Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (32): 5799-5805.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.32.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ginsenoside Rb1 affects the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells in vitro
Luo Zhi-jun1, Li Hong-mian1, Wang He-geng1, Liu Da-lie2, Nan Hua2
- 1 Department of Plastic and Aesthetic Surgery, Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Zhongshan 528403, Guangdong Province, China
2 Department of Plastic Surgery, Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510282, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2012-03-30Revised:2012-09-12Online:2013-08-06Published:2013-08-06 -
Contact:Li Hong-mian, M.D., Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Plastic and Aesthetic Surgery, Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Zhongshan 528403, Guangdong Province, China binrong2112@163.com -
About author:Luo Zhi-jun★, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Plastic and Aesthetic Surgery, Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Zhongshan 528403, Guangdong Province, China hardaway2159@sina.com Li Hong-mian☆, M.D., Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Plastic and Aesthetic Surgery, Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Zhongshan 528403, Guangdong Province, China binrong2112@163.com Luo Zhi-jun and Li Hong-mian contributed equally to this paper. -
Supported by:Medical Research Project of Guangdong Province, No. A2011739*; Zhongshan Municipal Science and Technology Planning Project, No. 20113A008*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Zhi-jun, Li Hong-mian, Wang He-geng, Liu Da-lie, Nan Hua. Ginsenoside Rb1 affects the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(32): 5799-5805.
share this article
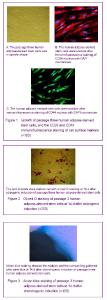
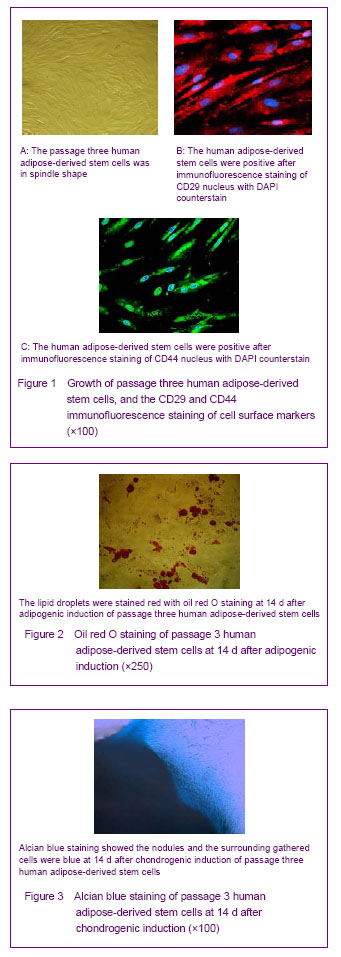
Biological characteristics and multi-directional differentiation results of human adipose-derived stem cells After primary cultured for 6 hours, a small amount of fibroblast-like cells began to scatter and adherent and most of the un-adherent cells were spherical or circular blood cells. After cultured for 24 hours, most of the adherent cells were presented as large and flat fibroblast-like cells, and a small amount of triangular and polygonal cells were observed. Additionally, the cells in the colony were spindle shaped. After cultured for 6-8 days, the cells could form 80%-90% confluent dense layer, and after cultured for 9-10 days, the cells could form 100% confluent dense monolayer. After passage, the morphology of the cells was spindle, a small amount of cells were triangular or polygonal, (Figure 1A). The growth speed of the cells after passage was faster than that before passage; the average doubling time was about 40 hours, and there was no significant change in the morphology of the cells in each generation, while the CD29 and CD44 immunofluorescence staining of passage three adipose-derived stem cells was positive (Figures 1B, C). After adipogenic induction for 14 days, translucent lipid droplets could be observed in the passage three adipose-derived stem cells, and the lipid droplets were red with oil red O staining (Figure 2); after chondrogenic induction for 14 days, highly aggregated cell mass were observed with patchy or nodular shape, and the surrounding cells were in radial-type; the nodules were large and visible; alcian blue staining showed the nodules and the surrounding gathered cells were blue (Figure 3)."
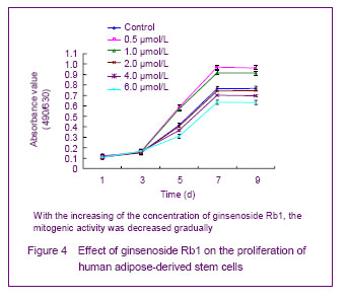
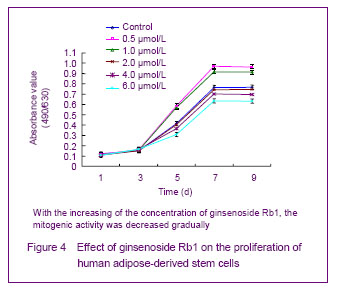
Effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on the proliferation of human adipose-derived stem cells The ginsenoside Rb1 could decrease the proliferative capacity of human adipose-derived stem cells and showed a time- and dose-dependent manner. Ginsenoside Rb1 (0.5 μmol/L) had significant promotion effect on the proliferation of human adipose-derived stem cells, and after cultured for 7 days, the cell growth reached plateau phase. With the increasing of the concentration of ginsenoside Rb1, the mitogenic activity was decreased gradually; 6.0 μmol/L ginsenoside Rb1 had significant inhibition effect on the proliferation. 2,3-bis-(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulphenyl)- (2H)-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide detection showed after cultured for 5, 7 and 9 days, the absorbance value in the 0.5 μmol/L and 1.0 μmol/L groups was significantly higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05), while the absorbance value in the 4.0 μmol/L and 6.0 μmol/L groups was significantly lower than that in the control group (P < 0.05; Figure 4)."
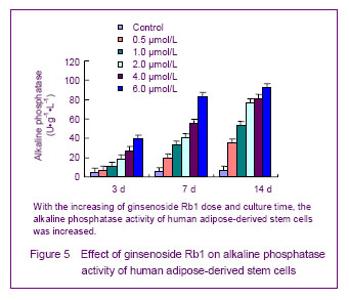
Effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on the alkaline phosphatase activity of human adipose-derived stem cells Compared with the control group, after cultured for 3 days, 6.0, 4.0 and 2.0 μmol/L ginsenoside Rb1 could increase the alkaline phosphatase activity of human adipose-derived stem cells (P < 0.05); after cultured for 7 days, 6.0, 4.0 and 2.0 μmol/L ginsenoside Rb1 could increase the alkaline phosphatase activity in human adipose-derived stem cells (P < 0.05), it indicated that the effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on the alkaline phosphatase activity of human adipose-derived stem cells was related with the culture time and dose (Figure 5). As alkaline phosphatase was the indicator to evaluate the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells, the results showed that ginsenoside Rb1 had the osteogenic activity that can early promote the oeteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells."

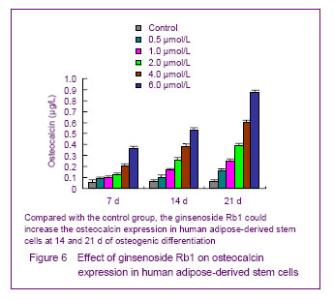
Effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on the expression of osteocalcin in human adipose-derived stem cells Osteocalcin is the sign to evaluate the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into mature osteoblasts[6]. Compared with the control group, 6.0, 4.0, 2.0, 1.0 and 0.5 μmol/L ginsenoside Rb1 could significantly increase the osteocalcin expression in human adipose-derived stem cells in the middle and advanced stage of osteogenic differentiation (14 and 21 days) (P < 0.05), and the increase degree of 6.0 and 4.0 μmol/L ginsenoside Rb1 was better than that of 2.0, 1.0 and 0.5 μmol/L ginsenoside Rb1 (Figure 6)."
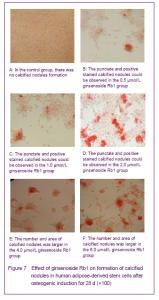
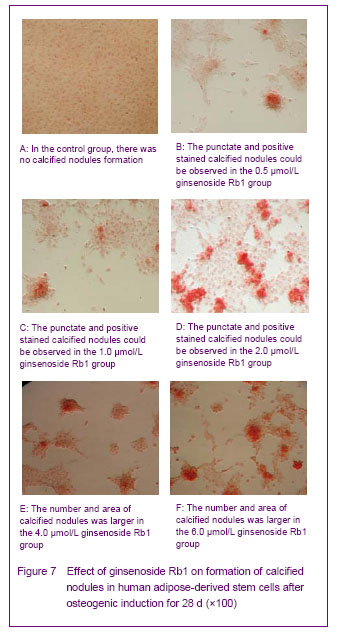
Effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on the formation of calcified nodules in human adipose-derived stem cells Alizarin red staining results showed that after cultured with ginsenoside Rb1 for 28 days, 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 μmol/L ginsenoside Rb1 could induce cell aggregation-like growth, and promote deposition of extracellular calcium, and the punctate and positive stained calcified nodules could be observed in the center of aggregation growth; 4.0 and 6.0 μmol/L ginsenoside Rb1 had more stronger promotion effect on the formation of calcified nodules, and the formed calcified nodules was larger in number, and the area (clumps shape) of the calcified nodules was larger than former; no calcified nodules formation was observed in the control group, and the cells were not in aggregation growth (Figure 7)."
| [1] Lee TK, Johnke RM, Allison RR, et al. Radioprotective potential of ginseng. Mutagenesis. 2005;20(4):237-243.[2] Lum JH, Fung KL, Cheung PY, et al. Proteome of Oriental ginseng Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer and the potential to use it as an identification tool. Proteomics. 2002;2(9):1123-1130.[3] Li X, Wu LH, Fan XH, et al. Network pharmacology study on major active compounds of Fufang Danshen formula. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi. 2011;36(21):2911-2915.[4] Han DL, Huang C, Guo SS, et al. Effects of Ginsenoside Rb_1 on growth of murine bone marrow MSC in vitro. Zhonghua Zhongyi Yaoxue Xuekan. 2008;26(6):1192-1193.[5] Li HM, Liu DL, Yu YL, et al. Experimental research of the promotion effect of autogeneic PRP on osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells in vitro. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2009;23(6): 732-736.[6] Wu XT, Wang B, Wei JN. Coumestrol promotes proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation in rat bone marrow stromal cells. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009;90(2): 621-628.[7] Okazaki H, Tazoe F, Okazaki S, et al. Increased cholesterol biosynthesis and hypercholesterolemia in mice overexpressing squalene synthase in the liver. J Lipid Res. 2006;47(9):1950-1958. [8] Liang Y, Zhao S. Progress in understanding of ginsenoside biosynthesis. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2008;10(4):415-421.[9] Kim MK, Lee BS, In JG, et al. Comparative analysis of expressed sequence tags (ESTs) of ginseng leaf. Plant Cell Rep. 2006;25(6):599-606.[10] Fujita K, Hakuba N, Hata R, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 protects against damage to the spiral ganglion cells after cochlear ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 2007;415(2):113-117. [11] Cheng Y, Shen LH, Zhang JT. Anti-amnestic and anti-aging effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and Rb1 and its mechanism of action. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005;26(2):143-149. [12] Shi AW, Wang XB, Lu FX, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes endothelial progenitor cell migration and proliferation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009;30(3):299-306.[13] Shi Q, Hao Q, Bouissac J, et al. Ginsenoside-Rd from Panax notoginseng enhances astrocyte differentiation from neural stem cells. Life Sci. 2005;76(9):983-995. [14] Joo SS, Won TJ, Kim MS, et al. Hematopoietic effect of ginsenoside Rg3 in ICR mouse primary cultures and its application to a biological response modifier. Fitoterapia. 2004;75(3-4):337-341.[15] Li HM, Gao JH, Lu F, et al. Comparison between kinds of myofascial flap encapsulating adipose-derived stromal cells carrier complex in terms of adipogenic efficacy in vivo. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2009;23(2):161- 165.[16] Zaminy A, Ragerdi Kashani I, Barbarestani M, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue in comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: melatonin as a differentiation factor. Iran Biomed J. 2008;12(3):133-141. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [3] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [6] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [7] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [8] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [9] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [10] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [11] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [12] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [13] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [14] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [15] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||