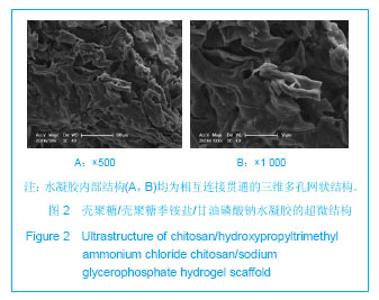
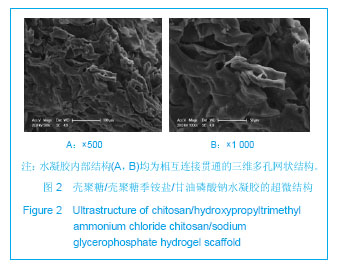
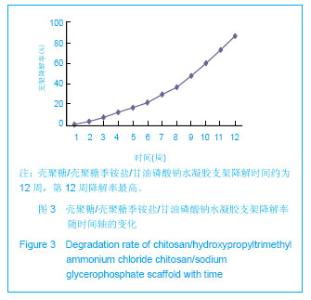
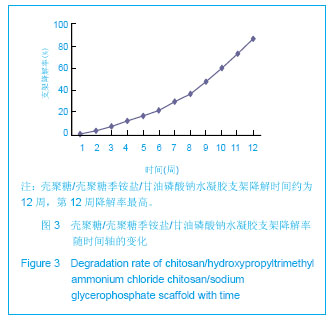
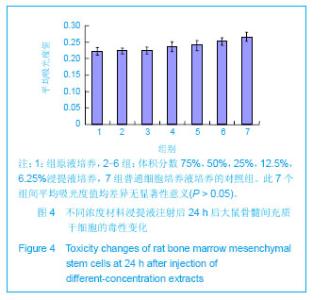
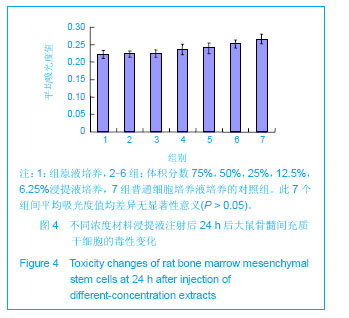
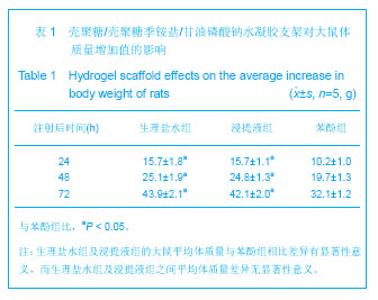
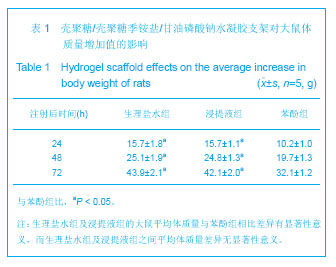
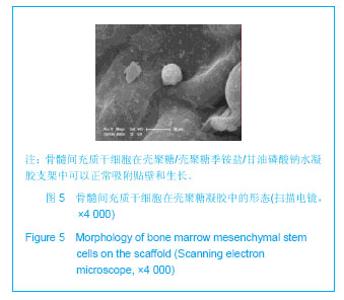
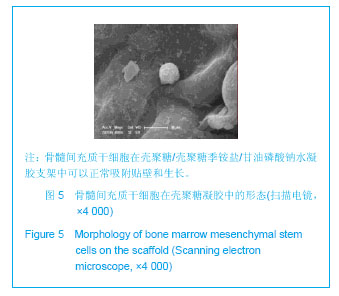
| [1] Mccarty RC,Xian CJ,Gronthos S,et al. Application of autologous bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells to an ovine model of growth plate cartilage injury. Open Orthop. 2010;4:204-210.
[2] Kotobuki N, Katsube Y, Katou Y, et al. In vivo survival and osteogenic differentiation of allogeneic rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell. Cell Transplant. 2008;17(6):705-712.
[3] Wang B, Han J, Gao Y, et al. The differentiation of rat adipose-derived stem cells into OEC-like cells on collagen scaffolds by co-culturing with OECs. Neurosci Lett. 2007; 421(3):191-196.
[4] Zhang N, Yan H, Wen X. Tissue-engineering approaches for axonal guidance. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005;49(1):48-64.
[5] Kim DH, Abidian M, Martin DC. Conducting polymers grown in hydrogel scaffol-ds coated on neural prosthetic devices. Biomed Mater Res A. 2004;71(4):577-585.
[6] Zhao L, Weir MD, Xu HH. An injectable calcium phosphate alginatehydrogel umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell paste for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2010;31(25): 6502-6510.
[7] Maklad A, Kamel S, Wong E, et al. Develoment and organnization of polarity-specific segregation of primary vestibular afferent fibers in mice. Cell Tissue Res. 2010; 340(2):303-321.
[8] Lee JY, Nam SH, ImSY, et al. Enhanced bone formation by controlled growth factor delivery from chitosan-based biomaterials. J Control Release. 2002;78(1-3):187-197.
[9] Bosnakovski D, Mizunl M, Kim G, et al. Chondrogenic dedifferentiation of bovine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells(MSCs) in different hydrogels: influence of collagen typeⅡextracellular matrix on MSC chondrogenesis. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006;93(6):1152-1163.
[10] Mahmood A, Lu D, Wang L, et al. Intracerebral transplantion of marrow stromal cells cultured with neurotrophic factors pro-motes functional recovery in adult rats subjected to traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2002;19(12): 1609- 1617.
[11] 许勇,朱立新,田京,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合材料与免骨髓间充质干细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(8):1423-1426.
[12] Mori T, Okumura M, Matsuura M, et al. Effects of chitin and its derivatives on the proliferation and cytokine production of fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials.1997;18(13):947-951.
[13] Dash M, Chiellini F, Ottenbrite RM, et al. Chitosa-A versatile semi-synthetic polymer in biomedical applications. Prog Polym Sci. 2011;36(8):981-1014.
[14] Zhou HY, Chen XG, Kong M, et al. Effect of molecular weight and degree of chitosan deacetylation on the preparation and characteristics of chitosan thermosensitive hydrogel as a delivery system. Carbohydr Polym. 2008;73:265-273.
[15] Chenite A, Chaput C, Wang D, et al. Novel injectable neutral solutions of chi-tosan form biodegradable gels in situ. Biomaterials. 2000;21(21):2155-2161.
[16] CheniteA, Buschmann M, Wang D, et al. Rheological characterisation of thermogelling chitosan/glycerol-phosphate solutions. Carbohydr Polym. 2001;46:39-47.
[17] Ganji F. Gelation time and degradation rate of chitosan-based injectable hydrogel. Sol Gel Sci Technol. 2007;42(1):47-53.
[18] Liu ZQ, Wang HB, Wang Y, et al. The infuence of chitosan hydrogel on stem cell engraftment, survival and homing in the ischemic myocardial microenvironment. Biomaterials. 2012; 33(11):3093-3106.
[19] Holappa J, Hjálmarsdóttir M, Másson M, et al. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan N-betainates. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2006;65(1):114-118.
[20] Lim SH, Hudson SM. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of a water-soluble chitosan derivative with a fiber-reactive group. Carbohydr Res. 2004;339(2):313-319.
[21] Jyh-Ping C, Chien-Hao S. Surface modification of electrospun PlIA nanofibers by plasma treatment and cationized gelatin immobilization for cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011;7:234-243.
[22] Shanti RM, Janjanin S, Li WJ, et al. In vitro adipose tissue engineering using an electrospun nanofibrous scaffold. Ann Plast Surg. 2008;61:566-571.
[23] Zhang N, Yan H, Wen X. Tissue-engineering approaches for axonal guidance. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005;49(1):48-64.
[24] Vacanti MP, Leonard JL, Dore B, et al. Tissue-engineered spinal cord. Transplant Proc. 2001;33(1-2):592-598.
[25] Takezuwa T. A strategy for the development of tissue engineering scaffolds that regulate cell behavior. Biomaterials. 2003;24(13):2267-2275.
[26] Petter-Puchner AH, Froetscher W, Krametter-Froetscher R, et al. The long-term neuro compatibility of human fibrin sealant and equine collagen as biomatr ices in experimental spinal cord injury. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2007;58(4):237-245
[27] Kwon JS, Kim GH, Kim da Y, et al. Chitosan-based hydrogels to induce neuronal differentiation of rat muscle-derived stem cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2012;51(5):974-979.
[28] Moreau JL, Xu HH. Mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and differentiation on an injectable calcium phosphate-Chitosan composite scaffold. Biomaterials. 2009;30(14):2675-2682.
[29] Leipzig ND, Wylie RG, Kim H, et al. Differentiation of neural stem cells in three-dimensional growth factor-immobilized chitosan hydrogel scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2011;32(1):57-64.
[30] Budiraharjo R, Neoh KG, Kang ET. Hydroxyapatite-coated carboxymethyl chitosan scaffolds for promoting osteoblast and stem cell differentiation. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2012; 366(1):224-232. |