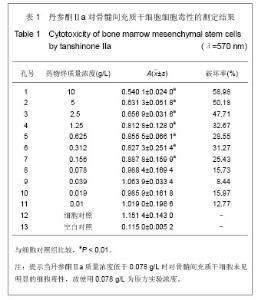
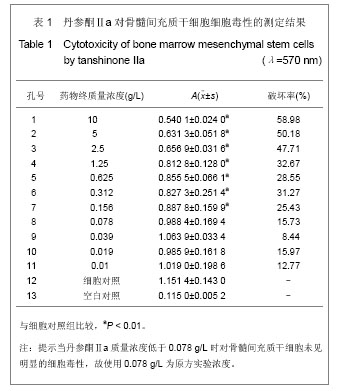
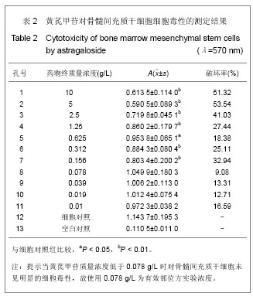
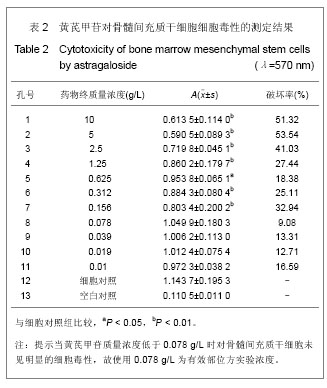
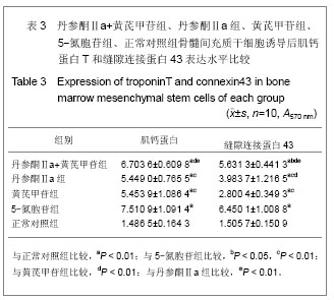
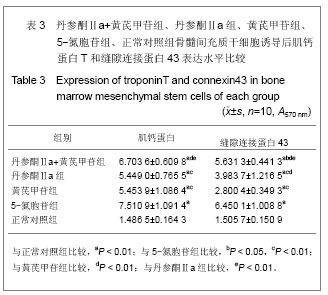
| [1] 郑景辉,李勇华,王丽萍,等.心血瘀阻证微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞向心肌样分化的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2010,30(9):38- 42.
[2] 李勇华,郑景辉,袁肇凯,等.养心通脉有效部位方对梗死心肌细胞因子分泌、血管新生及动员MSCs归巢的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2011,(5):514-516.
[3] 孙敬和,冼绍祥,黄习文,等. 中医药干预骨髓间充质干细胞体外定向诱导分化为心肌细胞的研究进展[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2012,23(1):115-118.
[4] 郑景辉.心血瘀阻证心肌微环境变化及对骨髓间充质干细胞移植的影响[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2010.
[5] 袁肇凯,黄献平,李勇华,等.养心通脉有效部位方动员骨髓间充质干细胞归巢大鼠梗死心肌的实验研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2012, 27(9):2321-2325.
[6] 李玉冰.丹参酮Ⅱa、川芎嗪联合体外诱导BMSCs分化为心肌样细胞的研究[D]. 长沙:湖南中医药大学,2011.
[7] 李广斌,苏金玲,姜希娟,等.中药心复康在大鼠急性心肌梗塞后对移植骨髓间充质干细胞的保护作用[J].时珍国医国药,2009, 20(12):3043-3045.
[8] Zhao BL,Jiang W,Zhao Y,et al. Scavenging effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza on free radicals and its protection for myocardial mitochondrial membranes from ischemia reperfusion injury. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1996;38(6):1171-1182.
[9] 许春萱.丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠注射液治疗不稳定型心绞痛临床疗效观察[J].中国医刊,2006,41(5):44-45.
[10] 李建新,白霞凤. 丹参酮治疗冠心病心绞痛疗效观察[J]. 中国现代医药杂志,2007,9(6):98-99.
[11] 王玉琴. 丹参酮IIA磺酸钠注射液治疗冠心病的临床疗效[J]. 中国现代药物应用,2011,5(15):141.
[12] 宋翠丽. 丹参酮IIA磺酸钠联合低分子肝素钙治疗老年不稳定型心绞痛53例临床研究[J]. 医学理论与实践,2008,3:289-290.
[13] 刘宣,王炎,李丹光,等. 丹参酮ⅡA对COX-2激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路介导的人肠癌细胞VEGF表达的调控作用[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2013,28(1):108-112.
[14] 杨乐,邹晓静,高翔,等. 丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠对AngⅡ诱导的心肌细胞氧化应激的影响[J]. 中国药学杂志,2012,32(4):270-274.
[15] Chan P, Liu IM, Li YX, et al. Antihypertension Induced by Tanshinone IIA Isolated from the Roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:392627.
[16] 杨征,邱敏.丹参酮ⅡA 的心血管作用及机制研究进展[J].中国动脉硬化杂志, 2011,19(4):372-375.
[17] 张川,柳润辉,李慧梁,等.黄芪甲苷对大鼠心肌基因表达谱的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2008,33(2):172-174.
[18] 柴丽娟,钟佩茹,周志焕,等.黄芪甲苷对体外神经干细胞增殖作用影响的研究[J].中国药理学通报, 2010,26(5):670-673.
[19] 关凤英,李红,杨世杰. 黄芪甲苷诱导NO生成并激活PKCε对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].吉林大学学报:医学版, 2010,26(2):340-344.
[20] Adolphe M, Parodi AL. Ethical issues in animal experimentation. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2009;193(8): 1803-1804.
[21] Zheng JH, Wan Y, Chi JH, et al. The active principle region of Buyang Huanwu decoction induced differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into neural-like cells: superior effects over original formula of Buyang Huanwu decoction. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(4):261-267.
[22] Chamberlain G, Fox J, Ashton B, et al. Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells: their phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and potential for homing. Stem Cells. 2007;25(11):2739-2749.
[23] 郑景辉,李勇华,王丽萍,等.不同血清微环境对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(14):2497-2502.
[24] 黄献平,袁肇凯,郑景辉,等.养心通脉有效部位方对MSCs向心肌样细胞分化的影响[J].中药新药与临床药理,2012,23(4):427- 430.
[25] Wakitani S, Saito T, Caplan AI.Myogenic cellsderivedfrom rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells exposed to 5-azacytidine. Muscle Nerve. 1995;18(12):1417-1426.
[26] 赵桂峰,范英昌,华声喻.丹酚酸B干预内皮祖细胞对骨髓间充质干细胞心脏移植后存活的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(8): 2172-2176.
[27] 华声瑜,赵桂峰,李庆雯,等. 丹酚酸B预处理EPCs对AMI大鼠移植骨髓间充质干细胞后心肌微环境的影响[J]. 天津中医药, 2012, 29(2):117-120.
[28] 王健,杨关林,陈岩,等.丹参联合骨髓间充质干细胞静脉移植对兔心肌梗死区血管再生影响的实验研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2010, 28(4):792-795.
[29] 武重阳,孙兰军,赵英强,等. 复方丹参滴丸含药血清诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分化为心肌样细胞[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2010, 30(16):2328-2330.
[30] Rose RA, Jiang H, Wang X, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells express cardiac-specific markers, retain thestromal phenotype, and do not become functional cardiomyocytes in vitro. Stem Cells. 2008;26(11):2884-2892.
[31] Freyman T, Polin G, Osman H, et al.A quantitative, randomized study evaluating three methods of mesenchymal stem cell delivery following myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2006;27(9):1114-1122.
[32] Pillarisetti K, Gupta SK. Cloning and relative expression analysis of rat stromal cell derived factor-1 (SDF-1)1: SDF-1 alpha mRNA is selectively induced in rat model of myocardial infarction. Inflammation. 2001;25(5):293-300.
[33] Kucia M, Jankowski K, Reca R, et al. CXCR4-SDF-1 signalling, locomotion, chemotaxis and adhesion.J Mol Histol. 2004;35(3):233-245.
[34] 郭永田.中药有效成分与肠道细菌的关系[J].医学与哲学, 1995, 16(11): 598.
[35] 陶金华,狄留庆,单进军,等.肠道微生态与中药有效成分代谢的相互作用[J].中草药,2008,39(12):1902-1904.
[36] 毕肖林,杜秋,狄留庆.肠道转运蛋白和代谢酶在中药有效成分胃肠处置中的作用研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2010,35(3): 397-400.
[37] 夏广萍,刘鹏,赵娜,等.β-葡萄糖苷酶水解黄芪甲苷的研究[J].中草药,2012,43(6):1112-1114.
[38] Argulian E.Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with increased high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T levels. Chest. 2013;143(1):277-278.
[39] 王海萍,张雷,赵静,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗心肌梗死的实验研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2012,30(2):209-213.
[40] 杨军,丁赛良,邓彪,等.通心络对异丙肾上腺素诱导的H9c2心肌细胞肥大及Cx43mRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2012,18(23):191-194.
[41] Fang JS, Dai C, Kurjiaka DT, et al.Connexin45 regulates endothelial-induced mesenchymal cell differentiation toward a mural cell phenotype. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013; 33(2):362-368.
[42] 商洪才,张伯礼,李幼平.中医药临床疗效评价实践中的思路与方法[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2008,28(3):266-268. |