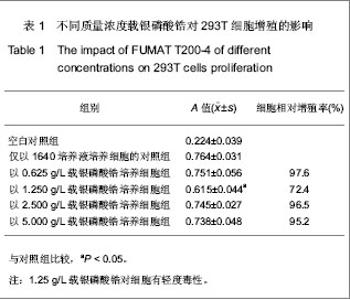
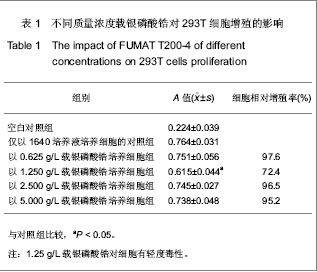
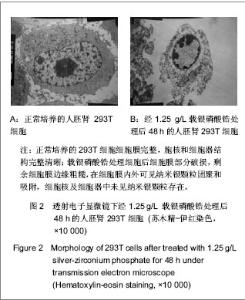
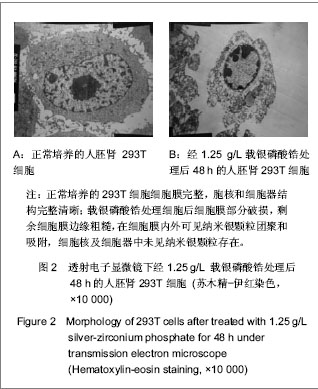
| [1] Hao HP. Zhongguo Biaozhun Chubanshe.郝和平.医疗器械生物学评价标准实施指南[S].中国标准出版社, 2000.[2] She WJ,Fu YF,Zhang FQ. Shanghai Jiaotong Daxue Xuebao:Yixueban. 2006;26(10): 1102-1104.佘文君,傅远飞,张富强. 纳米载银无机抗菌剂对义齿基托树脂细胞毒性的影响[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2006,26(10): 1102-1104.[3] Liu XJ,Chen DL.Zhongguo Wuzhenxue Zazhi. 2010;10(4): 766-768.刘雪婧,陈递林. 胰岛素生长因子-1的研究进展[J].中国误诊学杂志,2010,10(4):766-768.[4] Meng XW,Zhang YR,Mang L.Neimenggu Nongye Keji. 2007;35(6):31-32.孟祥伟,张焱如,芒来. 胰岛素样生长因子Ⅰ(IGF-Ⅰ)研究进展[J].内蒙古农业科技,2007,35(6):31-32.[5] Wei L,Tang J,Zhang Z,et al. Investigation of the cytotoxicity mechanism of silver nanoparticles in vitro. Biomed Mater. 2010;5(4):044103.[6] Kim HR,kim MJ,lee SY,et al.Genotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles stimulated by oxidative stress in human normal bronchial epithelial (BEAS-2B) cells. Mutation Res.2011; 726(2): 129-135.[7] Ahamed M,Siddiqui MK.Low level lead exposure and oxidative stress: current opinions.Clin Chim Acta.2007;383(1): 57-64.[8] Wise JP,Goodale BC,Wise SS,et al.Silver nanospheres are cytotoxic and genotoxic to fish cells. Aquatic Toxicol.2010;97(1):34-41.[9] Hsin YH,Chen CF,Huang S,et al.The apoptotic effect of nanosilver is mediated by a ROS- and JNK-dependent mechanism involving the mitochondrial pathway in NIH3T3 cells.Toxicol Lett.2008;179(3):130-139. [10] Asharani PV,Mun GK,Hande MP,et al. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano. 2009;3:279-290.[11] Park EJ,Yi J,Kim Y,et al.Silver nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity by a Trojan-horse type mechanism. Toxicol In Vitro. 2010;24(3):872-878.[12] Park MV, Neigh AM, Vermeulen JP, et al. The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles.Biomaterials. 2011; 32(36):9810-9817. |