Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Physicochemical property and safety of nanometer human demineralized bone matrix composite
Fang Lei1, Chen Xiong-sheng1, Huang Kai1, Zhou Sheng-yuan1, Zhu Wei1, Wang Hui1, Shao Jiang2, Jia Lian-shun1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Xin Hua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200092, China
-
Received:2013-02-16Revised:2013-02-28Online:2013-09-17Published:2013-09-17 -
Contact:Chen Xiong-sheng, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China chenxiongsheng@vip.sohu.com -
About author:Fang Lei★, Master, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China fangleihouse@vip.sohu.com -
Supported by:The Science and Technology Committee Foundation of Shanghai City, No. 0852nm03100*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fang Lei, Chen Xiong-sheng, Huang Kai, Zhou Sheng-yuan, Zhu Wei, Wang Hui, Shao Jiang,. Physicochemical property and safety of nanometer human demineralized bone matrix composite[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.38.001.
share this article
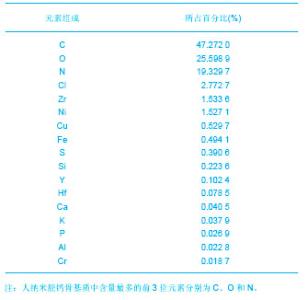
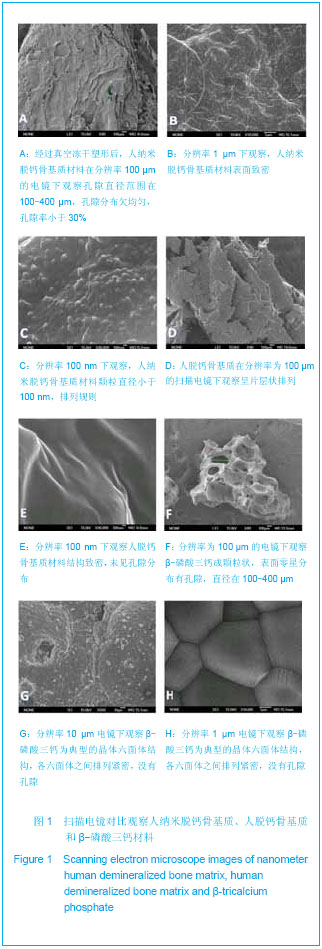
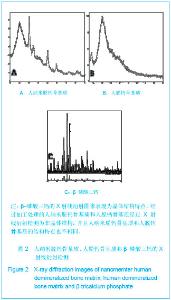
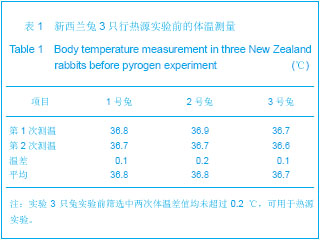
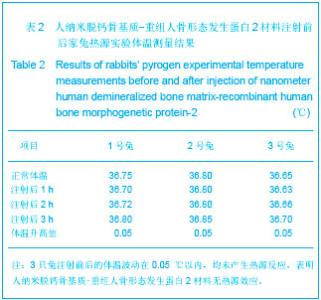
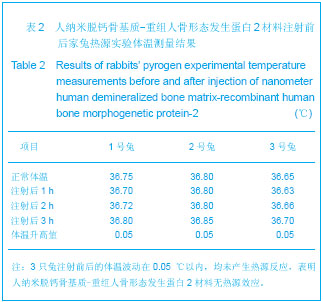
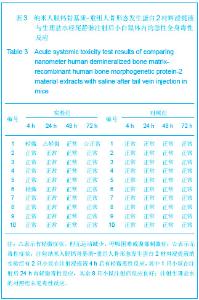
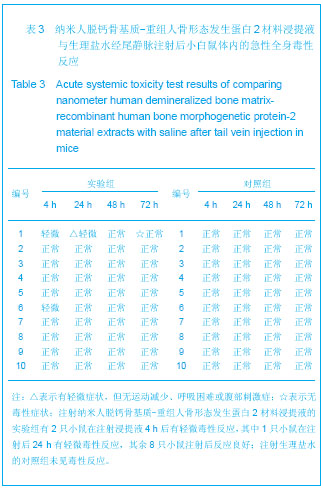
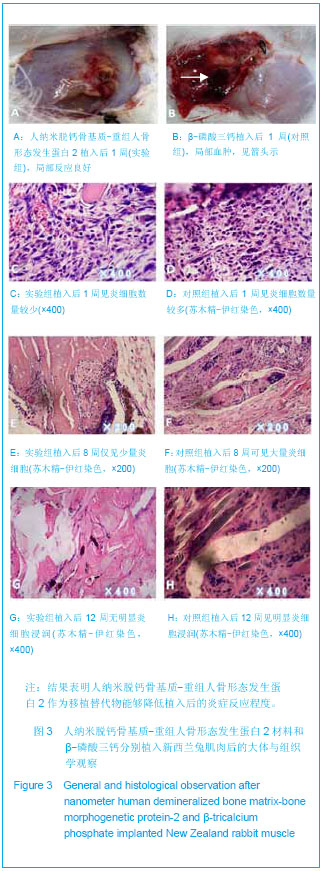
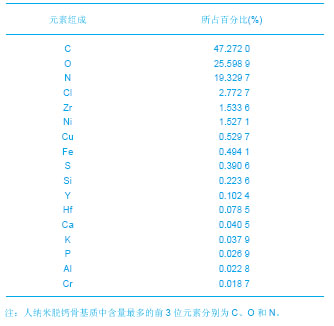
由图1可见,经过真空冻干塑形后,纳米人脱钙骨基质材料在分辨率100 μm的电镜下观察孔隙直径范围在100-400 μm,孔隙分布欠均匀,孔隙率小于30%;分辨率1 μm下观察,纳米人脱钙骨基质材料表面致密;分辨率100 nm下观察,纳米人脱钙骨基质材料颗粒直径小于100 nm,排列规则;人脱钙骨基质在分辨率为100 μm的扫描电镜下观察呈片层状排列;分辨率100 nm下观察人脱钙骨基质材料结构致密,未见孔隙分布;分辨率为100 μm的电镜下观察β-磷酸三钙成颗粒状,表面零星分布有孔隙,直径在100- 400 μm;分辨率10 μm和1 μm电镜下观察β-磷酸三钙为典型的晶体六面体结构,各六面体之间排列紧密,没有孔隙。 2.2 人纳米脱钙骨基质X射线荧光分析结果 没有对人脱钙骨基质和β-磷酸三钙进行X射线荧光分析,因为β-磷酸三钙的元素组成已经很明了,而人脱钙骨基质和纳米人脱钙骨基质的元素组成必然相同,所以只进行了纳米人脱钙骨基质的X射线荧光分析。 人纳米脱钙骨基质有17种元素,含量居前3位的元素分别是C、O和N,其他元素按含量从高到低排列:Cl、Zr、Ni、Cu、Fe、S、Si、Y、Hf、Ca、K、P、Al、Cr。 人纳米脱钙骨基质 X射线荧光检测结果:"
| [1] Li J,Yoon ST,Hutton WC. Effect of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) on matrix production, other BMPs, and BMP receptors in rat intervertebral disc cells.J Spinal Disord Tech.2004;17(5):423-328. [2] Delamarter R,Kropf M,Bae H,et al.Reduced Dose of Rhbmp‐2 With Demineralized Bone Matrix-Based Product for Spinal Fusion: Gp101. Spine J. 2011;11(2):113-118. [3] Zhang S, Doschak MR, Uluda? H.Pharmacokinetics and bone formation by BMP-2 entrapped in polyethylenimine-coated albumin nanoparticles. Biomaterials.2009;30(28):5143-5155. [4] Knippenberg M,Helder MN,Zandieh Doulabi B,et al. Osteogenesis versus chondrogenesis by BMP-2 and BMP-7 in adipose stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006; 342(3):902-908. [5] Lou J,Tu Y,Burns M,et al.BMP-12 gene transfer augmentation of lacerated tendon repair.J Orthop Res.2001;19(6): 1199-1202. [6] Dallari D,Savarino L,Albisinni U,et al.A prospective, randomised, controlled trial using a Mg-hydroxyapatite - demineralized bone matrix nanocomposite in tibial osteotomy. Biomaterials.2012;33(1):72-79. [7] Öztürk A,Yetkin H,Memis L,et al.Demineralized bone matrix and hydroxyapatite/tri-calcium phosphate mixture for bone healing in rats. Int Orthop.2006;30(3):147-152. [8] Becker V,Nardone E,Robbins S,et al.Comparison of autograft to DBX demineralized bone matrix putty combined with autograft used in posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion.Spine J.2005;5(4):1-189. [9] Schizas C, Triantafyllopoulos D, Kosmopoulos V, et al. Posterolateral lumbar spine fusion using a novel demineralized bone matrix: a controlled case pilot study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2008;128(6):621-625. [10] Topuz K,Çolak A,Kaya S,et al. Two-level contiguous cervical disc disease treated with peek cages packed with demineralized bone matrix:results of 3-year follow-up. Eur Spine J.2009;18(2):238-243. [11] Kim SE,Yun YP,Suh DH,et al.Recombinant human bone morphogenic protein-2 (Rhbmp-2) immobilization onto the surface of apatite-coated titanium significantly promotes osteoblast function and mineralization.Tissue Eng Regen Med.2012;9(4):216-223. [12] Kolk A,Handschel J,Drescher W,et al.Current trends and future perspectives of bone substitute materials – From space holders to innovative biomaterials. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40(8):706-718. [13] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局.GB/T 16886.5- 2003.医疗器械生物学评价 第5 部分:体外细胞毒性试验[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2003. [14] 国家技术监督局.GB/T 16886.6-1997.医疗器械生物学评价 第6部分:植入后局部反应实验[S].北京:中国标准出版社,1997. [15] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局中国家标准化管理委员.GB/T 14233.2-2005.医用输液、输血、注射器具检验方法第2部分:生物学实验方法[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2006. [16] Ma Y, Cai ZB. Bionic design of human bone microstructure based on fractal t-heory. J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res.2007; 11(14):2784-2786. [17] Zhang B, Liu MY, Zhao JH.Osteoinductive activity of demineralized bone matrix and deprotenized bone derived from human avascular necrotic femoral head. Chin J Traumatol. 2009;12(6):379-383. [18] Koch FP,Becker J,Terheyden H,et al. A prospective, randomized pilot study on the safety and efficacy of recombinant human growth and differentiation factor-5 coated onto β-tricalcium phosphate for sinus lift augmentation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(11):1301-1308. [19] Priestly B,Harford A,Sim M. Nanotechnology: a promising new technology but how safe? Med J Aust.2007;186(4): 187-188. [20] Edwards FC,Taheri A,Dann SC,et al.Characterization of cytolytic neutrophil activation in vitro by amorphous hydrated calcium phosphate as a model of biomaterial inflammation.J Biomed Mater Res A.2011;96(3): 552-565. [21] Nadra I,Mason JC,Philippidis P,et al.Proinflammatory activation of macrophages by basic calcium phosphate crystals via protein kinase C and MAP kinase pathways: a vicious cycle of inflammation and arterial calcification?Circ Res.2005;96(12): 1248-1256. [22] Zaichick S,Zaichick V,Karandashev VK,et al.The effect of age and gender on 59 trace-element contents in human rib bone investigated by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Biol Trace Elem Res.2011;143(1):41-57. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Deng Zhenhan, Huang Yong, Xiao Lulu, Chen Yulin, Zhu Weimin, Lu Wei, Wang Daping. Role and application of bone morphogenetic proteins in articular cartilage regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 798-806. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Xie Chengxin, Wang Wei, Wang Chenglong, Li Qinglong, Yin Dong. Systematic review and meta-analysis of bone morphogenetic protein for the treatment of acute tibial fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 486-492. |
| [13] | Zhou Wu, Wang Binping, Wang Yawen, Cheng Yanan, Huang Xieshan. Transforming growth factor beta combined with bone morphogenetic protein-2 induces the proliferation and differentiation of mouse MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3630-3635. |
| [14] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [15] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||