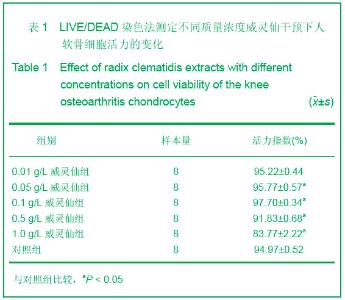
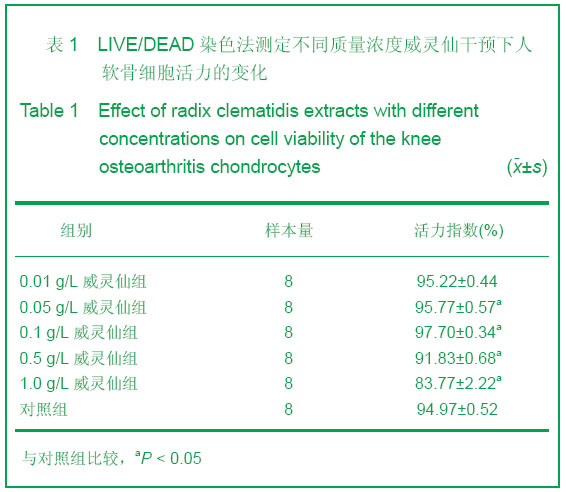
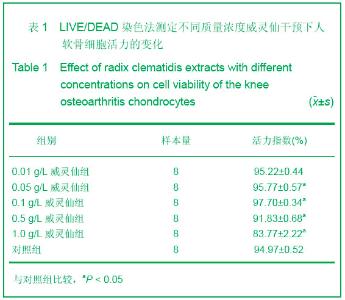
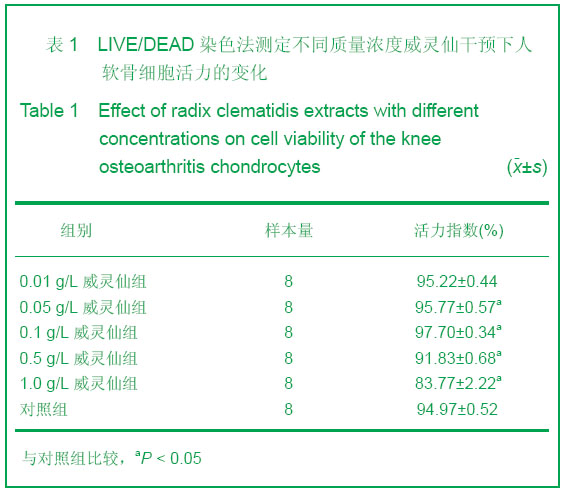
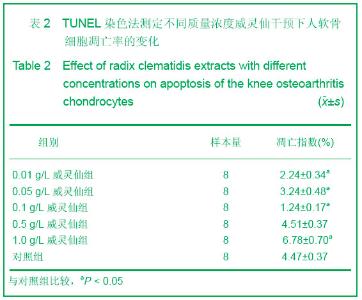
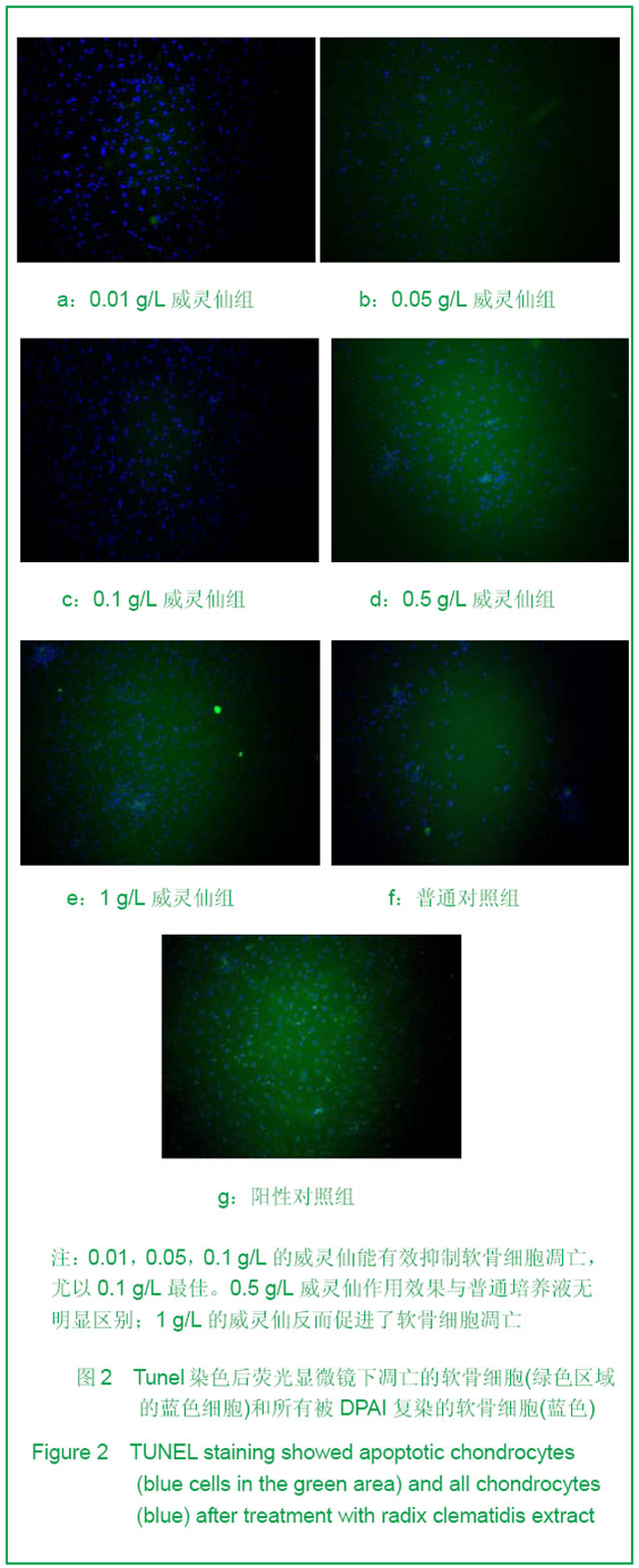
| [1] Ayache N, Boumediene K, Mathy-Hartert M,et al. Expression of TGF-betas and their receptors is differentially modulated by reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide in human articular chondrocytes.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002;10(5):344-352.[2] Kim HA, Blanco FJ.Cell death and apoptosis in osteoarthritic cartilage.Curr Drug Targets. 2007;8(2):333-345.[3] Li XL. Guoji Yiyao Weisheng Daobao. 2006;12(23):54-55.李肖斓.中医治疗膝关节骨性关节炎40例临床探讨[J].国际医药卫生导报,2006,12(23):54-55.[4] Sun YJ,Chen Y,Yu HK. Zhongguo Nongxue Tongbao. 2006; 22(11):86-89.孙玉军,陈彦,余宏凯.威灵仙多糖的提取工艺研究[J].中国农学通报,2006,22(11):86-89.[5] Enders JT, Otto TJ, Peters HC,et al. A model for studying human articular cartilage integration in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;94(2):509-514.[6] Zhang Z, McCaffery JM, Spencer RG,et al. Growth and integration of neocartilage with native cartilage in vitro.J Orthop Res. 2005;23(2):433-439.[7] Thomas CM, Fuller CJ, Whittles CE,et al. Chondrocyte death by apoptosis is associated with the initiation and severity of articular cartilage degradation. Int J Rheum Dis. 2011;14(2): 191-198.[8] Gao HF,Ren GL,Xu Y,et al. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2011;25(3):279-284.高航飞,任戈亮,徐燕,等. 在骨性关节炎发病中AQP-1表达量的变化与软骨细胞凋亡的相关性研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(3):279-284.[9] Sofat N.Analysing the role of endogenous matrix molecules in the development of osteoarthritis. Int J Exp Pathol. 2009; 90(5): 463-479.[10] Thomas CM, Murray R, Sharif M. Chondrocyte apoptosis determined by caspase-3 expression varies with fibronectin distribution in equine articular cartilage.Int J Rheum Dis. 2011; 14(3):290-297.[11] Scuderi GJ, Golish SR, Cook FF,et al. Identification of a novel fibronectin-aggrecan complex in the synovial fluid of knees with painful meniscal injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(4): 336-340.[12] Weng LH, Wang CJ, Ko JY,et al. Control of Dkk-1 ameliorates chondrocyte apoptosis, cartilage destruction, and subchondral bone deterioration in osteoarthritic knees. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(5):1393-1402.[13] Hashimoto S, Setareh M, Ochs RL,et al. Fas/Fas ligand expression and induction of apoptosis in chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40(10):1749-1755.[14] Dian LH. Xibei Yaoxue Zazhi. 2004;19(5):231-232.典灵辉.中药材威灵仙的研究进展[J].西北药学杂志,2004,19(5): 231-232.[15] Zhao YQ,Yang LX. Zhongyaocai. 2008;31(3):465-470.赵燕强,杨立新.威灵仙的成分、药理活性和临床应用的研究进展[J].中药材, 2008,31(3):465-470.[16] Chen FY,Wang X,Gu XJ,et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2006;14(5):360-363.陈飞雁,王旭,顾湘杰,等.威灵仙注射液对骨关节炎模型动物软骨组织形态和胶原表达的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006, 14(5): 360-363.[17] Ma Y,Zhang YS,Xu JA,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(11):1901-1909.马勇,张允申,许建安,等.威灵仙干预体外培养兔膝关节软骨细胞增殖及转化生长因子β1 mRNA基因的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(11):1901-1909.[18] Zhu XX,Zhi YF,Shao SJ,et al. Shiyong Zhongyi Neikexue Zazhi. 2006;20(6):603-604.朱萱萱,支月芳,邱召娟,等.痛痹颗粒及拆方的含药血清对家兔软骨细胞增殖与凋亡的影响[J].实用中医内科学杂志,2006,20(6): 603-604.[19] Zhang SH,Teng JW,Wang FJ,et al. Jilin Zhongyiyao. 2011; 31(11): 1126-1128.张世华,滕加文,王富军,等.补肾壮骨胶囊对兔膝骨性关节炎软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].吉林中医药,2011,31(11):1126-1128. |