Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Co-transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and islet cells in the treatment of diabetes mellitus
Wu Li-ping1, Li Meng2, Li Rui-yu3, Sun Yan-fu3, Yan Jun-li4
- 1Department of Laboratory, Xingtai People’s Hospital, Xingtai 054031, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Health, Hotan Detachment of the Xinjiang Armed Police Corps, Hotan 848011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Institute of Integrative Medicine, Second Hospital of Xingtai Medical College, Xingtai 054000, Hebei Province China; 4Ren County Hospital, Xingtai 055150, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2013-03-15Revised:2013-06-18Online:2013-07-30Published:2013-07-30 -
Contact:Li Rui-yu, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Institute of Integrative Medicine, Second Hospital of Xingtai Medical College, Xingtai 054000, Hebei Province China liruiyu651021@163.com -
About author:Wu Li-ping★, Master, Chief examiner, Department of Laboratory, Xingtai People’s Hospital, Xingtai 054031, Hebei Province, China 18233928966@163.com -
Supported by:Projects of Hebei Province Pharmaceutical Administration, No. 2012068*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Li-ping, Li Meng, Li Rui-yu, Sun Yan-fu, Yan Jun-li. Co-transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and islet cells in the treatment of diabetes mellitus[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.31.021.
share this article

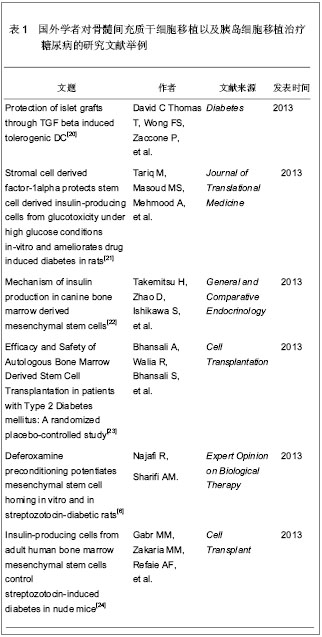
2.1 骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病 肖红珍等[11]对外源性骨髓间充质干细胞移植至糖尿病模型大鼠体内分化为胰岛细胞治疗糖尿病进行了研究。实验采用密度梯度离心结合贴壁培养的方法分离、纯化雄性大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞,并采用免疫组织荧光法进行鉴定。鉴定后将30只大鼠随机分为生理盐水组、骨髓间充质干细胞组以及糖尿病模型组,每组10只大鼠,骨髓间充质干细胞组给予大鼠尾静脉注射骨髓间充质干细胞悬液0.2 mL,生理盐水组给予大鼠尾静脉注射0.2 mL生理盐水,糖尿病模型组检测各大鼠血糖值及体质量,按一定剂量腹腔注射链脲佐菌素,检测各大鼠血糖值,当血糖≥ 16.7 mmol/L且稳定2 d后给予尾静脉注射骨髓间充质干细胞0.2 mL。应用原位杂交法检测各大鼠胰腺组织内Y染色体标志物及放射免疫法测定C-肽值。 研究结果显示,大鼠腹腔注射链脲佐菌素后 2 d,血糖水平开始迅速升高,4 d后血糖值大于 16.7 mmol/L,且稳定在21.0 mmol/L左右,注射骨髓间充质干细胞后,血清中C-肽值明显升高,而生理盐水组未予注射骨髓间充质干细胞,C-肽值无明显变化,且生理盐水组中各大鼠胰腺组织中未见黄绿荧光Y染色体标记物存在,而骨髓间充质干细胞组和糖尿病模型组各大鼠胰腺组织中均可见黄绿荧光Y染色体标记物存在,且糖尿病模型组大鼠胰腺组织中黄绿荧光强度较大,Y染色体标记物的数目较多。 刘弘光等[12]将体外培养的骨髓间充质干细胞移植至糖尿病模型大鼠体内,观察移植后各大鼠的血糖水平变化,结果发现,骨髓间充质干细胞移植3 d后,糖尿病模型大鼠的血糖为(21.84± 3.37) mmol/L,移植7 d后,糖尿病模型大鼠的血糖为(20.90±3.46) mmol/L,移植10 d后,糖尿病模型大鼠的血糖为(18.86±2.80) mmol/L,而未予以骨髓间充质干细胞移植糖尿病模型大鼠始终处于高血糖状态,并无下降趋势。此外,研究中还发现骨髓间充质干细胞移植3 d后,在大鼠胰腺血管周围可见大量BrdU阳性细胞。 孟凡彪[13]在实验中也对骨髓间充质干细胞进行分离培养,并将培养后的骨髓间充质干细胞注射至糖尿病模型大鼠尾静脉中,监测空腹血糖的变化,利用胰岛素免疫荧光染色评估胰岛的大小。结果发现,骨髓间充质干细胞移植后11 d,糖尿病模型大鼠的空腹血糖水平明显降低,但此后又再次升高。胰岛免疫荧光染色面积增大,损伤的胰岛细胞获得再生。胰腺组织中发现带有标记物的骨髓间充质干细胞,移植的骨髓间充质干细胞移植入胰腺组织内部,获得一定的增殖,但骨髓间充质干细胞本身不表达胰岛素。与胰岛细胞共培养后,能够增加胰岛细胞的表达量。 高斌等[14]对分离培养骨髓间充质干细胞并注射至糖尿病模型的大鼠进行对比观察,将注射骨髓间充质干细胞的糖尿病模型大鼠与注射生理盐水的糖尿病模型大鼠进行血糖监测比较,结果显示,移植2周后,骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病大鼠血糖为(23.63±6.42) mmol/L,胰岛素水平为(13.89± 7.89) mU/L,生理盐水对照组糖尿病大鼠血糖为(27.96±1.87) mmol/L,胰岛素水平为(11.57± 3.25) mU/L,而正常对照大鼠血糖水平为(7.97± 1.00) mmol/L,胰岛素水平为(33.68±6.21) mU/L。免疫组织化学染色观察可见正常对照大鼠胰岛中心部胰岛细胞的胰岛素为强阳性,细胞内可见深褐色粗大颗粒;生理盐水对照组大鼠可见胰岛及胰岛中心细胞数明显减少,胰岛素反应基本阴性,仅见个别胰岛细胞内出现少量微弱淡黄色细颗粒;而骨髓间充质干细胞移植糖尿病模型大鼠胰岛中心部细胞增多,大部分胰岛素反应阳性或强阳性呈黄色或褐色颗粒。 高赟等[15]和董庆玉[16]同样对同种异体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病大鼠分别进行了研究,研究均显示移植后大鼠的血糖有明显下降趋势,胰岛中增殖细胞明显增多。 2.2 骨髓间充质干细胞与胰岛细胞联合移植治疗糖尿病 田烁[17]、叶永峰[18]和贾辰乐等[19]分别对骨髓间充质干细胞与胰岛细胞联合移植治疗糖尿病进行了实验研究。田烁[17]在实验中选取三四周龄的大鼠,采用密度梯度离心法结合贴壁培养法分离纯化骨髓间充质干细胞,并进行传代扩增,取第4代细胞与胰岛细胞共培养。通过腹腔注射链脲佐菌素破坏胰腺组织设立糖尿病模型大鼠,经大鼠尾静脉分别注射磷酸盐缓冲液、骨髓间充质干细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞和胰岛细胞设立对照组及实验组。 研究结果显示,磷酸盐缓冲液治疗糖尿病模型大鼠血糖较治疗前无明显下降,骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病大鼠和骨髓间充质干细胞与胰岛细胞联合移植治疗糖尿病大鼠在移植后14 d血糖开始下降,且血糖水平与移植前相比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),并且骨髓间充质干细胞与胰岛细胞联合移植治疗糖尿病大鼠在移植后血糖下降更明显。 叶永峰[18]对骨髓间充质干细胞与胰岛细胞共培养进行了实验研究,分离大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞和胰岛,设立共培养组和单独培养组,并进行体外培养,结果显示,随体外培养时间的延长,胰岛与骨髓间充质干细胞混合培养组的存活率与胰岛单独培养组的存活率差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),随培养时间延长,胰岛对葡萄糖反应性逐渐减弱,刺激指数从第1天的3.1-3.3降至第7天的1-1.6。此外,研究结果还显示单独胰岛移植治疗(10.2±2.0) d内,血糖可控制在16.7 mmol/L以下,但随后血糖逐渐上升,半量胰岛联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植后(15.2±1.3) d内,血糖能够控制在16.7 mmol/L以下,胰岛联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植后(21.0±1.7) d内,血糖能够控制在16.7 mmol/L以下。胰岛联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗的糖尿病模型大鼠,移植治疗前尾部皮肤存在溃疡病变,移植治疗15 d后,皮毛变光滑,动作敏捷,尾部病变好转。 贾辰乐等[19]也对骨髓间充质干细胞与胰岛细胞共培养移植治疗糖尿病模型大鼠进行了研究,实验采用密度梯度离心法分离骨髓间充质干细胞,胶原酶消化法分离胰岛细胞,链脲佐菌素制备糖尿病模型大鼠,分别给予糖尿病模型大鼠单纯胰岛细胞移植和胰岛细胞联合骨髓间充质干细胞共移植,并设立生理盐水对照,比较血糖的变化。结果显示,生理盐水对照组糖尿病模型大鼠血糖水平一直较高,移植后1 d,血糖水平为(26.22±3.37) mmol/L,移植后5 d,血糖水平为(24.83±3.97) mmol/L,移植后 15 d,血糖水平为(27.47±2.65) mmol/L;单纯胰岛细胞移植治疗糖尿病模型大鼠,移植后1 d,血糖水平为(8.43±1.34) mmol/L,移植后5 d,血糖水平为(10.46±1.37) mmol/L,移植后15 d,血糖水平为(12.31±1.87) mmol/L;胰岛细胞联合骨髓间充质干细胞共移植治疗糖尿病模型大鼠,移植后1 d,血糖水平为(6.61±1.95) mmol/L,移植后5 d,血糖水平为(7.35±2.03) mmol/L,移植后15 d,血糖水平为(7.71±1.84) mmol/L。骨髓间充质干细胞与胰岛细胞联合移植和单纯胰岛细胞移植后的血糖水平相比较,差异有显著性差异意义。 2.3 国外学者对骨髓间充质干细胞移植以及胰岛细胞移植治疗糖尿病的研究文献举例 见表1。"
| [1] Phinney DG, Prockop DJ. Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair--current views. Stem Cells. 2007; 25(11):2896-2902.[2] Gronthos S, Zannettino AC, Hay SJ, et al. Molecular and cellular characterisation of highly purified stromal stem cells derived from human bone marrow. J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 9): 1827-1835. [3] Jahr H, Bretzel RG. Insulin-positive cells in vitro generated from rat bone marrow stromal cells. Transplant Proc. 2003; 35(6):2140-2141.[4] Oh SH, Muzzonigro TM, Bae SH, et al. Adult bone marrow-derived cells trans-differentiating into insulin-producing cells for the treatment of type I diabetes. Lab Invest. 2004;84(5):607-617.[5] Tang DQ, Cao LZ, Burkhardt BR, et al. In vivo and in vitro characterization of insulin-producing cells obtained from murine bone marrow. Diabetes. 2004;53(7):1721-1732. [6] Najafi R, Sharifi AM. Deferoxamine preconditioning potentiates mesenchymal stem cell homing in vitro and in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013; 13(7):959-972. [7] Chhabra P, Brayman KL. Stem cell therapy to cure type 1 diabetes: from hype to hope. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013; 2(5):328-336.[8] Tsai PJ, Wang HS, Lin CH, et al. Intraportal injection of insulin-producing cells generated from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells decreases blood glucose level in diabetic rats. Endocr Res. 2013. [9] Hao H, Liu J, Shen J, et al. Multiple intravenous infusions of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells reverse hyperglycemia in experimental type 2 diabetes rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. [10] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-6-10. https://www.cnki.net[11] 肖红珍,张慧芹,刘阁玲.外源性骨髓间充质干细胞在糖尿病模型大鼠体内向胰腺迁移并分化为胰岛细胞的趋势[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(15):2870-2873.[12] 刘弘光,夏鲲,刘晓玉,等.移植骨髓间充质干细胞治疗大鼠糖尿病的研究[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2007,16(1):104-109.[13] 孟凡彪.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞促进胰岛细胞再生的研究[D].辽宁:中国医科大学,2010:1-46.[14] 高斌,宓真,杜馨丽,等.同种异体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病大鼠的实验研究[J].中国医药导报,2011,8(14):32-33.[15] 高赟,张祥迅,史瑾瑜,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞同种异体移植治疗糖尿病的初步研究[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2009,17(7): 510-515.[16] 董庆玉.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对糖尿病大鼠治疗作用的实验研究[D].山东:山东大学,2008:1-86.[17] 田烁.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞与胰岛细胞共培养及对糖尿病大鼠的治疗[D].河北:河北医科大学,2009:1-70.[18] 叶永峰.胰岛-骨髓间充质干细胞联合移植治疗大鼠Ⅰ型糖尿病的研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2008:1-56.[19] 贾辰乐,商中华,张孝良,等.大鼠胰岛细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞联合移植治疗糖尿病小鼠的研究[J].中国现代医生,2010,48(3): 5-6.[20] David C Thomas T, Wong FS, Zaccone P, et al. Protection of islet grafts through TGF beta induced tolerogenic DC. Diabetes. 2013.[21] Tariq M, Masoud MS, Mehmood A, et al. Stromal cell derived factor-1alpha protects stem cell derived insulin-producing cells from glucotoxicity under high glucose conditions in-vitro and ameliorates drug induced diabetes in rats. J Transl Med. 2013;11:115.[22] Takemitsu H, Zhao D, Ishikawa S, et al. Mechanism of insulin production in canine bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2013;189:1-6.[23] Bhansali A, Walia R, Bhansali S, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Autologous Bone Marrow Derived Stem Cell Transplantation in patients with Type 2 Diabetes mellitus: A randomized placebo-controlled study. Cell Transplant. 2013.[24] Gabr MM, Zakaria MM, Refaie AF, et al. Insulin-producing cells from adult human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells control streptozotocin-induced diabetes in nude mice. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(1):133-145.[25] Schmid RA, Stammberger U, Hillinger S, et al. Fas ligand gene transfer combined with low dose cyclosporine A reduces acute lung allograft rejection. Transpl Int. 2000;13 Suppl 1: S324-328.[26] Tse WT, Pendleton JD, Beyer WM, et al. Suppression of allogeneic T-cell proliferation by human marrow stromal cells: implications in transplantation. Transplantation. 2003;75(3): 389-397.[27] Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood. 2002;99(10):3838-3843.[28] Le Blanc K, Tammik L, Sundberg B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit and stimulate mixed lymphocyte cultures and mitogenic responses independently of the major histocompatibility complex. Scand J Immunol. 2003;57(1): 11-20.[29] Le Blanc K, Tammik C, Rosendahl K, et al. HLA expression and immunologic properties of differentiated and undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Hematol. 2003; 31(10):890-896.[30] 肖承佐,章乐虹.骨髓间充质干细胞在1型糖尿病治疗中的应用[J].现代临床医学生物工程学杂志,2005,11(6):480-483.[31] 贾书辉,李彩萍.骨髓间充质干细胞在1型糖尿病中的应用[J].医学综述,2010,16(18):2800-2803.[32] Liu L, DiGirolamo CM, Navarro PA, et al. Telomerase deficiency impairs differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2004;294(1):1-8.[33] 崔红强,吴绍华.骨髓间充质干细胞研究进展[J].西南军医, 2009, 11(4): 715-717. |
| [1] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [2] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [3] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [6] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [7] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [8] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [9] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [10] | Wang Hanyue, Li Furong, Yang Xiaofei, Hu Chaofeng. Direct reprogramming hepatocytes into islet-like cells by efficiently targeting and activating the endogenous genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| [11] | Jiang Xin, Qiao Liangwei, Sun Dong, Li Ming, Fang Jun, Qu Qingshan. Expression of long chain non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 in serum of renal transplant patients and its regulation of human glomerular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 741-745. |
| [12] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [13] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [14] | Zeng Xianghong, Liang Bowei. A new strategy for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 431-437. |
| [15] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||