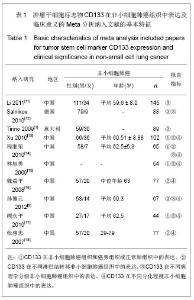
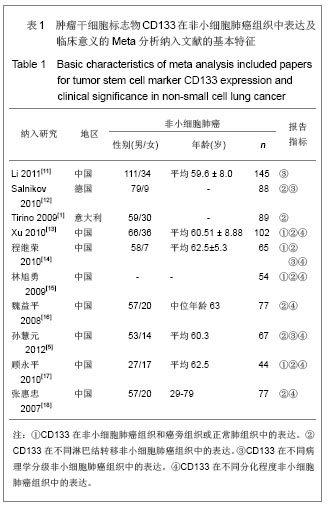
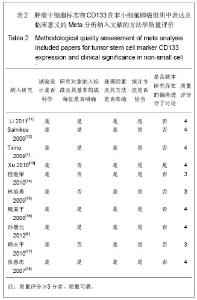
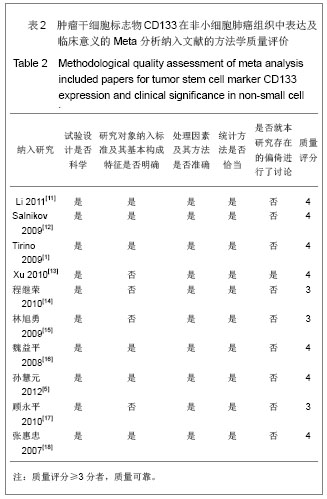
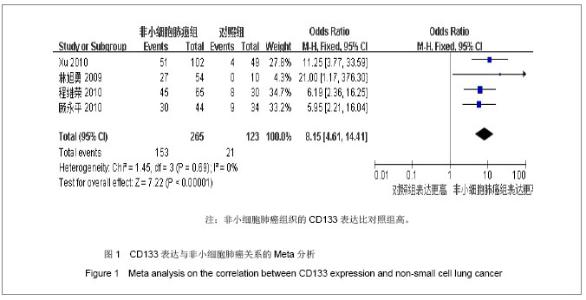
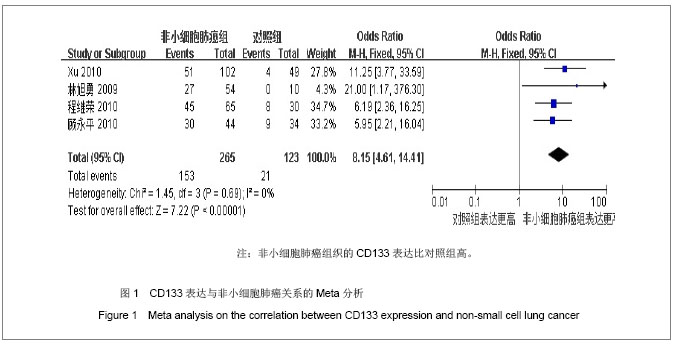
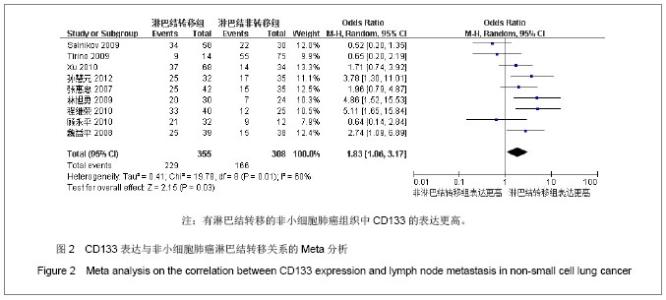
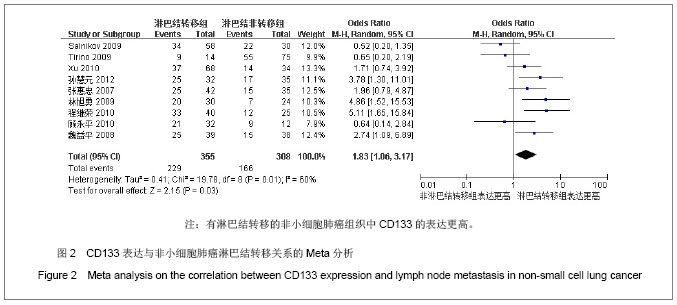
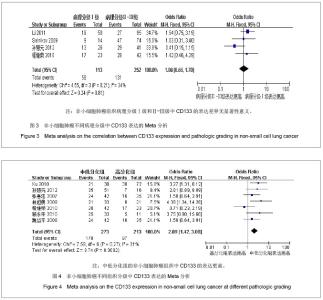
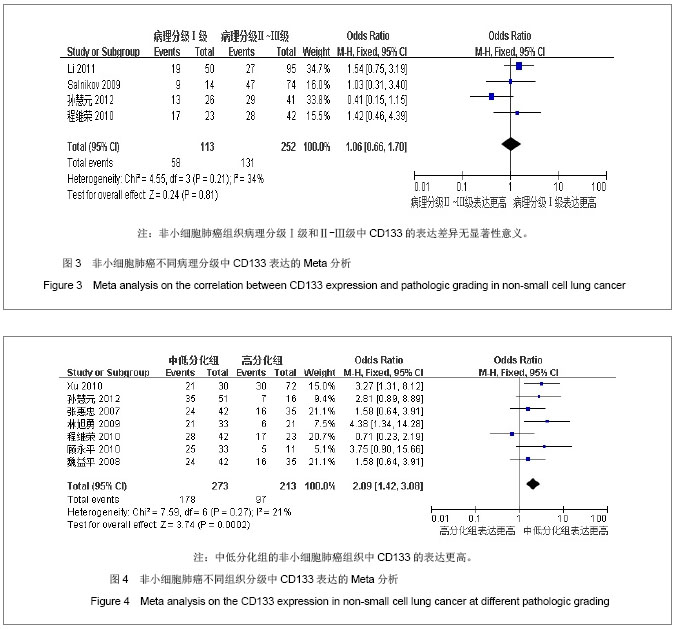
| [1]Tirino V, Camerlingo R, Franco R, et al. The role of CD133 in the identification and characterisation of tumour-initiating cells in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009; 36(3):446-453.[2]Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55(2):74-108.[3]Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83(5):584-594.[4]Collins LG, Haines C, Perkel R, Enck RE. Lung cancer: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2007;75 (1):56-63.[5]Sun HY,Yang YM,Zheng MJ,et al.Linchuang yu Shiyan Binglixue Zazhi. 2012;28(7):813-815.孙慧元,杨摇敏,郑茂金,等.非小细胞肺癌组织中CD133和ALDH1的表达及其临床意义[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2012, 28(7):813-815.[6]Soltysova A, Altanerova V, Altaner C. Cancer stem cells. Neoplasma. 2005;52(6):435-440.[7]Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, et al. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414(6859):105-111.[8]Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, et al. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature. 2004;432(7015):396-401.[9]O'Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S, Dick JE. A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature. 2007;445(7123):106-110.[10]Collins AT, Berry PA, Hyde C, et al. Prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2005; 65(23):10946-10951.[11]Li F, Zeng H, Ying K. The combination of stem cell markers CD133 and ABCG2 predicts relapse in stage I non-small cell lung carcinomas. Med Oncol. 2011;28(4):1458-1462.[12]Salnikov AV, Gladkich J, Moldenhauer G, et al. CD133 is indicative for a resistance phenotype but does not represent a prognostic marker for survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 2010;126(4):950-958.[13]Xu YH, Zhang GB, Wang JM, Hu HC. B7-H3 and CD133 expression in non-small cell lung cancer and correlation with clinicopathologic factors and prognosis. Saudi Med J. 2010; 31(9):980-986.[14]Chen JR,Wang SQ.Zhongliu. 2010;30(4):334-337.程继荣,王淑琴,祖木热提,等.肺癌组织中CD133和CD105的表达及其临床意义[J]. 肿瘤.2010,30(4):334-337.[15]Lin QY,Liu SL,Liu N,et al.Zhongguo Feiai Zazhi. 2009; 12(4): 316-321.林旭勇,刘树立,刘楠,等.干细胞标记物CK19、Notch3、CD133、P75NTR、STRO-1及ABCG2在肺鳞癌中的表达及意义[J].中国肺癌杂志,2009,12(4):316-321.[16]Wei YP,Wang M,Hua P,et al.Zhongshan Daxue Xuebao: Yixueban. 2008;29(3):312-316.魏益平,王梅,华平,等.肿瘤干细胞标志物CDl33在非小细胞肺癌中的表达及临床意义[J].中山大学学报:医学版,2008,29(3): 312-316.[17]Gu YP,Sun MM,Gu LQ,et al.Suzhou Daxue Xuebao:Yixueban. 2010;30(3):513-516, 572.顾永平,孙茂民,顾丽琴,等.肿瘤干细胞标志物CD133、ABCG2、p75NTR在非小细胞肺癌组织的表达及其生物学意义[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2010;30(3):513-516, 572.[18]Zhang HZ,Wei YP,Wang M,et al.Nanfang Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2007;27(5):696-699.张惠忠,魏益平,王梅,等.肿瘤干细胞标志物CD133和内皮素转化酶对非小细胞肺癌预后的影响[J].南方医科大学学报,2007; 27(5): 696-699.[19]Lichtenstein MJ, Mulrow CD, Elwood PC. Guidelines for reading case-control studies. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(9): 893-903.[20]Corbeil D, Roper K, Fargeas CA, et al. Prominin: a story of cholesterol, plasma membrane protrusions and human pathology. Traffic. 2001;2(2):82-91.[21]Chang JH,Meng AM.Shengming Kexue.2011;23(4):348-352.常建辉,孟爱民.肺干细胞和肺癌干细胞研究进展[J].生命科学, 2011,23(4):348-352.[22]Suetsugu A, Nagaki M, Aoki H, et al. Characterization of CD133+ hepatocellular carcinoma cells as cancer stem/ progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006; 351 (4):820-824.[23]Kim CF, Jackson EL, Woolfenden AE, et al. Identification of bronchioalveolar stem cells in normal lung and lung cancer. Cell. 2005;121(6):823-835.[24]Eramo A,Lotti F,Sette G,et al.Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung cancer stem cell population.Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(3):504-514.[25]Hilbe W, Dirnhofer S,Oberwasserlechner F, et al. CD133 positive endothelial progenitor cells contribute to the tumour vasculature in non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2004;57(9):965-969.[26]Levina V, Marrangoni AM, DeMarco R, et al. Drug-selected human lung cancer stem cells: cytokine network, tumorigenic and metastatic properties. PLoS One. 2008;3(8):e3077. [27]Tirino V, Camerlingo R, Franco R, et al. The role of CD133 in the identification and characterisation of tumour-initiating cells in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009; 36(3):446-453.[28]Tetsukan Woo, Koji Okudela, Hideaki Mitsui, et al. Prognostic value of CD 133 expression in stage I lung adenocarcinomas. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011;4(1):32-42.[29]Xu YH,Wang JM,Zhang GB,et al.Jiangsu Yiyao. 2011; (4) : 412-415. |