Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (32): 5834-5839.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.32.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Quantitative analysis of transplanted effect of human amniotic epithelial cells in mice with acute liver injury
Luo Hong-wu, Xun Quan, Huang Xiang-jun, Huang Fei-zhou
- First Department of General Surgery, Xiangya Third Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 413000, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2012-11-07Revised:2012-11-20Online:2013-08-06Published:2013-08-06 -
Contact:Xun Quan, Master, First Department of General Surgery, Xiangya Third Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 413000, Hunan Province, China xun155067@163.com -
About author:Luo Hong-wu☆, M.D., Professor, Master’s supervisor, First Department of General Surgery, Xiangya Third Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 413000, Hunan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Hong-wu, Xun Quan, Huang Xiang-jun, Huang Fei-zhou. Quantitative analysis of transplanted effect of human amniotic epithelial cells in mice with acute liver injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(32): 5834-5839.
share this article
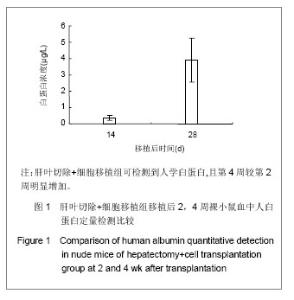
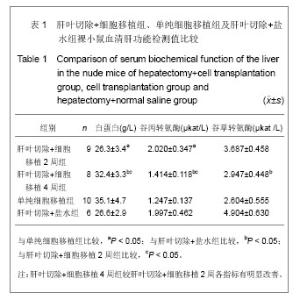
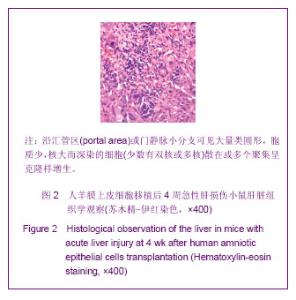
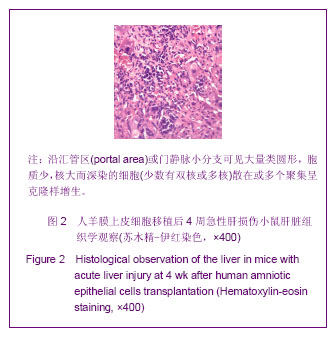
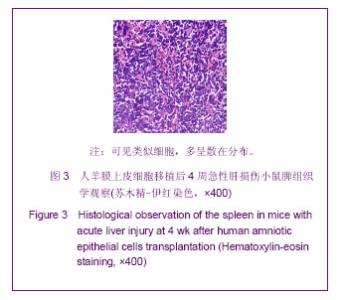
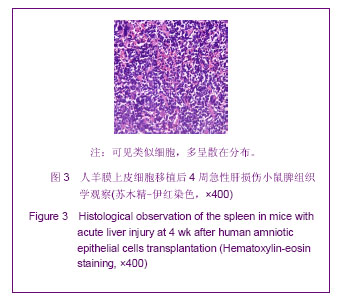
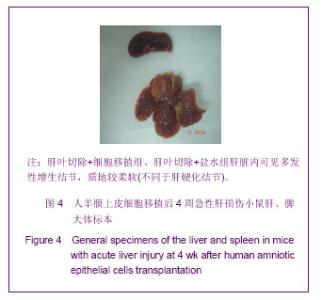
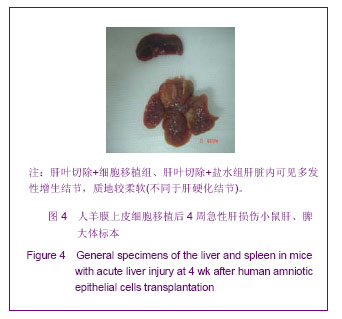
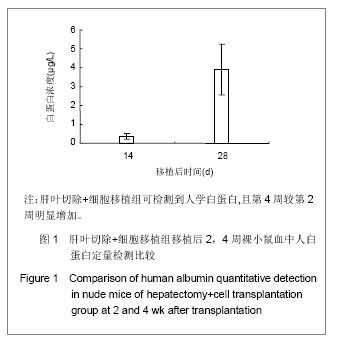
表1结果显示,肝叶切除+细胞移植2周组裸小鼠血液生化指标较之单纯细胞移植组有明显改变(P < 0.05)。肝叶切除+细胞移植4周组裸小鼠血液生化指标较之肝叶切除+盐水组有明显改变:肝叶切除+细胞移植组白蛋白水平明显高于肝叶切除+盐水组(P < 0.01),两组谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶水平差异亦有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。肝叶切除+细胞移植4周组血液生化指标较肝叶切除+细胞移植2周有明显改善:移植后4周白蛋白水平明显高于2周(P < 0.05),谷丙转氨酶水平差异亦有显著性意义(P < 0.05),而谷草转氨酶水平差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.3 小鼠血中人白蛋白检测 见图1。"
| [1] Stutchfield BM,Forbes SJ,Wigmore SJ,et al.Prospects for stem cell transplantation in the treatment of hepatic disease. Liver Transpl. 2010;16:827-836.[2] Manuelpillai U,Moodley Y,Borlongan CV,et al. Amniotic membrane and amniotic cells: Potential therapeutic tools to combat tissue inflammation and fibrosis? Placenta. 2011;32: S320-325.[3] Lysy PA,Campard D,Smets F,et al .Stem cells for liver tissue repair: Current knowledge and perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:864-875.[4] Laurson J,Selden C,Hodgson HJ,et al. Hepatocyte progenitors in man and in rodents multiple pathways, multiple candidates. Int J Exp Pathol. 2005;86:1-18.[5] Couto BG,Goldenberg RC,Fonseca LM,et al. Bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy for patients with cirrhosis: a Phase 1 study. Liver Int. 2011;31:391-400.[6] Moriya K,Yoshikawa M,Ouji Y,et al. Embryonicstem cells reduce liver fibrosis in CCl4-treated mice. J Exp Pathol. 2008; 89(6):401-409.[7] Gilchrist ES, Plevris JN. Bone marrow-derived stem cells in liver repair: 10 years down the line. Liver Transpl. 2010;16: 118-129.[8] Basma H,Soto-Gutierrez A,Yannam GR,et al.Differentiation and transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived hepatocytes. Gastroenterology.2009; 136(3):990-999.[9] Xu YQ. Liu ZC. Therapeutic potential of adult bone marrow stem cells in liver disease and delivery approaches. Stem Cell Rev. 2008;4(2):101-112.[10] Houlihan DD,Newsome PN. Critical review of clinical trials of bone marrow stem cells in liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(2):438-445.[11] Ilancheran S,Michalska A,Peh G,et al. Stem cells derived from human fetal membranes display multilineage differentiation potential. BiolReprod. 2007;77(3):577-588. [12] Parolini O,Alviano F,Bagnara GP,et al. Concise review: Isolation and characterization of cells from human term placenta: Outcome of the first international Workshop on Placenta Derived Stem Cells.Stem Cells. 2008;26:300-311.[13] Tamagawa T,Ishiwata I,Saito S,et al. Establishment and characterization of a pluripotent stem cell line derived from human amniotic membranes and initiation of germ layers in vitro. Hum Cell. 2004;17:125-130.[14] Evangelista M,Soncini M,Parolini O,et al Placenta derived stem cells: New hope for cell therapy? Cytotechnology. 2008; 58:33-42.[15] Takashima S. Human amniotic epithelial cells possess hepatocyte-like characteristics and functions. Cell Struct Funct.2004;29(3):73-84.[16] Miki T,Lehmann T,Cai H,et al.Stem cell characteristics of amniotic epithelial cells. Stem Cells. 2005; 23(10):1549-1559.[17] Sakuragawa N,Tohyama J,Yamamoto H,et al. Immunostaining of human amniotic epithelial cells: possible use as a transgene carrier in gene therapy for inborn errors of metabolism. Cell Transplant. 1995;4(3):343-346.[18] Diaz-Prado S. Multilineage differentiation potential of cells isolated from the human amniotic membrane. J Cell Biochem. 2010;111(4):846-857.[19] 罗宏武,黄湘俊,黄飞舟,等.人羊膜上皮细胞有向肝细胞样细胞分化的特性[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志,2011,19(8):683-684.[20] Eichna DM,Brown KS,Breen A,et al. Mucormycosis: A rare but serious infection. Clin. J Oncol Nurs. 2008; 12:108-112.[21] Li H, Niederkorn JY, Neelam S, et al.Immunosuppressive Factors in Amniotic Epithelial Cells. IOVS. 2005;46:900-907[22] Tseng SC,Meller D,Anderson DF,et al. Ex vivo preservation and expansion of human limbal epithelial stem cells on amniotic membrane for treating corneal diseases with total limbal stem cell defi ciency. AdvExp Med Biol. 2002;506(Pt B): 1323-1334.[23] Liu YH, Vaghjiani V, Tee JY, et al. Amniotic epithelial cells from the human placenta potently suppress a mouse model of multiple sclerosis .PLoS One.2012; 7(4): 357-358.[24] Sakuragawa N,Misawa H,Ohsugi K,et al. Evidence for active acetylcholine metabolism in human amniotic epithelial cells: applicable to intracerebral allografting for neurologic disease. Neurosci Lett. 1997;232(1): 53-56.[25] Diaz-PradoS. Multilineage differentiation potential of cells isolated from the human amniotic membrane. J Cell Biochem.2010;111(4): 846-857.[26] Manuelpillai U, Lourensz D, Vaghjiani V,et al.Human Amniotic Epithelial Cell Transplantation Induces Markers of Alternative Macrophage Activation and Reduces Established Hepatic Fibrosis.PLoS One. 2012; 7(6): e38631.[27] Manuelpillai U,Tchongue J,Lourensz D,et al. Transplantation of human amnion epithelial cells reduces hepatic fibrosis in immunocompetent CCl4-treated mice. Cell Transplantation. 2010;19: 1157-1168.[28] Luciana B,Cargnoni A,ResselL,et al. Amniotic Membrane Application Reduces Liver Fibrosis in a Bile Duct Ligation Rat Model. Cell Transplantation. 2011;20:441-453. [29] Dabeva MD,Petkov PM,Sandhu J,et al. Proliferation and differentiation of fetal liver epithelial progenitor cells after transplantation into adult rat liver. Am J Pathol. 2000;156(6): 2017-2031.[30] Kollet O,Shivtiel S,Chen YQ,et al. HGF. SDF-1.and MMP-9 are involved in stress-induced human CD34+ stem cell recruitment to the liver. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:160-169. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [5] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [6] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [7] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [8] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [9] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [10] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [11] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [12] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [13] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [14] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [15] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||