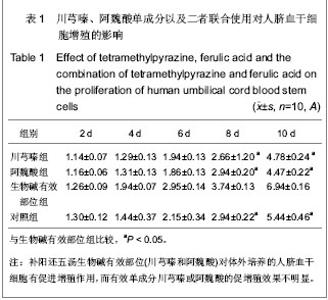
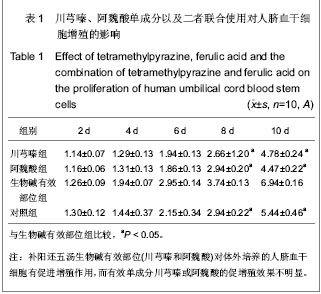
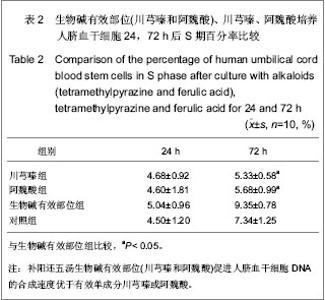
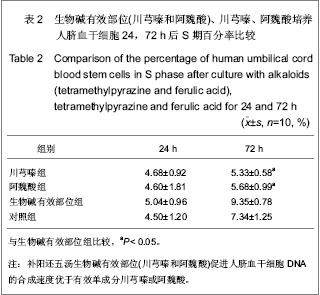
| [1] Danet GH, Luongo JL, Butler G, et al. C1qRp defines a new human stem cell population with hematopoietic and hepatic potential.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(16):10441- 10445. [2] Kadner A, Hoerstrup SP, Tracy J,et al. Human umbilical cord cells: a new cell source for cardiovascular tissue engineering. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;74(4):S1422-S1428.[3] Ma JX,La XL,Ma Y. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(45):8854-8860.马建勋,腊晓琳,马艳.两步法分离和培养人羊水来源胚胎间充质干细胞的生物学特征[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(45):8854-8860.[4] Henning RJ, Abu-Ali H, Balis JU,et al. Human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction.Cell Transplant. 2004;13(7-8):729-739. [5] Li CH. Hebei Beifang Xueyuan Xuebao. 2005;22(4):43-45.李春海. 脐带血干细胞移植治疗急性心肌缺血的实验研究[J].河北北方学院学报,2005,22(4):43-45. [6] Yin J,Shi GG,Li CH,et al. Zhenduanxue Lilun yu Shijian. 2006; 5(6):511-514.尹俊,石刚刚,李春海,等.人脐带血干细胞移植防治兔急性心肌缺血的实验研究[J].诊断学理论与实践,2006,5(6):511-514.[7] Deng CQ,Deng YH,Xiang HL. Zhongyao Yaoli yu Linchuang. 1999;15(5):3-5.邓常青,邓奕晖,向华林.补阳还五汤及其有效部位对沙鼠脑缺血后DND脑能量代谢、NO和NOS的影响[J].中药药理与临床, 1999,15(5):3-5.[8] Yan RH,Wang SM,Yan ZF. Zhongyao Yaoli yu Linchuang. 1999;15(1):7-9.闫润红,王世民,闫志芳. 不同黄芪剂量的补阳还五汤对“气虚血瘀”家兔血粘度的影响[J].中药药理与临床,1999,15(1):7-9.[9] Xie JG,Song RL. Zhongyao Yaoli yu Linchuang. 1997;13(6): 16-18.解建国,宋任龄.补阳还五汤对脑卒中兔颅脑内细胞生物学机制的保护作用研究[J].中药药理与临床,1997,13(6):16-18.[10] Deng CQ,Liu ZL,Ge ZW,et al. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jichu Yixue Zazhi. 1998;4(8):33-35.邓常青,刘志龙,葛金文,等.补阳还五汤抗脑缺血再灌注损伤作用机理的研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,1998,4(8):33-35.[11] Zheng GY,Zhang JS,Chen XD. Zhongxiyi Jiehe Shiyong Linchuang Jijiu. 1997;4(6):256-258.郑关毅,张景寿,陈晓东.补阳还五汤治疗脑梗塞的疗效及其机制探讨[J].中西医结合实用临床急救,1997,4(6):256-258.[12] Li F,He QF,Su YZ,et al. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi. 1998;23 (8): 493-495.李菲,胡奇芬,苏彦珍,等.补阳还五注射液对溶血卵磷脂引起脑微血管细胞增殖和损伤的保护作用[J].中国中药杂志,1998,23(8): 493-495.[13] Hou C,He Q,Li S,et al. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi. 2001;21(5):359-363.侯灿,何勤,李松,等.补阳还五汤防止兔模拟经皮冠脉腔内血管成形术后再狭窄的实验研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2001, 21(5): 359-363.[14] Mo SL,Zheng YS. Zhongyao Yaoli yu Linchuang. 1997;13(1) 1-4.莫孙炼,郑有顺.补阳还五汤拆方对实验性脑缺血损伤大鼠脑组织皮层梗塞面积及血浆内皮素的影响[J].中药药理与临床, 1997, 13(1):1-4.[15] Tang YH,Liang Y,Zhang SP,et al. Zhongguo Shiyan Fangjixue Zazhi. 2007;13(6):39-42.唐映红,梁燕,张淑萍,等. 补阳还五汤及其有效组分生物碱和苷对动脉血栓形成大鼠抗凝系统活性的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2007,13(6):39-42.[16] Feng YJ,Yang HD,Tang TJ,et al. Shiyong Yixue Zazhi. 2007; 23(5):613-615.冯应君,杨汉东,汤天军,等.脐带血干细胞诱导分化为心肌样细胞电生理特性的实验研究[J].实用医学杂志,2007,23(5):613-615. [17] Leor J, Guetta E, Feinberg MS, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived CD133+ cells enhance function and repair of the infarcted myocardium. Stem Cells. 2006;24(3):772-780. [18] Zou J, Gan MF, Zhu XS, et al. Protective effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell vein transplantation against spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Neural Regen Res. 2010;5(3):171-177.[19] Zhong Q,Zeng HL. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(40):7942-7946.钟启,曾慧兰.低氧对间充质干细胞生物学特性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(40):7942-7946.[20] Han MY,Feng SQ,Li H,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(19):3678-3682.韩明远,冯世庆,李辉,等.移植人脐带间充质干细胞修复大鼠脊髓损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010 ,14(19): 3678-3682.[21] Huang W,Zhu JZ,Miao ZN,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(3): 2464-2466.黄伟,祝建中,苗宗宁,等.人脐带血间充质干细胞的体外培养及其影响因素[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(3): 2464-2466.[22] Lin GT,Yin NN,Ma CY. Zhongguo Shiyan Fangjixue Zazhi. 1997;3(4):16-17.林桂涛,尹宁宁,马承严.灰色系统理论与均匀设计结合在补阳还五汤处方筛选中的应用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,1997,3(4): 16-17.[23] Wu YS,Li SL,Zhang DJ,et al. Zhongxiyi Jiehe Shiyong Linchuang Jijiu. 1996;3(8):343-346.吴玉生,李士林,张道杰,等.补阳还五汤对早期脑梗塞患者的治疗效果[J].中西医结合实用临床急救,1996,3(8):343-346.[24] Jin YL, Dong LY, Wu CQ,et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction fraction protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating the inflammatory response and cellular apoptosis. Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8(3): 197-207.[25] Cui W,Niu FL,He LY,et al. Beijing Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao. 2001;24(6):45-47.崔巍,牛福玲,何丽云,等.流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡的分析软件比较[J].北京中医药大学学报,2001,24(6):45-47. [26] Jin XG,Fang GA,Liu B. Shanghai Yixue Jianyan Zazhi. 2000; 15(3):151.金秀国,方国安,刘波.流式细胞术DNA分析影响因素探讨[J].上海医学检验杂志,2000,15(3):151.[27] Wu YS,Jiang LP,Wang ZK. Shandong Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao. 1999;23(2):117-119.吴玉生,姜立萍,王占奎. 补阳还五汤治疗急性脑梗死ET、CGRP检测的指导意义[J].山东中医药大学学报,1999,23(2):117-119.[28] Wu YS,Jiang LP. Zhongyao Yaoli yu Linchuang. 1998;14(2): 38-40.吴玉生,姜立萍.补阳还五汤对早期脑梗塞患者内皮素、降钙素基因相关肽的影响[J].中药药理与临床,1998,14(2):38-40.[29] Zhang JP,Zhang YP,Wen FN,et al. Zhongyi Zazhi. 1998;39 (10): 621-623.张继平,张玉萍,文凤妮,等.补阳还五汤对家兔血小板活化因子受体活性的影响[J].中医杂志,1998,39(10):621-623.[30] Lin H,Huang SL,Chen F,et al. Zhongyao Xinyao yu Linchuang Yaoli. 1997;8(4):239-241.林华,黄树莲,陈芳,等.加味补阳还五汤对大鼠的活血化瘀作用[J].中药新药与临床药理,1997,8(4):239-241.[31] Cao DH,Gao YQ. Shiyong Zhongyi Neike Zazhi. 1997;11(3): 37-38.曹东红,高幼奇.加味补阳还五汤对缺血性中风患者血浆D-二聚体的影响[J].实用中医内科杂志,1997,11(3):37-38. |