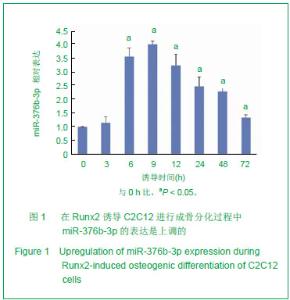
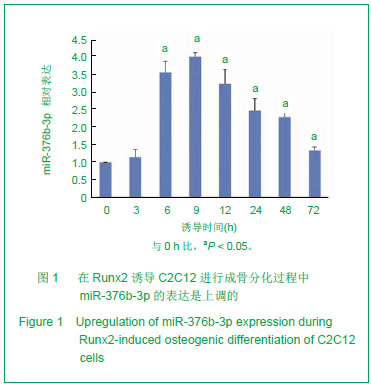
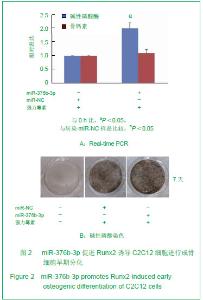
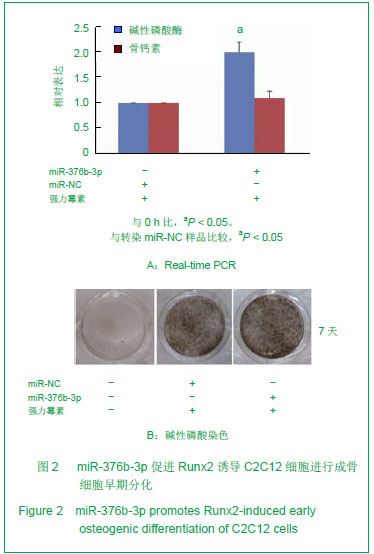
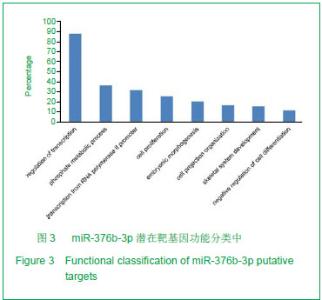
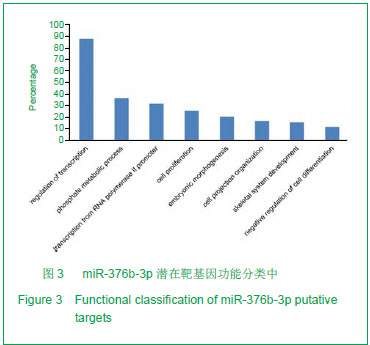
| [1]Otto F, Kanegane H, Mundlos S. Mutations in the RUNX2 gene in patients with cleidocranial dysplasia. Hum Mutat. 2002;19(3):209-216.[2]Zhang C, Zheng S, Wang Y, et al. Mutational analysis of RUNX2 gene in Chinese patients with cleidocranial dysplasia. Mutagenesis. 2010; 25(6):589-594. [3]李萍,余守和,高忠平,等.过表达Runx2促进C2C12细胞成骨分化[J],中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2010,26(3):236-242[4]Hassan MQ, Gordon JA, Beloti MM,et al. A network connecting Runx2, SATB2, and the miR-23a-27a-24-2 cluster regulates the osteoblast differentiation program. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2010;107(46): 19879-19884.[5]Crist CG, Montarras D, Pallafacchina G,et al. Muscle stem cell behavior is modified by miRNA-27 regulation of Pax3 expression. ProcNatlAcad Sci U S A.2009;106 (32):13383-13387[6]Pan Z,Guo Y,Qi H.M(3) Subtype of Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Promotes Cardioprotection via the Suppression of miR-376b-5p. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32571.[7]Wang F, Yu J, Yang GH. Regulation of erythroid differentiation by miR-376a and its targets. Cell Res.2011;21(8):1196-1209.[8]Pan K, Sun Q, Zhang J, et al. Multilineage differentiation of dental follicle cells and the roles of Runx2 over-expression in enhancing osteoblast/cementoblast-related gene expression in dental follicle cells. Cell Proliferation, 2010; 43(3): 219-228.[9]Otto F, Kanegane H, Mundlos S. Mutations in the RUNX2 gene in patients with cleidocranial dysplasia. Human Mutation. 2002; 19(3):209-216.[10]Xuan D, Li S, Zhang X, et al. Mutational analysis of RUNX2 gene in Chinese patients with cleidocranial dysplasia. Mutagenesis. 2008; 38(1):15-24.[11]Liu W, Toyosawa S, Furuichi T. Overexpression of Cbfa1 in osteoblasts inhibits osteoblast maturation and causes osteopenia with multiple fractures. J Cell Biol. 2001; 155(1):157-166.[12]Geoffroy V, Kneissel M, Fournier B,et al. High bone resorption in adult aging transgenic mice overexpressing Cbfa1/Runx2 in cells of the osteoblastic lineage. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(17): 6222-6233.[13]Kapinas K, Delany AM. MicroRNA biogenesis and regulation of bone remodeling. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(3): 220.[14]Hu R, Li H, Liu W,et al. Targeting miRNAs in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011;14(10):1109-1120.[15]Kapinas K, Kessler CB, Delany AM. miR-29 suppression of osteonectin in osteoblasts: Regulation during differentiation and by canonical Wnt signaling. J Cell Biol.2009;108(1): 216-224.[16]Li Z, Hassan MQ, Volinia S,et al. A microRNA signature for a BMP2-induced osteoblast lineage commitment program. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(37): 13906-13911.[17]Luzi E, Marini F, Sala SC,et al. Osteogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells is modulated by the miR-26a targeting of the SMAD1 transcription factor. J Bone Miner Res. 2007; 23(2):287-295.[18]Eskildsen T, Taipaleenmaki H, Stenvang J,et al. MicroRNA-138 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human stromal (mesenchymal) stem cells in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108(15): 6139-6144.[19]Govoni KE, Linares GR, Chen ST,et al. T-box 3 negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation by inhibiting expression of osterix and runx2. J Cell Biochem. 2009; 106(3):482-490. |