Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (16): 2466-2471.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3101
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bone cement distribution of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures
Li Qiang, Li Jun, Luan Jian, Jin Canghai, Hao Meng, Lin Yong
- East Branch, Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2020-05-08Revised:2020-05-13Accepted:2020-06-12Online:2021-06-08Published:2021-01-07 -
Contact:Lin Yong, Associate Professor, Master’s supervisor, East Branch, Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Li Qiang, MD, Associate chief physician, East Branch, Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Qiang, Li Jun, Luan Jian, Jin Canghai, Hao Meng, Lin Yong. Bone cement distribution of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2466-2471.
share this article
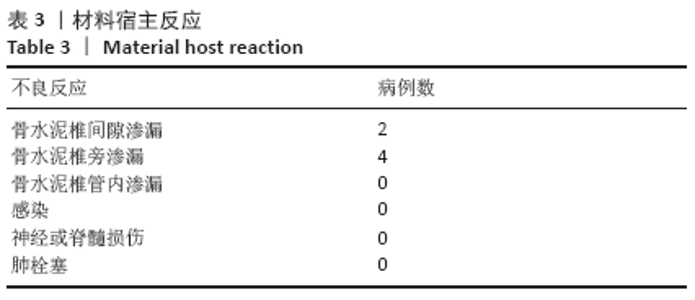
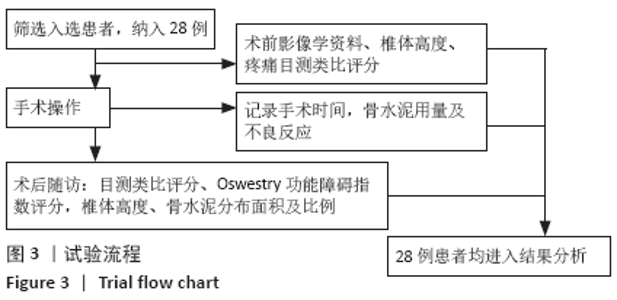
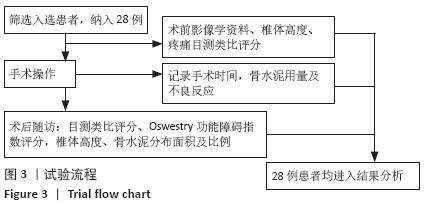
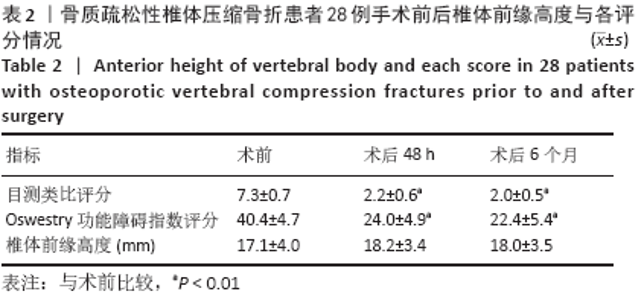
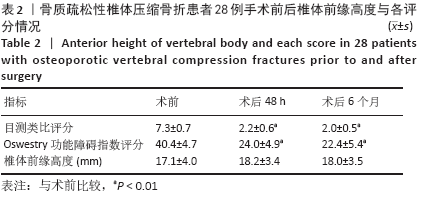
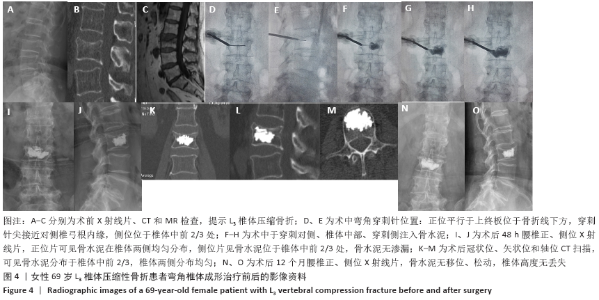
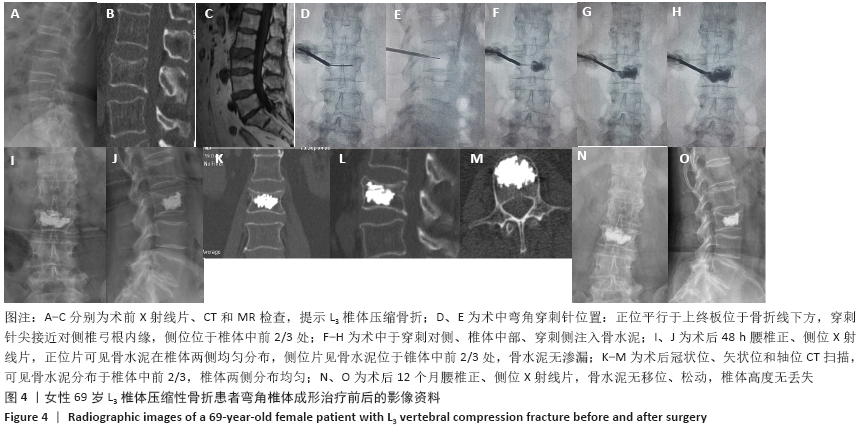
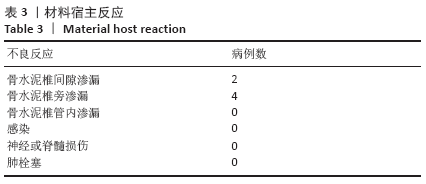
CT扫描见所有患者a+b+c+d区均有骨水泥分布,其中15例f区有骨水泥分布,4例在所有6区均有骨水泥分布,e区仅4例患者有骨水泥分布,骨水泥主要分布于椎体中前2/3(a+b+c+d区)。骨水泥最大分布层面骨水泥面积为(4.5±0.9)cm2,穿刺对侧骨水泥面积为(2.0±0.5)cm2,穿刺侧骨水泥面积为(2.5±0.7)cm2,骨水泥分布面积穿刺对侧/穿刺侧为0.85±0.27。 2.5 临床疗效 28例患者术后腰背痛症状均明显缓解,术后48 h、6个月时的目测类比评分与Oswestry功能障碍指数评分均低于术前(P < 0.01),术后48 h与术后6个月的目测类比评分与Oswestry功能障碍指数评分比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表2。 2.6 材料宿主反应 28例患者均未发生感染、神经或脊髓损伤、肺栓塞等并发症,其中2椎体渗漏至椎间隙,4椎体渗漏至椎旁,无椎管内渗漏,总渗漏率22.2%,均未出现不良临床症状,见表3。 "
| [1] GALIBERT P, DERAMOND H, ROSAT P, et al. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neurochirurgie. 1987;32(2):166-168. [2] GEORGY BA. Clinical experience with high-viscosity cements for percutaneous vertebral body augmentation: occurrence, degree, and location of cement leakage compared with kyphoplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(3):504-508. [3] STEVENSON M, GOMERSALL T, LLOYD JONES M, et al. Percutaneousvertebroplasty and percutaneous balloon kyphoplastyfor the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures:a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2014;18(17):1-290. [4] 张磊,汪凌骏,杨惠林,等.椎体后凸成形骨水泥注射治疗不同部位骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(14): 2140-2146. [5] 朱迪,尚春风,刘宏建,等.弯角穿刺针椎体成形技术治疗胸、腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(12):737-746. [6] 钟睿,姜威,熊森,等.单侧弯角与直行人路椎体成形治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折疗效的对照研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2018,34(2):102-108. [7] 熊森,毛克亚,韩振川,等.应用弯角椎体成形装置修复胸腰段骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(17):24456-24462. [8] 寇红伟,周权发,刘宏建,等.弯角椎体成形装置对单侧椎弓根穿刺角度及骨水泥分布的影响 [J].中华实验外科杂志,2017,34(2):338-341. [9] 张大鹏,强晓军,杨光.应用弯角装置单侧穿刺行PVP治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折的疗效分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(7):599-604 [10] CHEN C, BIAN J, ZHANG W, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral vertebroplasty for severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(8):E301-304. [11] TOHMEH A. Biomechanical efficacy of unipedicular versus bipedicular vertebroplasty for the management of osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(17):1772-1776. [12] 吴智辉,徐长科,朱鑫.单侧与双侧椎弓根入路PKP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(3):281-283. [13] ZHANG L, LIU Z, WANG J, et al. Unipedicular versus bipedicular percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a prospective randomized study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16(1):145. [14] SUN H, LI C. Comparison of unilateral and bilateralpercutaneousvertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review andmeta-analysis. J OrthopSurg Res. 2016;11:156. [15] CHEN W, XIE W, XIAO Z, et al. Incidence of Cement Leakage Between Unilateral and Bilateral Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:342-348. [16] CHEN YC, ZHANG L, LI EN, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in elderly patients: A meta-analysis. Medicine. 2019;98(8):e14317. [17] KNAVEL EM, RAD AE, THIELEN KR, et al. Clinical Outcomes with Hemivertebral Filling during Percutaneous Vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(3):496-499. [18] 江永发,郑召民,尚平,等.单侧入路椎体强化术治疗单节段骨质疏松性压缩性骨折2年随访[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2014,11(4):28-31. [19] YANG SP, CHEN CX, WANG HL, et al. A systematic review of unilateral versus bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty/percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2017;51(4):290-297. [20] KIM H, BAEK KH, LEE SY, et al. Association of circulating dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 levels with osteoporotic fracture in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(3):1-10. [21] 杨辉,张家立,李奕军,等.骨质疏松骨折患者骨水泥分布类型对椎体强化术后再骨折的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2019,35(12):1930-1934. [22] 贺宝荣,许正伟,郝定均,等.骨水泥在骨质疏松性骨折椎体内分布状态与生物力学性能的关系[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(8):768-773. [23] LIEBSCHNER MAK, ROSENBERG WS, KEAVENY TM. Effects of Bone Cement Volume and Distribution on Vertebral Stiffness After Vertebroplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1547-1554. [24] 陈柏龄,谢登辉,黎艺强,等.单侧PKP骨水泥注射过中线分布对压缩性骨折椎体两侧刚度的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(2):118-121. [25] 谢华,李继春,何劲,等.骨水泥分布对椎体成形手术后疗效影响的研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(22):1400-1406. [26] 江晓兵,莫凌,梁德,等.骨水泥在椎体骨折线内弥散情况对椎体成形术治疗效果的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,11(2):144-149. [27] WANG W, DUAN K, MA M, et al. Can an unipedicular approach replace bipedicular percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture? J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2019;32(2):261-267. [28] 王松,杨剑,杨函,等.侧卧位单侧经横突-椎弓根入路椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效[J].实用医学杂志,2017,33(23): 3901-3905 [29] YAN L, HE B, HAO D. A Comparison between Unilateral Transverse Process-Pedicle and Bilateral Puncture Techniques in Percutaneous Kyphoplasty. Spine J. 2014;14(11):S54-S55. [30] 刘玉刚,王炳辉,龙游,等.经横突上缘椎弓根外侧入路单侧穿刺经皮椎体成形术治疗上腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].中华创伤杂志, 2018,34(4):312-318. [31] ERKAN S, WU C, MEHBOD AA, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Transpedicular Versus ExtrapedicularVertebroplasty Using Polymethylmethacrylate. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(3):180-185. [32] CHO SM, NAM YS, CHO BM, et al. Unilateral ExtrapedicularVertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty in Lumbar Compression Fractures:Technique, Anatomy and Preliminary Results. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011;49(5):273. [33] WANG YF, SHEN J, LI SY, et al. Kambin’s triangle approach in percutaneous vertebroplasty for the treatment ofosteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(44):e17857. [34] 赵亮,张锴,曹臣,等.侧卧位单侧入路无痛椎体强化术治疗合并内科重症骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2019,35(8):693-699. [35] HEO D, CHO Y. Segmental artery injury followingpercutaneous vertebroplasty using extrapedicular approach. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011;49(2):131-133. [36] HUNT CH, KALLMES DF, THIELEN KR. A Unilateral Vertebroplasty Approach Using a Curved Injection Cannula for Directed, Site-specific Vertebral Body Filling. JVIR. 2009;20(4):553-555. [37] MASALA S, NANO G, MAMMUCARI M, et al. Kummel Disease Treatment by Unipedicular Vertebral Augmentation Using Curved Injection Cannula. J Radiol. 2011;34(5):1014-1020. [38] HARSTE U. Modified Vertebroplasty using a Curved Probe:Technique and Preliminary Results. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2008;51(3):187-191. [39] 王新虎,张军,刘夏君,等.弹性弧形骨钻对小牛椎体骨质疏松模型 PVP 术中骨水泥分布的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(9):1062-1065. [40] BROOK AL, MILLER TS, FAST A, et al. Vertebral Augmentation with a Flexible Curved Needle: Preliminary Results in 17 Consecutive Patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008;19(12):1785-1789. [41] SOON WC, MATHEW RK, TIMOTHY J. Comparison of vertebroplasty using directional versus straight needle. Acta Radiol Open. 2015;4(3):1-6. [42] ZHONG R, LIU J, WANG R, et al. Unilateral curved versus bipedicularvertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.BMC Surg. 2019;19(1):193. [43] SAXENA A, HAKIMELAHI R, JHA RM, et al. The Safety and Effectiveness of a Curved Needle for Vertebral Augmentation: Comparison with Traditional Techniques. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;21(10):1548-1553. |
| [1] | Che Yanjun, Hu Dan, Si Weibing, Gu Xueping, Hao Yuefeng. Bone cement interval perfusion in hyperextension position for treatment of senile osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1555-1561. |
| [2] | An Yang, Liao Yinan, Xie Chengxin, Li Qinglong, Huang Ge, Jin Xin, Yin Dong. Mechanism of Inulae flos in the treatment of osteoporosis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||