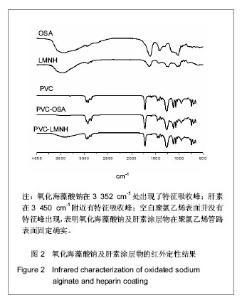
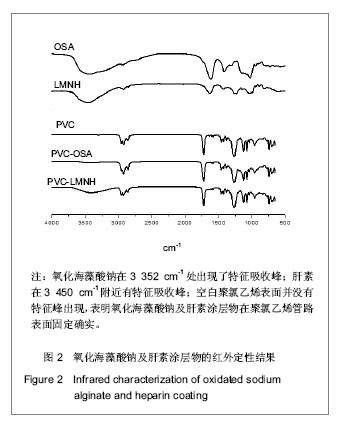
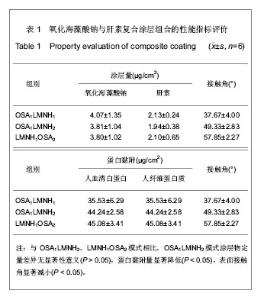
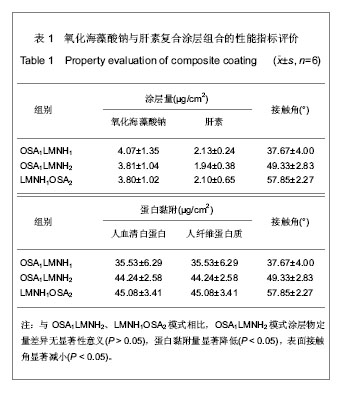
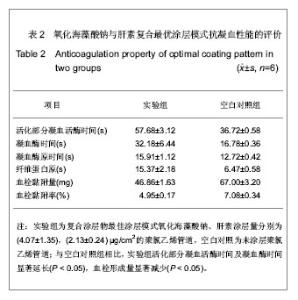
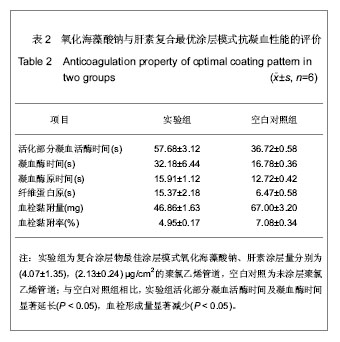
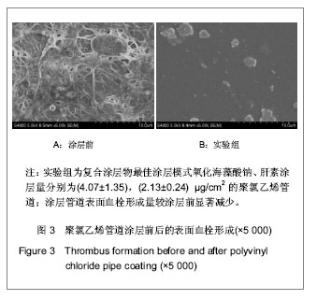
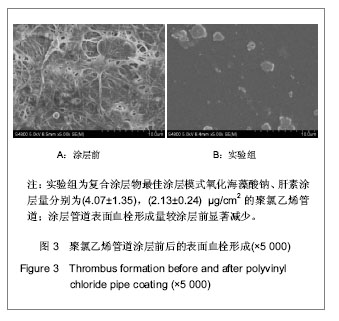
| [1] Apostolakis EE,Koletsis EN,Baikoussis NG,et al.Strategies to prevent intraoperative lung injury during cardiopulmonary bypass. J Cardiothorac Surg.2010;11(5):1.[2] Suzuki Y,Daitoku K,Minakawa M,et al.Poly-2- methoxyethylacrylate-coated bypass circuits reduce activation of coagulation system and inflammatory response in congenital cardiac surgery.J Artif Organs. 2008;11(3): 111-116.[3] Bai SY,Zhu DM,Wang W.Zhongguo Tiwai Xunhuan Zazhi. 2009; 7(2):124-128.柏淑颖,朱德明,王伟.涂层技术在体外循环装置中的应用及意义[J].中国体外循环杂志,2009,7(2):124-128.[4] Larm O,Larsson R,Olsson P.A new non-thrombogenic surface prepared by selective covalent binding of heparin via a modified reducing terminal residue.Biomater Med Devices Artif Organs. 1983; 11(2-3):161-234.[5] Andersson LO,Hoffman J, Holmer E, et al. Mechanisms of anticoagulant effects of some sulphated polysaccharides. Thromb Res. 1982; 28(6):741-748. [6] Bouhadir KH,Lee KY,Alsberg E,et al.Degradation of partially oxidized alginate and its potential application for tissue engineering.Biotechnol Prog.2001;17(5):945-995.[7] Petitou M,Barzu T,Herault JP,et al.A unique trisaccharide sequence in heparin mediates the early step of antithrombin IIIactivation.Glycobiology.1997;7(3):323-327.[8] Santerre JP, Woodhouse K, Laroche G, et al. Understanding the biodegradation of polyurethanes: from classical implants to tissue engineering materials. Biomaterials.2005;26(35): 7457-7470.[9] Gunaydin S.Clinical significance of coated extracorporeal circuits: a review of novel technologies. Perfusion. 2004; 19(1):33-41.[10] Nishino T,Yokoyama G,Dobashi K,et al.Isolation, purification,and characterization of fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from the brown seaweed Ecklonia kurome and their blood-anticoagulant activities. Carbohydr Res.1989; 186(1):119-148.[11] Manju S,Muraleedharan CV,Rajeev A,et al.Evaluation of alginate dialdehyde cross-linked gelatin hydrogel as a biodegradable sealant for polyester vascular graft.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2011;98(1):139-188.[12] Bron JL,Vonk LA,Smit TH,et al.Engineering alginate for intervertebral disc repair. Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2011; 4(7):1196-1205. [13] Popa EG,Gomes ME,Reis RL.Cell delivery systems using alginate--carrageenan hydrogel beads and fibers for regenerative medicine applications.Biomacromolecules.2011; 12(11):3952-3961. [14] Wang QH,Zhang YX,Li ZP,et al.Yingyong Huaxue. 2010;27(2): 155-158.王琴梅,张亦霞,李卓萍,等. 多醛基海藻酸钠交联剂的制备及性能[J]. 应用化学,2010,27(2):155-158. [15] Smith PK,Mallia AK,Hermanson GT.Colorimetric Method for the Assay of Heparin content in immobilized heparin preparations.Anal Biochem.1980;109(2):466-473.[16] Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, et al. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances.Anal Chem. 1956; 28(3): 350-356.[17] Ishihara K,Fukumoto K,Iwasaki Y,et al. Modification of polysulfone with phospholipid polymer for improvement of the blood compatibility. Part 1. Surface characterization.Biomaterials.1999; 20(17):1545-1551.[18] Islam T,Butler M,Sikkander SA,et al.Further evidence that periodate cleavage of heparin occurs primarily through the antithrombin binding site. Carbohydr Res.2002;337(21): 2239-2243.[19] Murugesan S,Xie J,Linhardt RJ. Immobilization of heparin: approaches and applications.Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(2): 80-100.[20] GOTT VL,WHIFFEN JD,DUTTON RC.Heparin bonding on colloidal graphite surface.Scinece.1963;142 (3597): 1297-1298.[21] Larsson R,Larm O,Olsson P.The search for thromboresistance using immobilized heparin.Ann NY Acad Sci.1987;516:102-107.[22] Favia P,Palumbo F,D'Agostino R,et al.Immobilization of heparin and highly-sulfated hyaluronic acid onto plasma-treated polyethylene.Plasmas Polym.1998;3(2): 77-96. [23] Favia P,Stendardo MV,d' Agostino R.Selective grafting of amine groups on polyethylene by means of NH3-H2 RF glow discharges.Plasmas Polym.1996; 1(2):91-112.[24] Stryer L.Biochemistry.4nd. New York:W H Freeman and Company,1995:252-257.[25] Henry BL,Desai UR. Recent research developments in the direct inhibition of coagulation proteinases--inhibitors of the initiation phase.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem.2008; 6(4): 323-36.[26] Keuren JF,Wielders SJ,Willems GM,et al.Thrombogenicity of polysaccharide-coated surfaces.Biomaterials.2003;24 (11): 1917-1924.[27] Matsubara K,Matsuura YM,Baci A,et al.Anticoagulant properties of a sulfated galactan preparation from a marine green alga, Codium cylindricum.Int J Biol Macromol.2001; 28(5):395-399.[28] Farias WRL,Valente AP,Pereira MS,et al.Structure and anticoagulant activity of sulfated galactans. Isolation of a unique sulfated galactan from the red algae Botryocladia occidentalis and comparison of its anticoagulant action with that of sulfated galactans from invertebrates.J Biol Chem. 2000; 275(38):29299-307.[29] Pereira MS,Mulloy B,Mourao PAS. Structure and anticoagulant activity of sulfated fucans. Comparison between the regular, repetitive, and linear fucans from echinoderms with the more heterogeneous and branched polymers from brown algae. J Biol Chem.1999,274(12):7656-7667. |