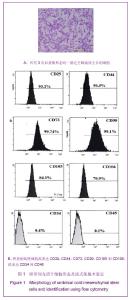
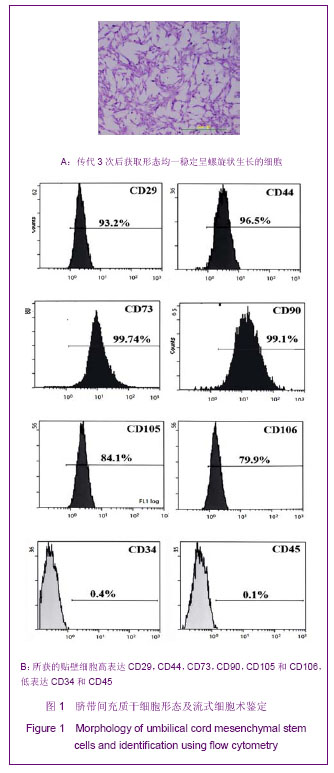
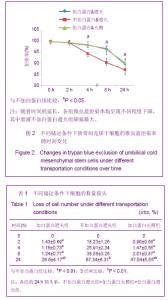
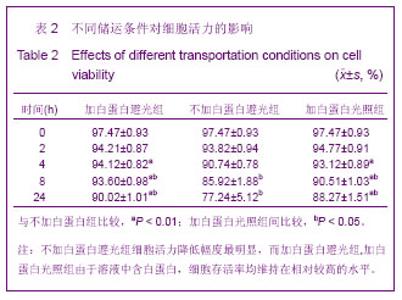
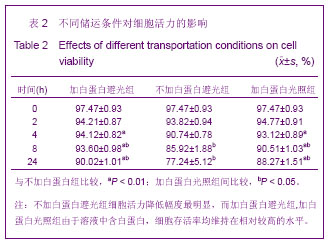
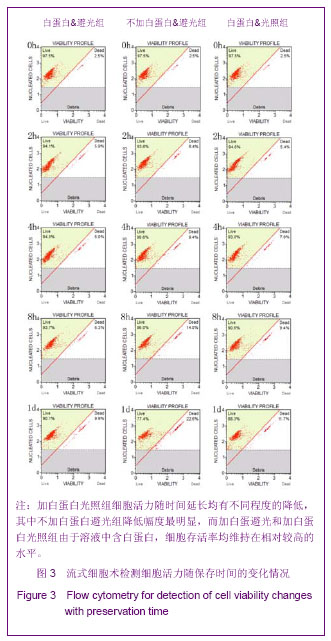
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (36): 6430-6435.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.36.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of transportation conditions on survival rate of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
Wang Da-kun1, Wang Zhi-hui2, Guo Hong2, Zhang Le-ling3
- 1Cryomedicine Lab, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China; 2Shangdong Qilu Stem Cells Co., Ltd., Jinan 250004, Shandong Province, China; 3Qilu Children’s Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan 250022, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2012-11-21Revised:2013-01-29Online:2013-09-03Published:2013-09-03 -
Contact:Zhang Le-ling, Master, Chief physician, Qilu Children’s Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan 250022, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wang Da-kun, Cryomedicine Lab, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China sagittariuswong@hotmail.com -
Supported by:the Autonomous Innovation Project of Shandong University, No. 2012ZD023*; the Shandong Provincial Technology Development Project, No. 2010G0020213*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Da-kun, Wang Zhi-hui, Guo Hong, Zhang Le-ling. Effects of transportation conditions on survival rate of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(36): 6430-6435.
share this article
| [1] Fridenshtein A.[Stromal bone marrow cells and the hematopoietic microenvironment]. Arkh Patol.1982;44(10): 3-11.
[2] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al.Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411): 143-147.
[3] Paolo Bianco,Pamela Gehron Robey.Marrow stromal stem cells. J Clin Invest. 2000;105(12): 1663-1668.
[4] Wakitani S, Saito T, Caplan AI. Myogenic cells derived from rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells exposed to 5-azacytidine. Muscle Nerve.1995;18(12): 1417-1426.
[5] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al.Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res.2000;61(4): 364-370.
[6] Reyes M, Lund T, Lenvik T, et al.Purification and ex vivo expansion of postnatal human marrow mesodermal progenitor cells. Blood.2001;98(9): 2615-2625.
[7] Venkataramana NK, Kumar SK, Balaraju S, et al. Open-labeled study of unilateral autologous bone-marrow- derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in Parkinson's disease. Transl Res.2010;155(2):62-70.
[8] Hare JM, Traverse JH, Henry TD, et al.A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation study of intravenous adult human mesenchymal stem cells (prochymal) after acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol.2009; 54(24):2277-2286.
[9] Mohamadnejad M, Alimoghaddam K, Mohyeddin-Bonab M,et al.Phase 1 trial of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. Arch Iran Med.2007;10(4): 459-466.
[10] Matthay MA, Thompson BT, Read EJ, et al.Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for severe acute lung injury. Chest.2010;138(4):965-972.
[11] Le Blanc K, Frassoni F, Ball L, et al.Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. Lancet.2008; 371(9624):1579-1586.
[12] Baksh D, Yao R, Tuan RS. Comparison of proliferative and multilineage differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow. Stem Cells. 2007;25(6):1384-1392.
[13] Yoo KH, Jang IK, Lee MW, et al.Comparison of immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult human tissues. Cell Immunol.2009; 259(2): 150-156.
[14] La Rocca G, Anzalone R, Corrao S,et al.Isolation and characterization of Oct-4+/HLA-G+ mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord matrix: differentiation potential and detection of new markers. Histochem Cell Biol.2009;131(2): 267-282.
[15] Jo CH, Kim OS, Park EY,et al.Fetal mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord sustain primitive characteristics during extensive expansion. Cell Tissue Res.2008;334(3):423-433.
[16] Yoon JH, Roh EY, Shin S, JH.et al.Introducing pulsed low- intensity ultrasound to culturing human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechnol Lett.2009;31(3): 329-335.
[17] Kim JW, Kim SY, Park SY, et al.Mesenchymal progenitor cells in the human umbilical cord. Ann Hematol.2004;83(12): 733-738.
[18] Zhang L, Zhang HT, Hong SQ, et al.Cografted Wharton's jelly cells-derived neurospheres and BDNF promote functional recovery after rat spinal cord transection. Neurochem Res. 2009;34(11): 2030-2039.
[19] Secco M, Moreira YB, Zucconi E, et al.Gene expression profile of mesenchymal stem cells from paired umbilical cord units: cord is different from blood. Stem Cell Rev.2009;5(4): 387-401.
[20] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,et al.Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy.2006;8(4):315-317.
[21] Horwitz EM, Le Blanc K, Dominici M, et al.Clarification of the nomenclature for MSC: The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2005;7(5):393-395.
[22] Karahuseyinoglu S, Cinar O, Kilic E, et al.Biology of stem cells in human umbilical cord stroma: in situ and in vitro surveys. Stem Cells.2007;25(2): 319-331.
[23] Wang HS, Hung SC, Peng ST, et al.Mesenchymal stem cells in the Wharton's jelly of the human umbilical cord. Stem Cells. 2004;22(7):1330-1337.
[24] Lu LL, Liu YJ, Yang SG, et al.Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with hematopoiesis-supportive function and other potentials. Haematologica.2006;91(8):1017-1026.
[25] Pang KM, Sung MA, Alrash-dan MS, et al. Trans-plantation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord versus human umbilical cord blood for peripheral nerve regenera-tion. Neural Regen Res. 2010;5(11):838-845.
[26] Hunt CJ.Cryopreservation of Human Stem Cells for Clinical Application: A Review. Transfus Med Hemother.2011;38(2): 107-123.
[27] Ball LM, Bermardo ME, Roelofs H, et al. Cotransplantation of ex vivo expanded mesenchymal stem cells accelerates lymphocyte recovery and may reduce the risk of graft failure in haploidentical hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Blood, 2007;110(7): p. 2764-2767.
[28] Mohyeddin-Bonab M, Mohamad-Hassani MR, Alimoghaddam K, et al.Autologous in vitro expanded mesenchymal stem cell therapy for human old myocardial infarction. Arch Iran Med. 2007;10(4):467-473.
[29] Centeno CJ, Busse D, Kisiday J,et al.Increased knee cartilage volume in degenerative joint disease using percutaneously implanted, autologous mesenchymal stem cells. Pain Physician.2008;11(3):343-353.
[30] Sun L, Akiyama K, Zhang H, et al.Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation reverses multiorgan dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus mice and humans. Stem Cells.2009; 27(6):1421-1432.
[31] Wang D, Zhang F, Shen W, et al.Mesenchymal stem cell injection ameliorates the inducibility of ventricular arrhythmias after myocardial infarction in rats. Int J Cardiol.2011;152(3): 314-320.
[32] Pal R, Hanwate M, Totey SM. Effect of holding time, temperature and different parenteral solutions on viability and functionality of adult bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells before transplantation. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2008;2(7):436-444.
[33] Cramer C, Freisinger E, Jones RK, et al.Persistent high glucose concentrations alter the regenerative potential of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev.2010;19(12): 1875-1884.
[34] Stolzing A, Coleman N, Scutt A.Glucose-induced replicative senescence in mesenchymal stem cells. Rejuvenation Res. 2006;9(1): p.31-35.
[35] Lo T, Ho JH, Yang MH,et al.Glucose reduction prevents replicative senescence and increases mitochondrial respiration in human mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(6):813-825.
[36] Grzelak A, Rychlik B, Bartosz G.Light-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species in cell culture media. Free Radic Biol Med.2001;30(12): 1418-1425. |
| [1] | Wang Jian-ji, Yang Long, Li Jing, Sun Qi, Zuo Wei-min, Ren Qi-feng, Sun Yu, Wu Zhan-yu, Zou Qiang, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Development and application of special-purpose grafter by femoral head decompression combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation based on three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6636-6642. |
| [2] | Liang Jing, Zhang Yuan, Zhao Yu-rong, Meng Xiang-long, Wang Li. Model rats with membranous nephropathy induced by cationic bovine serum albumin: expressions of related proteins in podocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6028-6033. |
| [3] | Zhou Chang-yan, Zhou Qing-huan, Bian Jing, Chen Ke, Chen Wen. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with calcium phosphate cement to repair articular cartilage defects in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1195-1199. |
| [4] | Xu Xiang, Yin He-ping. Platelet-rich plasma accelerates the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2144-2148. |
| [5] | Ma Fa-ku, Wang Huan, Liu Bin, Yang Yan-li, Su Qin-jun, Qian Zhen, Dong Liang. Expression of CD44+/C-myc+ cancer stem cells and its relationship with the prognosis of patients in colorectal tumors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2161-2166. |
| [6] |
Chen Ping, Wang Jian.
Enrichment of lung cancer stem cells and expression of related markers
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2167-2171.
|
| [7] | Fan Zhi-gang, Fan Hong-liang. Oxidative stress response in diabetic nephropathy rats following injection of embryonic stem cells via the tail vein [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2199-2204. |
| [8] | Wang Yong, Zhao Wei, Feng Jian-zhou, Chen Xiao-chun. Nerve growth factor-modified adipose derived stem cells for repair of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2224-2229. |
| [9] | Sha Wen-qiong, She Rui-lian, Wang Zi-neng, Ke Ru. Ultrastructure and phagocytotic function of human placental mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2230-2235. |
| [10] | Du Qing-hua, Cao Jun-kai, Dong Xi-xi, E Ling-ling, Wei Li-jun. Osteogenic differentiation of pluripotent stem cells induced by akermanite extracts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2236-2242. |
| [11] | Wu Yan, Huang Lan . Bone morphogenetic protein 9-induced osteogenic differentiation of dental follicle cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2255-2260. |
| [12] | Rao Li-jia, Li Qi-meng, Li Jin-ling, Xu Qiong. Expression pattern of ten-eleven translocation family during differentiation of human dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2261-2266. |
| [13] | Gao Zhuo-yue, Liu Yong-qi, He Jian-xin, Wu Zhi-wei, Luo Ya-li, Su Yun, Zhang Li-ying, Zhang Qi, Wu You-ming, Zhou Ni-na. Regulatory effects of warming yang and invigorating qi treatment on the inflammatory balance and genetic stability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under tumor microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2267-2272. |
| [14] | Wang Fang, Chen Shao-wei. In vitro culture of embryos and establishment of embryonic stem cell lines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2273-2277. |
| [15] |
Du Wei-bin, Quan Ren-fu, Zheng Xuan, Wang Tuo.
Hair follicle stem cells promote the healing of skin wound
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||