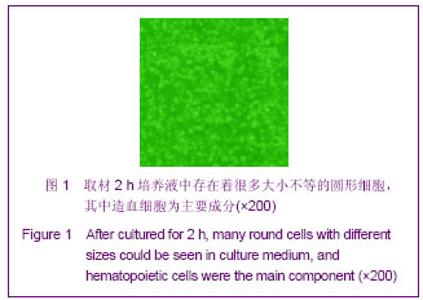
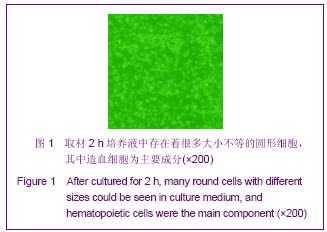
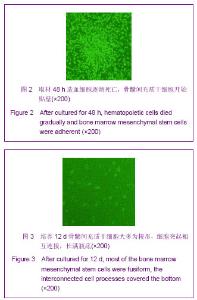
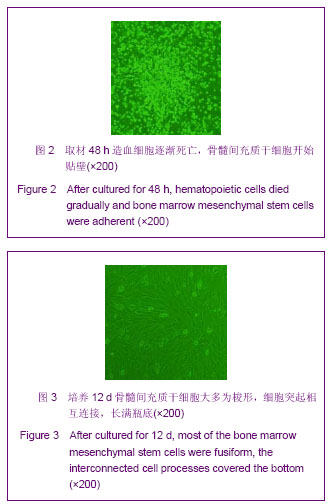
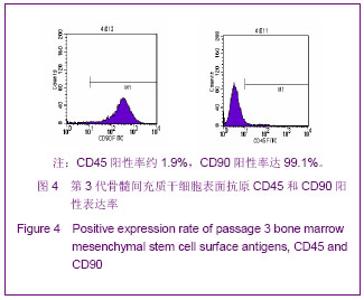
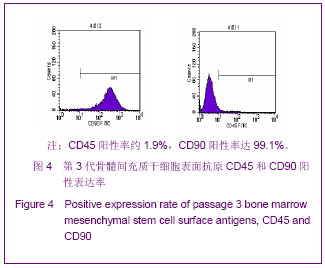
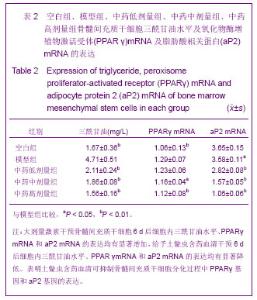
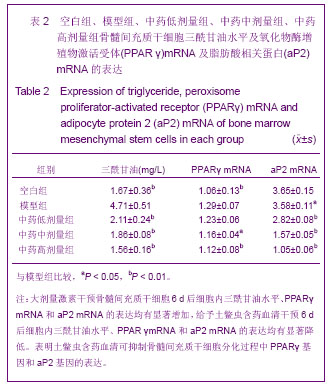
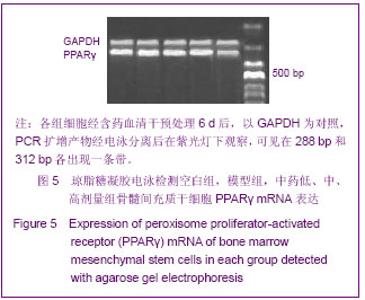
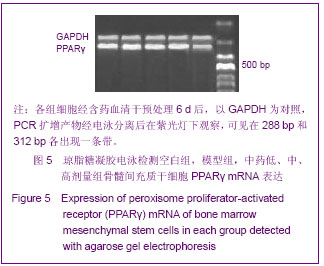
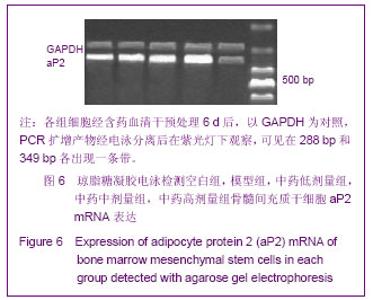
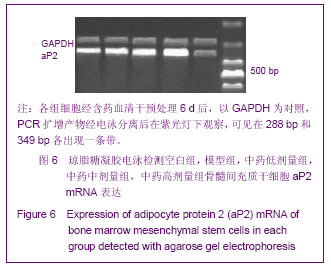
| [1] Minguell JJ, Erices A, Conget P. Mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2001;226(6):507-520.[2] Beresford JN, Bennett JH, Devlin C, et al. Evidence for an inverse relationship between the differentiation of adipocytic and osteogenic cells in rat marrow stromal cell cultures.J Cell Sci. 1992;102 ( Pt 2):341-351.[3] Yin L,Li YB,Xu JZ,et al. Henan Yixue Yanjiu. 2000; 9(4): 311-312.殷力,李月白,许建中,等.地塞米松调节骨髓基质细胞成脂及成骨分化的组织化学研究[J].河南医学研究,2000,9(4):311-312.[4] He ZY,Yuan LY,Chen Y,et al. Zhongguo Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2004;33(5):395-396.何志义,原丽英,陈晏,等.大鼠骨髓基质细胞的体外分离、培养和鉴定的实验研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2004,33(5):395-396.[5] Li X, Jin L, Cui Q,et al. Steroid effects on osteogenesis through mesenchymal cell gene expression. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(1):101-108.[6] Cui Q, Wang GJ, Balian G.Steroid-induced adipogenesis in a pluripotential cell line from bone marrow. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(7):1054-1063.[7] Qiu LY,Wang JF. Shengwu Gongcheng Xuebao. 2003;19(2): 136-140.邱丽燕,王金福.骨髓间充质干细胞的研究进展[J].生物工程学报, 2003,19(2):136-140.[8] Liu YY,Cui L,Wu T,et al. Zhongguo Yaolixue Tongbao. 2005; 21(7):842-847.刘钰瑜,崔燎,吴铁,等.大黄素对体外大鼠骨髓基质细胞向脂肪细胞方向分化的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2005, 21(7):842-847.[9] Wang YS,Xiong TB,Li YB,et al. Zhongguo Guzhongliu Gubing. 2004;3(1):55-57.王义生,熊腾滨,李月白,等.葛根素抑制酒精诱导骨髓基质细胞成脂分化的实验研究[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病,2004,3(1):55-57.[10] Ahdjoudj S, Lasmoles F, Oyajobi BO,et al. Reciprocal control of osteoblast/chondroblast and osteoblast/adipocyte differentiation of multipotential clonal human marrow stromal F/STRO-1(+) cells. J Cell Biochem. 2001;81(1):23-38.[11] Li XQ,Guo YN,Wang XH,et al. Xiandai Yiyuan. 2006; 6(10): 24-25.李新强,郭燕妮,王燮衡,等.SD大鼠骨髓基质细胞的分离培养和鉴定[J].现代医院,2006,6(10):24-25.[12] Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S,et al. Bone marrow cells regenerate infarcted myocardium. Nature. 2001;410(6829): 701-705.[13] Poulsom R, Forbes SJ, Hodivala-Dilke K,et al. Bone marrow contributes to renal parenchymal turnover and regeneration. J Pathol. 2001;195(2):229-235.[14] Hess D, Li L, Martin M,et al. Bone marrow-derived stem cells initiate pancreatic regeneration. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21(7): 763-770.[15] Gori F, Thomas T, Hicok KC,et al. Differentiation of human marrow stromal precursor cells: bone morphogenetic protein-2 increases OSF2/CBFA1, enhances osteoblast commitment, and inhibits late adipocyte maturation. J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14(9):1522-1535.[16] Li XC,Du JY,Mao BY. Zhejiang Yixue. 2007;29(10):1035-1037.李新春,杜靖远,毛宾尧. 微波加热后脱钙骨基质诱导成骨中Ⅰ、Ⅱ型胶原mRNA及碱性磷酸酶的表达[J]. 浙江医学,2007,29 (10): 1035-1037.[17] Huang JB,Feng GZ,Liu XS,et al. Changzhi Yixueyuan Xuebao. 1994;8(2): 102-104.黄金保,冯改壮,刘骁驷,等.土鳖虫抗兔心脑缺氧实验研究[J]. 长治医学院学报, 1994,8(2): 102-104.[18] Yuan FH,Cheng L,Yu KJ,et al. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2006;12(10):447-448.袁风红,程力,俞可佳,等.地塞米松和1,25(OH)2D3对体外人骨髓基质细胞成骨及成脂分化的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2006, 12(10):447-448.[19] Pereira RC, Delany AM, Canalis E. Effects of cortisol and bone morphogenetic protein-2 on stromal cell differentiation: correlation with CCAAT-enhancer binding protein expression. Bone. 2002;30(5):685-691.[20] Banfi A, Muraglia A, Dozin B,et al. Proliferation kinetics and differentiation potential of ex vivo expanded human bone marrow stromal cells: Implications for their use in cell therapy. Exp Hematol.2000;28(6):707-715. |