Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Primary culture of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in serum free medium
Zhou Ting-ting1, Wei Chao1, Chen Xiao-dong2, Li Hai1, Wang Zheng1
- 1Department of Digestion, Renji Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University Medical School, Shanghai 200001, China; 2Department of Restorative Dentistry, Division of Biomaterials, the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, San Antonio, Texas, USA
-
Received:2012-12-10Revised:2013-01-24Online:2013-07-02Published:2013-07-02 -
Contact:Li Hai, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Digestion, Renji Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University Medical School, Shanghai 200001, China haili_17@yahoo.com Corresponding author: Wang Zheng, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Digestion, Renji Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University Medical School, Shanghai 200001, China zheng.w.dr@gmail.com -
About author:Zhou Ting-ting★, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Digestion, Renji Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University Medical School, Shanghai 200001, China Guxinglei1005@126.com -
Supported by:the Specific Foundation for Key Laboratory of Digestion Medicine, Ministry of Health, No. 30972751*; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30971468
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Ting-ting, Wei Chao, Chen Xiao-dong, Li Hai, Wang Zheng. Primary culture of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in serum free medium[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.27.006.
share this article

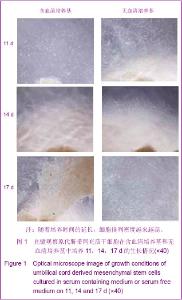
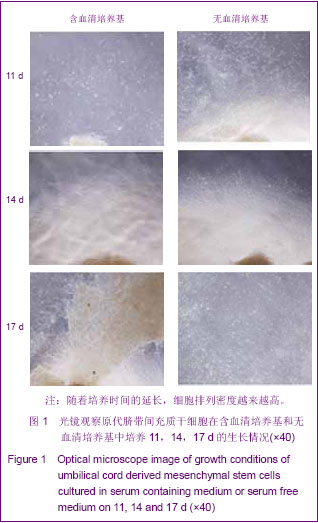
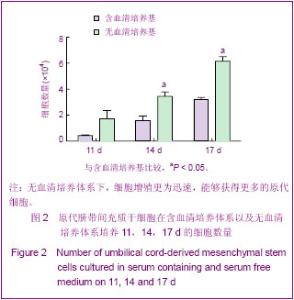
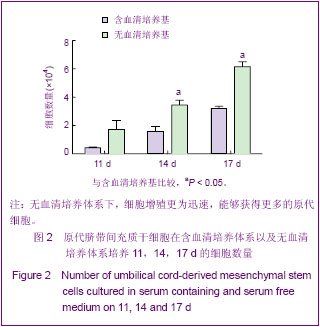
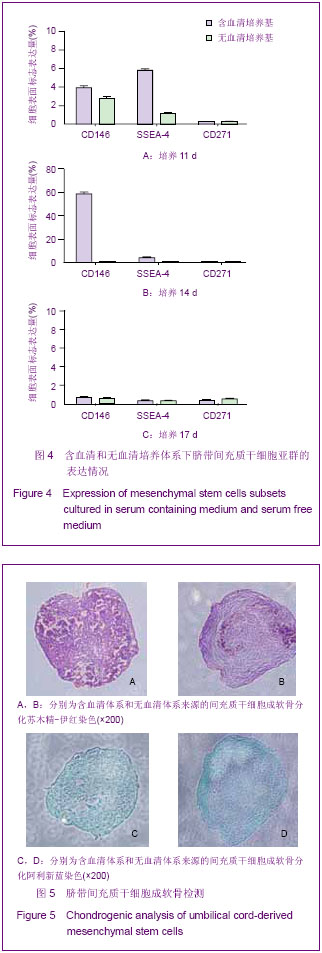
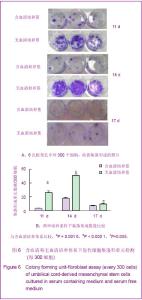
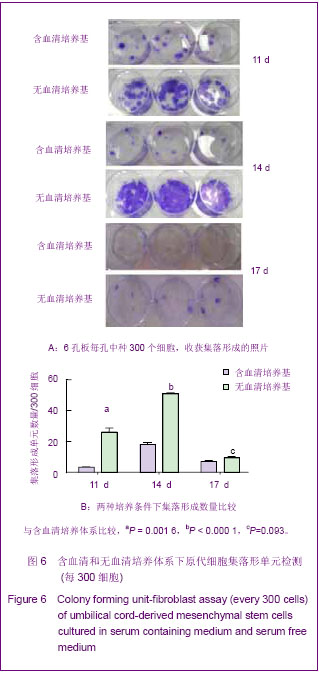
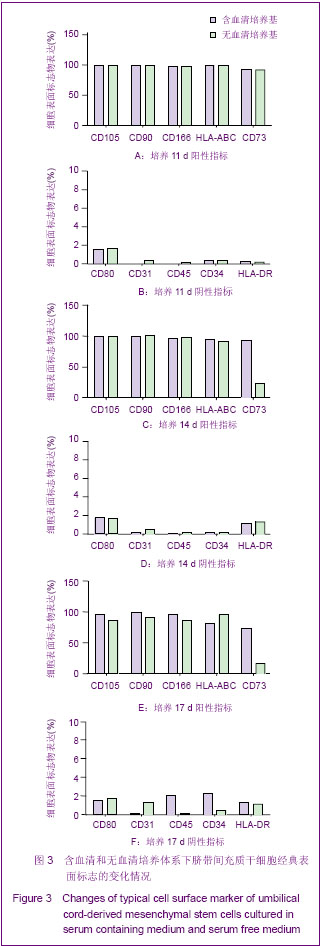
2.3 不同培养体系经典干细胞原代表面标志的变化 两种培养体系下获得的细胞均高表达CD44[37],CD73,CD166[38-39],CD105和HLA-ABC(约为95%)等,不表达CD34,CD31,CD80,HLA-DR,CD45(<2%)等[40],见图3。 2.4 不同培养体系下干细胞原代亚群表面标志的变化 两种培养体系下干细胞亚群标志SSEA-4表达很低,在含血清培养体系中CD146先升高后下降[41],最高超过50%,SSEA-4表达量最高值不超过7%[42-43]。无血清培养条件下,以上表面标志均没有明显变化。另外,两种培养条件下均不表达骨髓间充质干细胞高表达的CD271[44],见图4。 2.5 不同培养条件下成软骨分化结果 含血清培养条件下和无血清培养条件下,脐带间充质干细胞均可以成软骨分化成功,见图5。 2.6 不同培养条件下集落形成实验检测结果的变化 无血清培养体系相对于含血清体系,原代干细胞增殖能力明显提高,并且在培养到14 d时达到高峰;含血清培养体系中,随着培养时间的延长,形成的集落数逐渐呈下降趋势。另外,在不同的培养时间,观察发现集落形成实验中无血清培养体系下形成的集落数均多于含血清培养体系下形成的集落数,并且在11 d和14 d时,差异有显著性意义,见图6。"
| [1] Dennis JE, Merriam A, Awadallah A,et al.A quadripotential mesenchymal progenitor cell isolated from the marrow of an adult mouse.J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14(5):700-709.[2] Ferrari G, Cusella-De Angelis G, Coletta M,et al.Muscle regeneration by bone marrow-derived myogenic progenitors.Science. 1998;279(5356):1528-1530.[3] Liu S, Yuan M, Hou K,et al.Immune characterization of mesenchymal stem cells in human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly and derived cartilage cells.Cell Immunol. 2012;278(1-2):35-44.[4] Ma L, Zhou Z, Zhang D,et al.Immunosuppressive function of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord matrix in immune thrombocytopenia patients.Thromb Haemost. 2012; 107(5):937-950.[5] Zhang YK, Han XY, Che ZY. Effects of buyang huanwu tang combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on the expression of VEGF and Ki-67 in the brain tissue of the cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model rat.J Tradit Chin Med. 2010;30(4):278-282.[6] Motaln H, Gruden K, Hren M,et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exploit the Immune Response Mediating Chemokines to Impact the Phenotype of Glioblastoma.Cell Transplant. 2012. [Epub ahead of print][7] Ji YR, Yang ZX, Han ZB,et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Support Proliferation and Terminal Differentiation of B Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;30(6):1526-1537.[8] McGuirk JP, Weiss ML. Promising cellular therapeutics for prevention or management of graft-versus-host disease (a review).Placenta. 2011;32 Suppl 4:S304-310.[9] Mathiasen AB, Jørgensen E, Qayyum AA,et al. Rationale and design of the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of intramyocardial injection of autologous bone-marrow derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in chronic ischemic Heart Failure (MSC-HF Trial).Am Heart J. 2012;164(3):285-291.[10] Kim SM, Woo JS, Jeong CH,et al. Effective combination therapy for malignant glioma with TRAIL-secreting mesenchymal stem cells and lipoxygenase inhibitor MK886.Cancer Res. 2012;72(18):4807-4817.[11] Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI,et al. Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues.Transplantation. 1968; 6(2):230-247.[12] Deng Y, Li TQ, Yan YE,et al. Effect of nicotine on chondrogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in alginate bead culture. Biomed Mater Eng. 2012;22(1-3):81-87.[13] Leng Y, Zheng Z, Zhou C,et al. A comparative study of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell functionality in C57BL and mdx mice.Neurosci Lett. 2012;523(2):139-144.[14] Guo QS, Zhu MY, Wang L,et al. Combined transfection of the three transcriptional factors, PDX-1, NeuroD1, and MafA, causes differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-producing cells.Exp Diabetes Res. 2012; 2012:672013. [15] Al Faqeh H, Nor Hamdan BM, Chen HC,et al.The potential of intra-articular injection of chondrogenic-induced bone marrow stem cells to retard the progression of osteoarthritis in a sheep model.Exp Gerontol. 2012;47(6):458-464.[16] Grove JE, Bruscia E, Krause DS. Plasticity of bone marrow-derived stem cells.Stem Cells. 2004;22(4):487-500.[17] Pietilä M, Lähteenmäki K, Lehtonen S,et al. Monitoring mitochondrial inner membrane potential for detecting early changes in viability of bacterium-infected human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;3(6):53.[18] Yagi H, Tan J, Tuan RS. Polyphenols suppress hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human bone-marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2012. [Epub ahead of print][19] Kocsis JD, Honmou O.Bone marrow stem cells in experimental stroke. Prog Brain Res. 2012;201:79-98. [20] Iwamoto T, Terai S, Hisanaga T,et al.Bone-marrow-derived cells cultured in serum-free medium reduce liver fibrosis and improve liver function in carbon-tetrachloride-treated cirrhotic mice.Cell Tissue Res. 2012. [Epub ahead of print][21] Wei T, Lv Y. Immediate intraportal transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells prevents death from fulminant hepatic failure in pigs.Hepatology. 2012. [Epub ahead of print][22] Lu LL, Liu YJ, Yang SG,et al. Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with hematopoiesis-supportive function and other potentials. Haematologica. 2006;91(8):1017-1026.[23] Prockop DJ. Repair of tissues by adult stem/progenitor cells (MSCs): controversies, myths, and changing paradigms.Mol Ther. 2009;17(6):939-946.[24] Zhang X, Zhang L, Xu W,et al. Experimental therapy for lung cancer: umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-mediated interleukin-24 delivery.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013;13(1):92-102.[25] Hu J, Yu X, Wang Z,et al. Long term effects of the implantation of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells from the umbilical cord for newly-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus. Endocr J. 2012. [Epub ahead of print][26] Liu R, Zhang Z, Lu Z,et al. Human Umbilical Cord Stem Cells Ameliorate Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Regulating Immunoinflammation and Remyelination.Stem Cells Dev. 2012. [Epub ahead of print][27] Xue G, He M, Zhao J, et al. Intravenous umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell infusion for the treatment of combined malnutrition nonunion of the humerus and radial nerve injury.Regen Med. 2011;6(6):733-741.[28] Kim J, Shin JM, Jeon YJ,et al. Proteomic validation of multifunctional molecules in mesenchymal stem cells derived from human bone marrow, umbilical cord blood and peripheral blood. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e32350. [29] Meng MY, Pang W, Jiang LH,et al. Stemness gene expression profile analysis in human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012;237(6):709-719.[30] Wang D, Ji YR, Chen K,et al. IL-6 production stimulated by CD14(+) monocytes-paracrined IL-1β does not contribute to the immunosuppressive activity of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;29(3-4): 551-560.[31] Manochantr S, U-Pratya Y, Kheolamai P,et al. Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from amnion, placenta, Wharton's jelly and umbilical cord.Intern Med J. 2012. [Epub ahead of print][32] Zhang Y, Hao H, Liu J,et al. Repair and regeneration of skin injury by transplanting microparticles mixed with Wharton's jelly and MSCs from the human umbilical cord. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2012;11(4):264-270.[33] Salehinejad P, Alitheen NB, Ali AM,et al.Comparison of different methods for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2012;48(2):75-83.[34] Montanucci P, Basta G, Pescara T,et al. New simple and rapid method for purification of mesenchymal stem cells from the human umbilical cord Wharton jelly.Tissue Eng Part A. 2011; 17(21-22):2651-2661.[35] Tsagias N, Koliakos I, Karagiannis V,et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells using the total length of umbilical cord for transplantation purposes.Transfus Med. 2011;21(4): 253-261.[36] Lai Y, Sun Y, Skinner CM,et al. Reconstitution of marrow-derived extracellular matrix ex vivo: a robust culture system for expanding large-scale highly functional human mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(7):1095-1107.[37] Javazon EH, Beggs KJ, Flake AW. Mesenchymal stem cells: paradoxes of passaging. Exp Hematol. 2004;32(5):414-425.[38] Bowen MA, Aruffo AA, Bajorath J. Cell surface receptors and their ligands: in vitro analysis of CD6-CD166 interactions. Proteins. 2000;40(3):420-428.[39] Tsai MS, Lee JL, Chang YJ,et al. Isolation of human multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from second-trimester amniotic fluid using a novel two-stage culture protocol.Hum Reprod. 2004;19(6):1450-1456.[40] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[41] Sorrentino A, Ferracin M, Castelli G,et al. Isolation and characterization of CD146+ multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells.Exp Hematol. 2008;36(8):1035-1046.[42] Gang EJ, Bosnakovski D, Figueiredo CA, et al. SSEA-4 identifies mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow.Blood. 2007;109(4):1743-1751. [43] Ouhtit A, Gaur RL, Abd Elmageed ZY,et al. Towards understanding the mode of action of the multifaceted cell adhesion receptor CD146.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1795 (2):130-136.[44] Battula VL, Treml S, Bareiss PM,et al. Isolation of functionally distinct mesenchymal stem cell subsets using antibodies against CD56, CD271, and mesenchymal stem cell antigen-1.Haematologica. 2009;94(2):173-184.[45] Li W, Ren G, Huang Y,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: a double-edged sword in regulating immune responses.Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(9):1505-1513.[46] Pelosi E, Castelli G, Testa U. Human umbilical cord is a unique and safe source of various types of stem cells suitable for treatment of hematological diseases and for regenerative medicine. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2012;49(1):20-28.[47] Selvaggi TA, Walker RE, Fleisher TA. Development of antibodies to fetal calf serum with arthus-like reactions in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients given syngeneic lymphocyte infusions.Blood. 1997;89(3):776-779.[48] Tonti GA, Mannello F. From bone marrow to therapeutic applications: different behaviour and genetic/epigenetic stability during mesenchymal stem cell expansion in autologous and foetal bovine sera.Int J Dev Biol. 2008;52(8): 1023-1032.[49] Chachques JC, Herreros J, Trainini J,et al. Autologous human serum for cell culture avoids the implantation of cardioverter-defibrillators in cellular cardiomyoplasty.Int J Cardiol. 2004;95 Suppl 1:S29-33.[50] Mizuno N, Shiba H, Ozeki Y,et al. Human autologous serum obtained using a completely closed bag system as a substitute for foetal calf serum in human mesenchymal stem cell cultures.Cell Biol Int. 2006;30(6):521-524. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [3] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [4] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [5] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [6] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [7] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [8] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [9] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [10] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [11] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [12] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [13] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [14] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [15] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||