-kappa B, and by 17beta-estradiol through Sp-1 in human vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275 (33):25781-25790.
[10] El-Osta A, Brasacchio D, Yao D, et al. Transient high glucose causes persistent epigenetic changes and altered gene expression during subsequent normoglycemia. J Exp Med. 2008;205(10):2409-2417.
[11] Migita H, Morser J.15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2) signals through retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor-alpha but not peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in human vascular endothelial cells: the effect of 15d-PGJ2 on tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced gene expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005 ;25(4):710-716.
[12] Piga R, Naito Y, Kokura S, et al. Short-term high glucose exposure induces monocyte-endothelial cells adhesion and transmigration by increasing VCAM-1 and MCP-1 expression in human aortic endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 2007; 193(2): 328-334.
[13] Xu J,Zou MH.Molecular insights and therapeutic targets for diabetic endothelial dysfunction.Circulation.2009;120(13): 1266-1286.
[14] Seneviratne AN,Sivagurunathan B,Monaco C. Toll-like receptors and macrophage activation in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta.2012 ;413(1-2):3-14.
[15] Hoekstra T,Geleijnse JM,Schouten EG,et al.Plasminogen activator inhibitor-type 1: its plasma determinants and relation with cardiovascular risk. Thromb Haemost. 2004;91(5): 861-872.
[16] Denk A, Goebeler M, Sybille S, et al. Activation of NF-κB via the IκB Kinase Complex Is Both Essential and Sufficient for Proinflammatory Gene Expression in Primary Endothelial Cells. J Biol Chem.2001;276(30):28451-28458.
[17] Kim MH, Yoo DS, Lee SY, et al. The TRIF/TBK1/IRF-3 activation pathway is the primary inhibitory target of resveratrol, contributing to its broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory effects. Pharmazie.2011;66(4):293- 300.
[18] Schober A, Thum T, Zernecke A. MicroRNAs in vascular biology-metabolism and atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107(4):603-604.
[19] Schächinger V, Assmus B, Britten MB, et al.Transplantation of progenitor cells and regeneration enhancement in acute myocardial infarction: final one-year results of the TOPCARE-AMI Trial.J Am Coll Cardiol.2004;44(8): 1690-1699. |