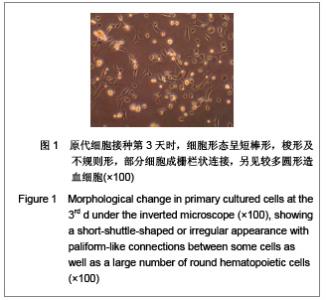
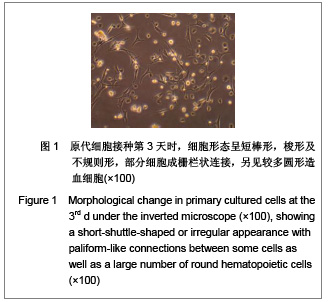
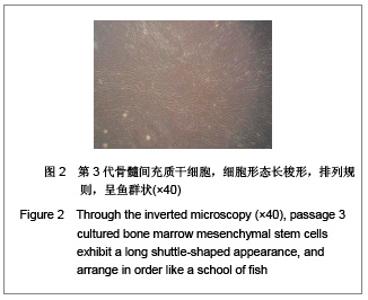
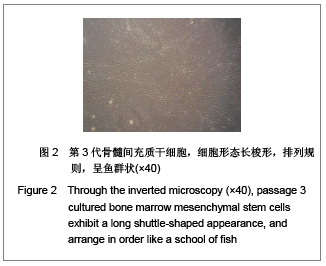
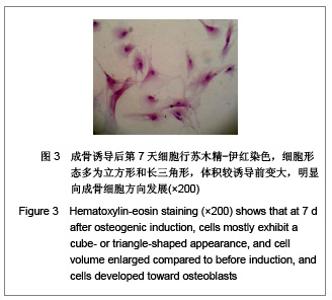
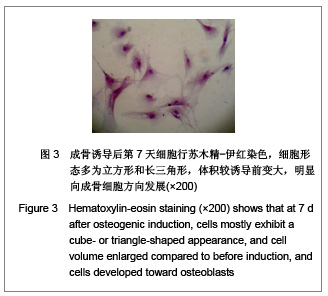
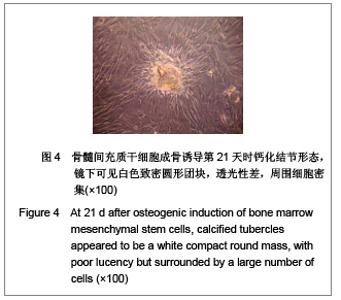
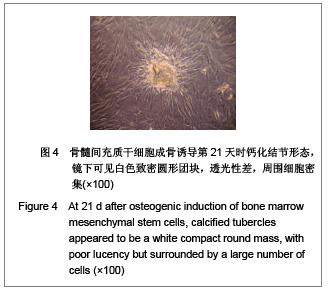
| [1] |
Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan.
Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-.
|
| [2] |
Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang.
Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171.
|
| [3] |
Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng.
Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255.
|
| [4] |
Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan.
Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080.
|
| [5] |
Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan.
Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087.
|
| [6] |
Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo.
Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103.
|
| [7] |
Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping.
Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115.
|
| [8] |
Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling.
Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121.
|
| [9] |
Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli.
Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128.
|
| [10] |
Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng.
Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134.
|
| [11] |
Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei.
In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141.
|
| [12] |
Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian.
Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148.
|
| [13] |
Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao.
Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990.
|
| [14] |
Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing.
Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995.
|
| [15] |
Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei.
Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001.
|