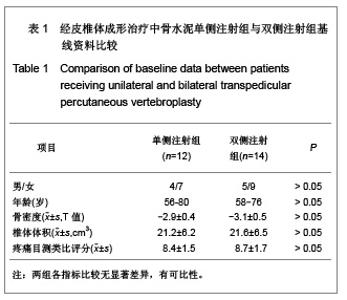
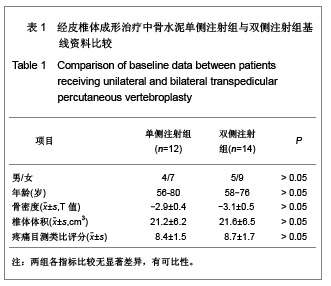
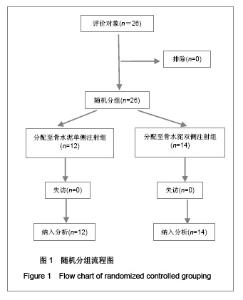
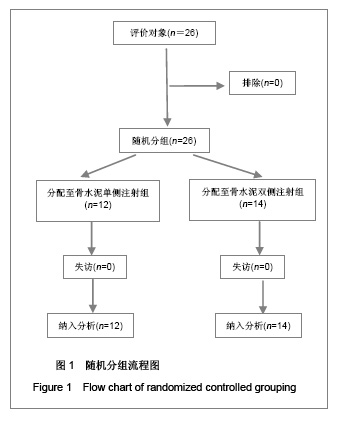
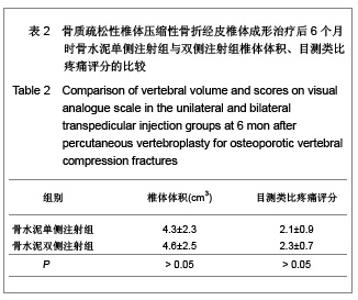
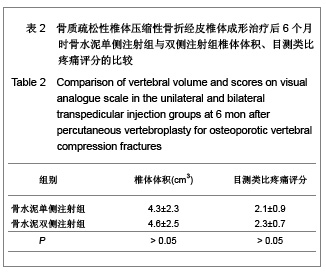
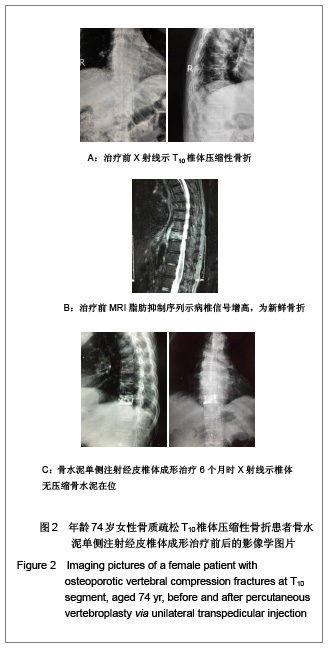
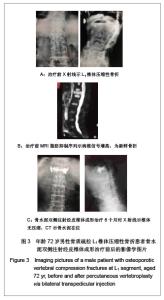
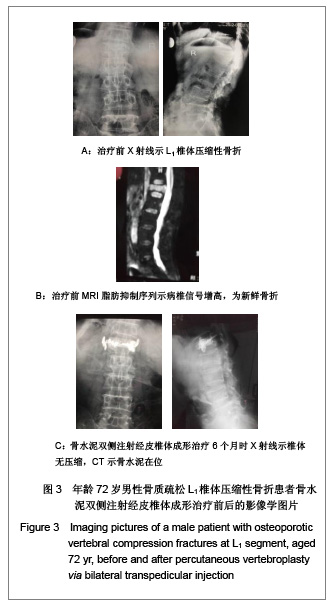
| [1] Cotton A,Dewatre F,Corter B,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma: effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of methyl methacrylate at clinical followup.Radology.1996; 200(3): 525-536. [2] Huskisson EC.Measurement of pain.Lancet.1974;2:112-1131.[3] Komemushi A,Tanigawa N,Kariya S,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for compression fracture: analysis of vertebral body volume by CT volumetry. Acta Radiol.2005;46(3): 276-279.[4] Muto M,Muto E,Izzo R,et al.Vertebroplasty in the treatment of back pain. 2005;109(3):208-219.[5] Lieberman IH,Dudeney S,Reinhardt MK,et al.Initial outcome and efficacy of “Kyphoplasty” in the treatment of painful osteoportic vertebral compression frature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976 ). 2001;26:1631-1638.[6] Liebschner MA,Rosenberg WS,Keaveny TM,et al.Effects of bone cement Volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976 ).2001;26: 1547-1554.[7] Akkaya T,Ersozlu S,Ozgur AF,et al.Early results of kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc.2007;41(2):127-131.[8] Lee JH, Lee SH.Multiple vertebral compression fractures associated with post partum osteoporosis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil.2011;24(2):117-121.[9] Yang XM,Wu TL,Xu HG,et al.Modified unilateral transpedicular percutaneous vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Orthop Surg. 2011;3(4):247-252.[10] Nieuwenhuijse MJ,van Erkel AR,Dijkstra PD.Percutaneous vertebroplasty in very severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: feasible and beneficial. J Vasc Interv Radiol.2011;22(7):1017-1023.[11] Ishiguro S,Kasai Y,Sudo A,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures using calcium phosphate cement.A J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong).2010; 18(3):346-351.[12] Patel N.Percutaneous vertebroplasty: role in treatment of vertebral compression fractures. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am.2010;21(4):869-876.[13] Yan D,Duan L,Li J,et al.Comparative study of percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2011;131(5):645-650.[14] Thillainadesan J,Schlaphoff G,Gibson KA,et al.Long-term outcomes of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol.2010;54(4):307-314.[15] Sun ZG,Miao XG,Yuan H,et al.Assessment of percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty for treatment of senile osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Zhongguo Gu Shang.2010;23(10):734-738.[16] Komemushi A,Tanigawa N,Kariya S,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for compression fracture: analysis of vertebral body volume by CT volumetry. Acta Radiol. 2005;46(3): 276-279.[17] Muijs SP,van Erkel AR,Dijkstra PD.Treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a brief review of the evidence for percutaneous vertebroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2011;93(9):1149-1153. [18] Chen LH,Lai PL,Chen WJ.Current status of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fracture.Chang Gung Med J.2011; 34(4):352-359. [19] Kim YJ,Lee JW,Park KW,et al.Pulmonary cement embolism after percutaneous vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: incidence, characteristics, and risk factors.Radiology.2009;251(1):250-259. [20] Nieuwenhuijse MJ,Van Erkel AR,Dijkstra PD.Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: identification of risk factors. Spine J. 2011;11(9):839-848.[21] Brown DB,Glaiberman CB,Gilula LA,et al.Correlation between preprocedural MRI findings and clinical outcomes in the treatment of chronic symptomatic vertebral compression fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;184(6):1951-1955.[22] Syed MI,Patel NA,Jan S,et al.New symptomatic vertebral compression fractures within a year following vertebroplasty in osteoporotic women.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26(6): 1601-1604. [23] Anselmetti GC,Zoarski G,Manca A,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty and bone cement leakage: clinical experience with a new high-viscosity bone cement and delivery system for vertebral augmentation in benign and malignant compression fractures.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol.2008; 31(5): 937-947.[24] Han KR,Kim C,Eun JS,et al. Extrapedicular approach of percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of upper and mid-thoracic vertebral compression fracture.Acta Radiol.2005; 46(3):280-287.[25] Kamano H,Hiwatashi A,Kobayashi N,et al.New vertebral compression fractures after prophylactic vertebroplasty in osteoporotic patients.AJR Am J Roentgenol.2011;197(2): 451-456.[26] Vcelak J,Toth L,Slegl M,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty-treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures.Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech.2009;76(1):54-59.[27] Kim HW,Song JW,Kwon A,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pregnancy-associated osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2010;47(5):399-402.[28] Tseng YY,Yang TC,Tu PH,et al.Repeated and multiple new vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(18): 1917-1922. |