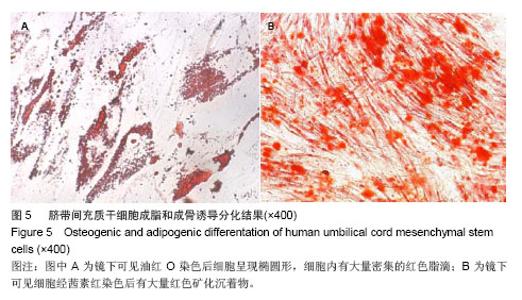
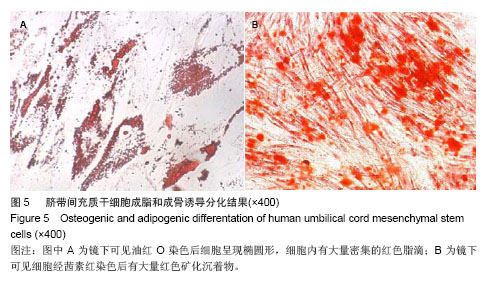
| [1]Kadivar M, Khatami S, Mortazavi Y,et al.In vitro cardiomyogenic potential of human umbilical vein-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;340(2):639-647.
[2]Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[3]Wakitani S, Saito T, Caplan AI.Myogenic cells derived from rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells exposed to 5-azacytidine.Muscle Nerve. 1995;18(12):1417-1426.
[4]Pittenger MF, Martin BJ.Mesenchymal stem cells and their potential as cardiac therapeutics.Circ Res. 2004;95(1):9-20.
[5]唐欣,王岩,易海波,等.人脐带间充质干细胞诱导分化为心肌细胞的特异性基因表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(27): 4988-4991.
[6]Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI,et al. Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues.Transplantation. 1968; 6(2):230-247.
[7]Horwitz EM, Le Blanc K, Dominici M,et al.Clarification of the nomenclature for MSC: The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement.Cytotherapy. 2005;7(5):393-395.
[8]Prockop DJ."Stemness" does not explain the repair of many tissues by mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells (MSCs). Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;82(3):241-243.
[9]马锡慧,冯凯,石炳毅.人脐带间充质干细胞生物学特性及其研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(32):6064-6067.
[10]Le Blanc K, Ringdén O.Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells and clinical experience.J Intern Med. 2007;262(5): 509-525.
[11]da Silva Meirelles L, Chagastelles PC, Nardi NB. Mesenchymal stem cells reside in virtually all post-natal organs and tissues.J Cell Sci. 2006;119(Pt 11):2204-2213.
[12]Herzog EL, Chai L, Krause DS.Plasticity of marrow-derived stem cells.Blood. 2003;102(10):3483-3493.
[13]Conget PA, Minguell JJ.Phenotypical and functional properties of human bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells.J Cell Physiol. 1999;181(1):67-73.
[14]Deans RJ, Moseley AB.Mesenchymal stem cells: biology and potential clinical uses.Exp Hematol. 2000;28(8):875-884.
[15]Minguell JJ, Conget P, Erices A.Biology and clinical utilization of mesenchymal progenitor cells.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2000; 33(8):881-887.
[16]Baksh D, Yao R, Tuan RS.Comparison of proliferative and multilineage differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow.Stem Cells. 2007;25(6):1384-1392.
[17]Rao MS, Mattson MP.Stem cells and aging: expanding the possibilities.Mech Ageing Dev. 2001;122(7):713-734.
[18]Wang S, Qu X, Zhao RC.Clinical applications of mesenchymal stem cells.J Hematol Oncol. 2012;5:19.
[19]余丽菲,夏宁,梁瑜祯.干细胞移植治疗下肢缺血性疾病[J].医学综述,2006,12(9):544-546.
[20]Karnieli O, Izhar-Prato Y, Bulvik S,et al.Generation of insulin-producing cells from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by genetic manipulation.Stem Cells. 2007;25(11):2837-2844.
[21]Rice CM, Scolding NJ.Autologous bone marrow stem cells--properties and advantages.J Neurol Sci. 2008; 265 (1-2):59-62.
[22]庞荣清,何洁,李福兵,等.一种简单的人脐带间充质干细胞分离培养方法[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版),2011,1(2):30-33.
[23]王娟,陆琰,何冬梅,等.人脐带间充质干细胞体外分离、纯化及鉴定[J].暨南大学学报:自然科学与医学版,2009,30(4):367-372.
[24]徐燕,李长虹,孟恒星,等.人脐带间充质干细胞分离培养条件的优化及其生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(32): 6289-6294.
[25]Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC,et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
|