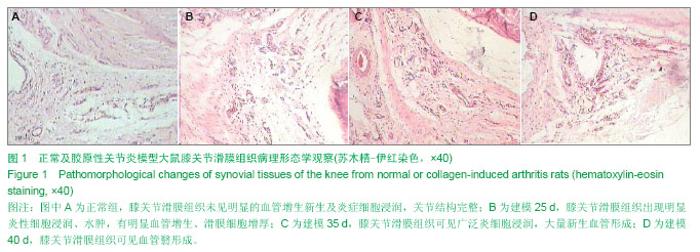
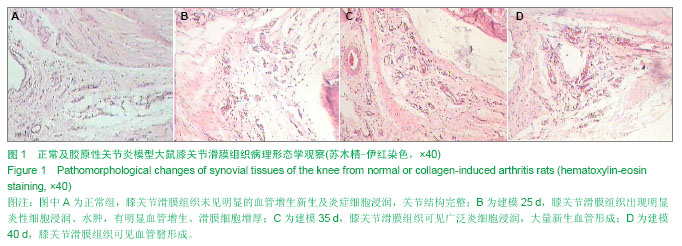
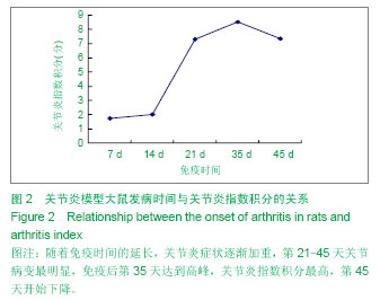
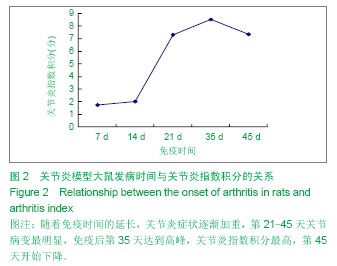
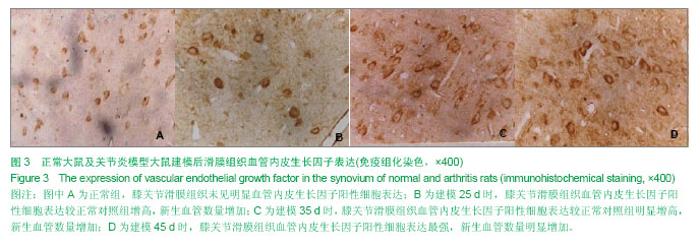
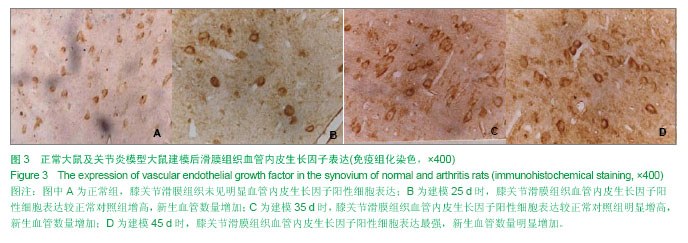
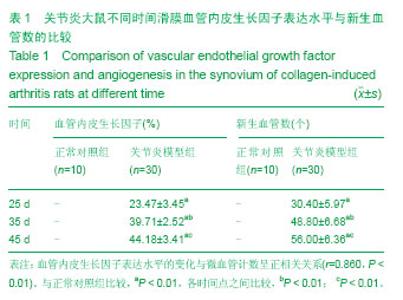
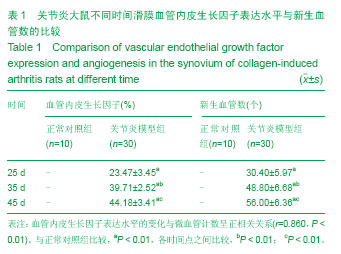
| [1] Miotla J, Maciewicz R, Kendrew J, et al. Treatment with soluble VEGF receptor reduces disease severity in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Lab Invest. 2000;80(8):1195-1205. [2] Afuwape AO, Feldmann M, Paleolog EM. Adenoviral delivery of soluble VEGF receptor 1 (sFlt-1) abrogates disease activity in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Gene Ther. 2003 ;10(23): 1950-1960. [3] 张延辉,高春阳,李少华.骨性关节炎患者退变软骨及滑膜组织中细胞因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(37):6671- 6675.[4] Koch AE. The role of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis: recent developments. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59 Suppl 1:i65-71.[5] Yoo SA, Kwok SK, Kim WU. lammatory role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: prospects for therapeutic intervention. Mediators Inflamm. 2008;2008:129873. [6] Yin H, Gao L, Shen B, et al. Kallistatin inhibits vascular inflammation by antagonizing tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced nuclear factor kappaB activation. Hypertension. 2010;56(2):260-267.[7] Wauke K, Nagashima M, Ishiwata T, et al. Expression and localization of vascular endothelial growth factor-C in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. J Rheumatol. 2002;29(1): 34-38. [8] Lu J, Kasama T, Kobayashi K, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and regulation of murine collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 2000;164(11): 5922-5927. [9] Sawaguchi Y, Hirata K, Suzuki R, et al. Suppression of murine collagen-induced arthritis by vaccination of synovial vascular endothelial cells. Life Sci. 2013;92(23):1125-1130. [10] 梁清华,何金华,李霞玲,等.痹肿消汤对实验性关节炎大鼠滑膜VEGF表达水平的影响[J]. 湖南医科大学学报,2002,27(6): 491-494.[11] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.[12] 杨波,梁清华,谢薇,等,胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠滑膜病变的蛋白质组学研究[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2006,10(8):474-477[13] Sumariwalla PF, Cao Y, Wu HL, et al. The angiogenesis inhibitor protease-activated kringles 1-5 reduces the severity of murine collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003; 5(1):R32-39. [14] Nataraj NB, Krishnamurthy J, Salimath BP. Treatment with anti-NAP monoclonal antibody reduces disease severity in murine model of novel angiogenic protein-induced or ovalbumin-induced arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013;171(2): 155-163. [15] Venco vsk J, Pavelka K, Ospelt C, et al. Prospective new biological therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;9(2):102-107. [16] Xi ZD,Zhang DQ. Clinical values and mechanism of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. For Med Sci(Sect Int Med). 2006;33(7):301-305.[17] Belaidi E, Beguin PC, Levy P, et al. Delayed myocardial precon- ditioning induced by cobalt chloride in the rat: HIF-1 alpha and iN-OS involvement. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2012; 26(4):454-462.[18] Ellabban AS, Kamel SR, Ahmed SS, et al. Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand serum and synovial fluid level. A comparative study between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Rheumatollnt. 2012;32(6):1589-1596.[19] 李香斌,连金饶,林娜,等. 类风湿关节炎滑膜血管生成和血管翳[J]. 医学综述,2010,16(1):7-9. [20] 储永良,黄清春. 血管内皮生长因子及其受体与类风湿关节炎的相关性[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志,2005,9(6):359-362.[21] 黄娴倩,陈勇,陈立斌,等. 类风湿关节炎患者血清血管内皮生长因子血管生成素-1和2的检测及其与关节滑膜病变的相关性研究[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志,2012,16(10):679-683.[22] 彭勇,陈勇,邬秀娣,等. HIF-1α及 VEGF 在类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞中的表达及意义[J]. 浙江医学,2013,18(34): 1628-1631.[23] Walsh DA, McWilliams DF, Turley M J, et al. Angiogenesis and nerve growth factor at the osteochondral junction in rheumatoid ar- thritis and osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49(10):1852-1861.[24] 张征,郭发金,任俊红,等. 早期类风湿关节炎患者外周血管病变和内皮功能的超声研究[J]. 中国心血管杂志,2013,17(2): 103-106.[25] 达古拉,李鸿斌. 血管内皮细胞生长因子与类风湿关节炎发病机制及其治疗的相关性[J]. 中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志,2012, 6(1):55-59.[26] 王伟东,陈如平,肖鲁伟,等.雷公藤甲素对类风湿关节炎滑膜新生血管中血管内皮生长因子、白细胞介素-6抑制机理的探讨[J]. 中医正骨,2012,24(2):3-5.[27] 吕嘉,向川,卫小春,等. 血管内皮生长因子及水通道蛋白1与类风湿关节炎滑膜血管生成的相关性分析[J].中华风湿病学杂志, 2012, 16(3):200-202.[28] 陈勇,黄娴倩,陈立斌,等. 类风湿关节炎患者超声评估滑膜病变与血清血管内皮生长因子检测的相关性研究[J]. 现代实用医学,2011,23(9):973-976.[29] 王志文,丁春菊,张爱国,等. 麝香乌龙丸对佐剂性关节炎大鼠滑膜病理形态及血管内皮生长因子、内皮抑素表达的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(19):241-244.[30] 王艳娇,李琳芸,彭长华,等. 类风湿关节炎患者血清炎性因子、ANCA水平与血管内皮损伤标志物的相关性分析[J]. 微循环学杂志,2012,22(1):49-51.[31] 朱尚玲,彭蔚湘,罗敏琪,等. 类风湿关节炎滑膜血管内皮细胞中Smoothened的表达及其意义[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2013, 29(2):225-230.[32] 谢庆云,魏萌,张波,等. 外周血炎性细胞因子与类风湿关节炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(42):7945-7950.[33] 严瀚,刘恩志,周汉城,等. 类风湿关节炎中巨噬细胞移动抑制因子对内皮细胞功能及血管内皮生长因子的影响[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2013,7(3):67-70.[34] 王一凡,韦登明. 雷公藤内酯醇治疗类风湿关节炎分子机制的研究进展[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志,2005,9(10):628-630.[35] Szekanecz Z, Besenyei T, Szentpétery A,et al. Angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010;22(3):299-306. [36] Kawashiri S,Kawakami A,Iwamoto N,et al.The power Doppler ultrasonography score from 24 synovial sites or 6 simplified synovial sites,including the metacarpophalangeal joints,reflects the clinical disease activity and level of serum biomarkers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2011;50(5):962-965.[37] Clavel G, Bessis N, Lemeriter D et al. Angiogenesis markers(VEGF, soluble receptor of VEGF and angiopoictin-1 in very early arthritis and their association with inflammation and joint destruction. Clin Immunol. 2007;124(2):158-164.[38] 赵绵松,夏蓉晖,王玉华,等. 骨关节炎与类风湿关节炎患者膝关节滑膜中血管内皮生长因子及血管形态的特征[J]. 北京大学学报:医学版,2012,44(6):927-931.[39] Margolin K,Gordon MS,Holmgren E,et al.Phase Ib trial of intravenous recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody to vascular endothelial growth factor in combination with chemotherapy in patients with advanced cancer:Pharmacologic and long-term safety data.J Clin Oncol.2001;19(10):851-856.[40] de Bandt M,Meriem H,Mahdi B ,et al. Blockade of vascular Endothdial. Growth Factor Receptor 1 (VEGF-RI), but not VEGF-RII, Suppresses Joint Destruction in the K/BxN Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis. TheJournalofImmunology. 2003;171(9): 4853-4859. |