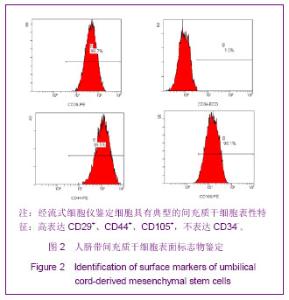
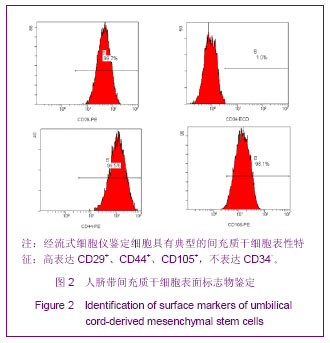
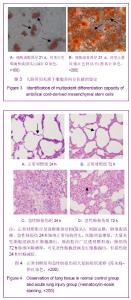
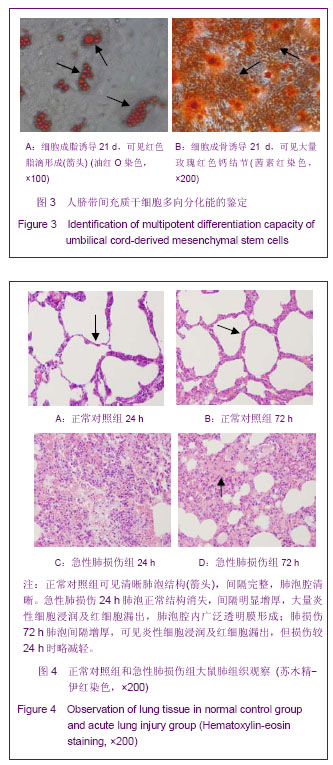
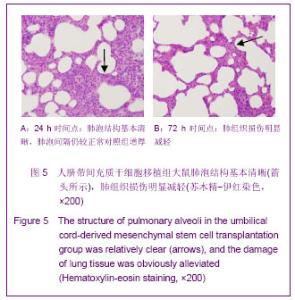
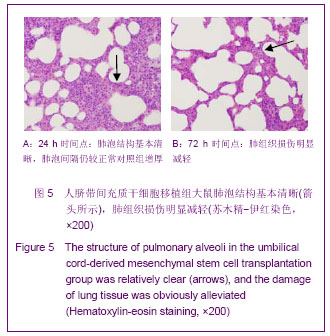
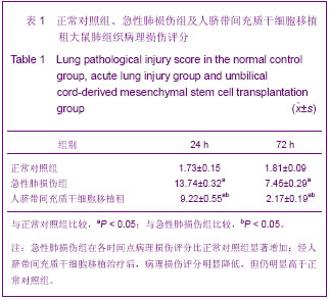
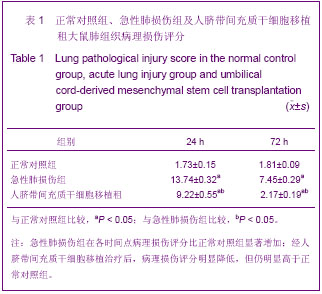
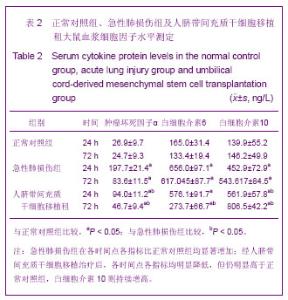
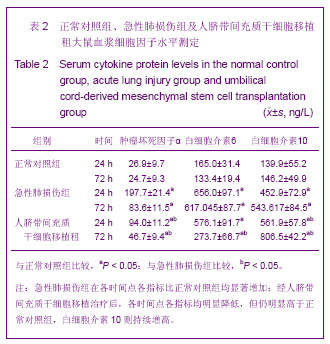
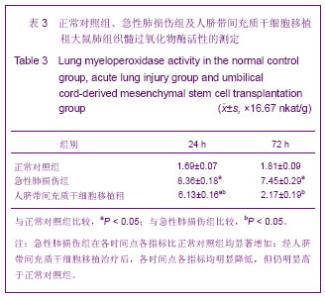
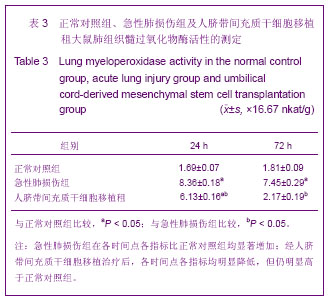
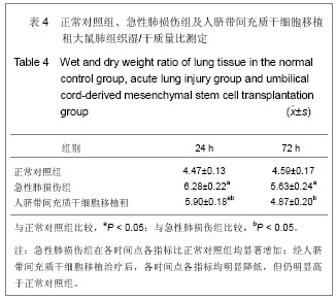
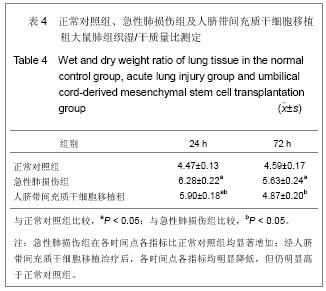
| [1] Matthay MA,Ware LB,Zimmerman GA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(8):2734-2740.[2] Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E, et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(16): 1685-1693.[3] Baudouin SV. Manipulation of inflammation in ARDS: achievable goal or distant target? Thorax. 2006;61(6): 464-465.[4] Bianco P, Robey PG, Simmons PJ. Mesenchymal stem cells: revisiting history, concepts, and assays. Cell stem cell. 2008; 2(4):313-319.[5] Caplan AI. Adult mesenchymal stem cells for tissue engineering versus regenerative medicine. J Cellular Physiology. 2007;213(2):341-347.[6] Igura K, Zhang X, Takahashi K, et al. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal progenitor cells from chorionic villi of human placenta. Cytotherapy. 2004;6(6): 543-553.[7] Lee OK, Kuo TK, Chen WM, et al. Isolation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Blood. 2004;103(5):1669-1675.[8] Lu LL, Liu Y, Yang SG, et al. Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with hematopoiesis-supportive function and other potentials. Haematologica. 2006;91(8):1017-1026.[9] Baksh D, Yao R, Tuan RS. Comparison of proliferative and multilineage differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow. Stem cells. 2007;25(6):1384-1392.[10] Gupta N, Su X, Popov B, et al. Intrapulmonary delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves survival and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. The Journal of Immunology. 2007;179(3):1855-1863.[11] Kim ES, Chang YS, Choi SJ, et al. Intratracheal transplantation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates Escherichia coli-induced acute lung injury in mice. Respir Res. 2011;12:108.[12] Liang Z, Sun J, Wang P, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect rats from endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Chinese Medical Journal. 2011;124(17): 2715-2722.[13] Ge ZJ, Jiang GJ, Zhao YP, et al. Systemic perfluorohexane attenuates lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats: the role of heme oxygenase-1. Pharmacol Rep. 2010;62(1): 170-177.[14] Wang H, Bodenstein M, Markstaller K. Overview of the pathology of three widely used animal models of acute lung injury. European Surgical Research. 2008;40(4):305-316.[15] McElreavey KD, Irrine AI, Ennis KT, et al. Isolation, culture and characterisation of fibroblast-like cells derived from the Wharton's jelly portion of human umbilical cord. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991;19(1):29s.[16] Mihu CM, Mihu D, Costin N, et al. Isolation and characterization of stem cells from the placenta and the umbilical cord. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2008;49(4):441-446.[17] Horwitz EM, Le Blanc K, Dominici M, et al. Clarification of the nomenclature for MSC: The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2005;7(5):393-395.[18] Conconi MT, Burra P, Di Liddo R, et al. CD105(+) cells from Wharton's jelly show in vitro and in vivo myogenic differentiative potential. Int J Mol Med. 2006;18(6):1089-1096.[19] Karahuseyinoglu S, Cinar O, Kilic E, et al. Biology of stem cells in human umbilical cord stroma: in situ and in vitro surveys. Stem Cells. 2007;25(2):319-331.[20] Mao M, Wang SN, Lv XJ, et al. Intravenous delivery of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells improves survival and attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in rats. Shock. 2010;34(2):196-204. [21] Yamada M, Kubo H, Kobayashi S, et al. Bone marrow-derived progenitor cells are important for lung repair after lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury. J Immunology. 2004; 172(2):1266-1272.[22] Mei SH, McCarter SD, Deng Y, et al. Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing angiopoietin. PLoS Med. 2007;4(9):e269.[23] Glennie S, Soeiro I, Dyson PJ, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce division arrest anergy of activated T cells. Blood. 2005;105(7):2821-2827.[24] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372. |