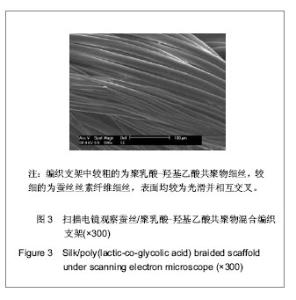
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (25): 4676-4683.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.25.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Silk/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold degradation fluid and proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Zhang Wen-yuan, Yang Ya-dong, Li Ying, Zhang Ke-ji, Fang Guo-jian, Tang Liang, Li Yue-zhong, Wang Han, Lu Ming-yang
- Zhejiang Academy of Medical Science, Hangzhou 310013, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Received:2012-10-26Revised:2012-12-03Online:2013-06-18Published:2013-06-18 -
About author:Zhang Wen-yuan★, Master, Researcher, Zhejiang Academy of Medical Science, Hangzhou 310013, Zhejiang Province, China zhangwy61@163.com -
Supported by:General Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81071467; Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, No. LY13H060004; Biomedicine Key Discipline of Medical Key Discipline Group of Zhejiang Province, No. XKQ-010-001; Medical and Hygienic Technology Plan of Zhejiang Province, No. 2010KYB001
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Wen-yuan, Yang Ya-dong, Li Ying, Zhang Ke-ji, Fang Guo-jian, Tang Liang, Li Yue-zhong, Wang Han, Lu Ming-yang. Silk/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold degradation fluid and proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(25): 4676-4683.
share this article

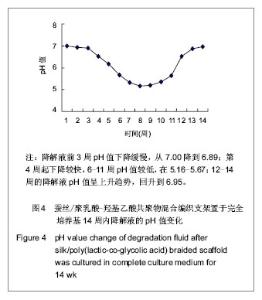
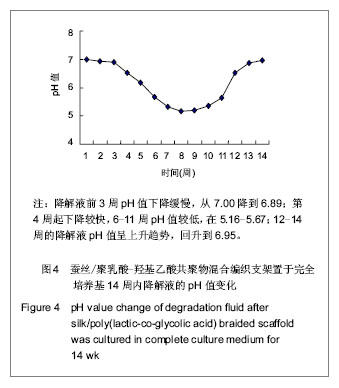
结果提示,前3周支架材料中的PLGA尚未进入实质性降解阶段,pH值变化不大。第4周开始支架材料中的PLGA进入实质性降解阶段,pH值逐渐下降至第8周的5.16,第9周的5.21,第10周的5.34,之后随着支架中PLGA量的逐渐减少,pH值逐渐回升。第13.0-14.0周,支架中PLGA量已很少,剩下的基本上是蚕丝丝素,降解液pH值回升到近中性水平。 2.4 在支架降解液中骨髓间充质干细胞的形态观察 在总体上,通过全程1-4 d观察,实验组及阴性对照组细胞增殖生长及形态状况基本相似。 细胞与蚕丝/PLGA材料降解液共同培养1-4 d时的结果:实验组及阴性对照组细胞相似,开始时,呈梭形,折光性强,细胞突伸展。随着时间的延长,实验组及阴性对照组细胞生长状态与先前相似,均为形态均一的长梭形,并呈旋涡状生长,细胞生长旺盛,随着时间延长,细胞数量进一步增多,排列密集、规则,并逐渐连接成片;支架材料降解7-10周的降解液对细胞生长可见有抑制作用,可见实验组细胞数量相对较少、较疏,见图5,6;而其余各周的降解液对细胞的增殖生长无明显抑制作用。"


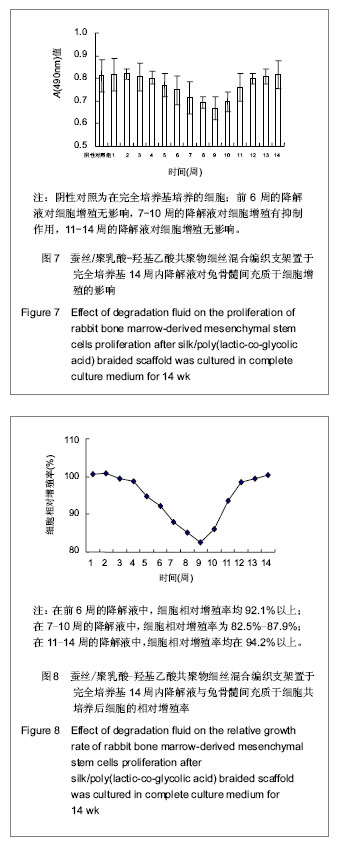
2.5 在支架降解液中骨髓间充质干细胞的生长曲线及其相对增殖率情况 见图7,8。 前6周的降解液对骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖生长没有显著影响,细胞相对增殖率为92.1%以上,毒性分级为0或1级,基本上无细胞毒性。从统计学角度分析,7-10周的降解液对骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖生长可见有抑制作用(P < 0.05);但从细胞相对增殖率角度分析,其细胞相对增殖率为82.5%-87.9%,毒性分级为1级,为合格,即为在可接受范围内。11-14周的降解液对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖生长无显著影响,细胞相对增殖率为94.2%以上,毒性分级为0或1级,基本上无细胞毒性。结果表明支架材料降解液的pH值变化影响细胞的增殖生长,结果也提示蚕丝/PLGA混合编织支架释放的酸性物质对细胞的增殖有一定的影响,但其细胞相对增殖率均在82.5%以上,毒性分级为0或1级,为合格,即为在可接受的范围内。提示蚕丝/PLGA混合编织支架可望作为组织工程韧带/肌腱的候选支架材料。"
| [1] Zhang WY,Yang YD,Fang GJ,et al.Zhongguo Weisheng Jianyan Zazhi.2011;21(12):2868-2870.张文元,杨亚冬,房国坚,等. 蚕丝-PLGA混合编织支架材料的细胞毒性检测[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2011,21(12):2868-2870.[2] Zhang WY,Yang YD,Fang GJ,et al.Zhongguo Weisheng Jianyan Zazhi.2012;22(2):237-239.张文元,杨亚冬,房国坚,等. 蚕丝-PLGA编织支架生物安全性评价方法研究和应用[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2012,22(2):237-239.[3] Zhang WY,Yang YD,Fang GJ,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2006;10(13):44-46.张文元,杨亚冬,房国坚,等.不同冻存时间与温度对兔骨髓基质干细胞存活率的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2006, 10(13):44-46.[4] Kim UJ,Park J,Kim HJ,et al.Three dimensional aqueous-derived biomaterial scaffolds from silk fibroin. Biomaterials.2005;26(15):2775-2785.[5] Cao Y,Wang B.Biodegradation of silk biomaterials.Int J Mol Sci.2009;10(4):1514-1524.[6] Wang Y,Rudym DD,Walsh A,et al.In vivo degradation of three-dimensional silk fibroin scaffolds. Biomaterials.2008; 29(24-25):3415-3428.[7] Laurencin CT,Freeman JW.Ligament tissue engineering:an evolutionary materials science approach.Biomaterials. 2005; 26(36):7530-7536.[8] Altman GH,Horan RL,Lu HH,et al.Silk matrix for tissue engineered anterior cruciate ligaments.Biomaterials.2002; 23(20):4131-4141.[9] James AC,Helen HL,Frank KK,et al.Fiber-based tissue-engineered scaffold for ligament replacement:design considerations and in vitro evaluation. Biomaterials.2005; 26(13):1523-1532.[10] Mandal BB,Kundu SC.Biospinning by silkworms:Silk fiber matrices for tissue engineering applications.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(2):360-371.[11] Cooper JA Jr,Sahota JS,Gorum WJ 2nd,et al.Biomimetic tissue-engineered anterior cruciate ligament replacement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(9):3049-3054.[12] Seo YK,Yoon HH,Song KY,et al.Increase in cell migration and angiogenesis in a composite silk scaffold for tissue-engineered ligaments.J Orthop Res.2009;27(4): 495-503.[13] Fan H,Liu H,Toh SL,et al.Anterior cruciate ligament regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells and silk scaffold in large animal model. Biomaterials.2009;30(28):4967-4977.[14] Li M,Ogiso M,Minoura N.Enzymatic degradation behavior of porous silk fibroin sheets.Biomaterials.2003;24(2):357-365.[15] Wang Y,Kim HJ,Karageorgiou V,et al.Stem cell-based tissue engineering with silk biomaterials. Biomaterials.2006;27(36): 6064-6082.[16] Fan H,Liu H,Wong EJ,et al.In vivo study of anterior cruciate ligament regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells and silk scaffold. Biomaterials.2008;29(23):3324-3337.[17] Park BH,Zhou L,Jang KY,et al.Enhancement of tibial regeneration in a rat model by adipose-derived stromal cells in a PLGA scaffold.Bone.2012;51(3):313-323.[18] van Eijk F,Saris DB,Fedorovich NE,et al.In vivo matrix production by bone marrow stromal cells seeded on PLGA scaffolds for ligament tissue engineering.Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(10):3109-3117.[19] van Eijk F,Saris DB,Creemers LB,et al.The effect of timing of mechanical stimulation on proliferation and differentiation of goat bone marrow stem cells cultured on braided PLGA scaffolds.Tissue Eng Part A.2008;14(8):1425-1433.[20] Vaquette C,Slimani S,Kahn CJ,et al.A poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)knitted scaffold for tendon tissue engineering:an in vitro and in vivo study.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2010;21(13): 1737-1760.[21] Urita Y,Komuro H,Chen G,et al.Evaluation of diaphragmatic hernia repair using PLGA mesh-collagen sponge hybrid scaffold:An experimental study in a rat model.Pediatr Surg Int.2008;24(9):1041-1045.[22] Wang X,Sui S.Pulsatile culture of a poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid) sandwiched cell/hydrogel construct fabricated using a step-by-step mold/extraction method.Artif Organs.2011; 35(6): 645-655.[23] Jenner JM,van Eijk F,Saris DB,et al.Effect of transforming growth factor-beta and growth differentiation factor-5 on proliferation and matrix production by human bone marrow stromal cells cultured on braided poly lactic-co-glycolic acid scaffolds for ligament tissue engineering. Tissue Eng.2007; 13(7):1573-1582.[24] Li S,Wu H,Hu XD,et al.Preparation of electrospun PLGA-silk fibroin nanofibers-based nerve conduits and evaluation in vivo. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol.2012;40(1-2): 171-178.[25] Sahoo S,Toh SL,Goh JC.PLGA nanofiber-coated silk microfibrous scaffold for connective tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;95(1):19-28.[26] Sahoo S,Toh SL,Goh JC.A bFGF-releasing silk/PLGA-based biohybrid scaffold for ligament/tendon tissue engineering using mesenchymal progenitor cells.Biomaterials. 2010;31 (11): 2990-2998.[27] Shao HJ,Chen CS,Lee IC,et al.Designing a three-dimensional expanded polytetrafluoroethylene-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold for tissue engineering.Artif Organs.2009;33(4): 309-317.[28] Sahoo S,Ouyang H,Goh JC,et al.Characterization of a novel polymeric scaffold for potential application in tendon/ligament tissue engineering.Tissue Eng.2006;12(1):91-99.[29] Stoll C,John T,Endres M,et al.Extracellular matrix expression of human tenocytes in three-dimensional air-liquid and PLGA cultures compared with tendon tissue:implications for tendon tissue engineering.J Orthop Res.2010;28(9):1170-1177.[30] Heidemann W,Jeschkeit-Schubbert S,Ruffieux K,et al.pH-stabilization of predegraded PDLLA by an admixture of water-soluble sodiumhydrogenphosphate--results of an in vitro- and in vivo-study.Biomaterials.2002;23(17):3567-3574. |
| [1] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [2] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [3] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [4] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [5] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [6] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [7] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [8] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [9] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [10] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [11] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [12] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [13] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [14] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [15] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||