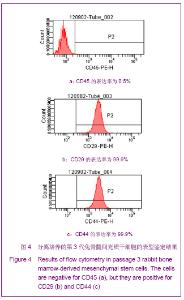
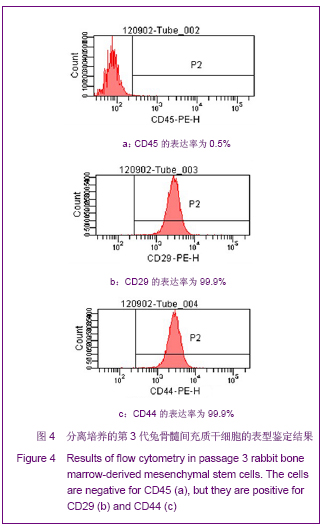
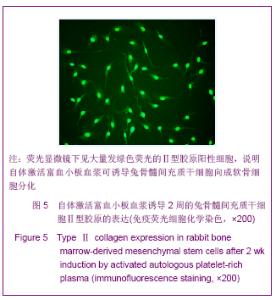
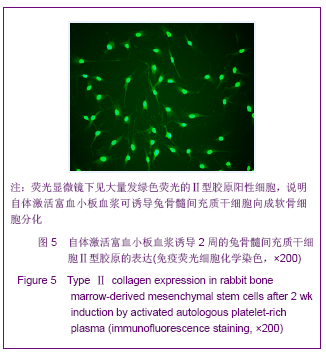
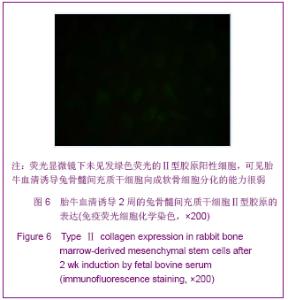
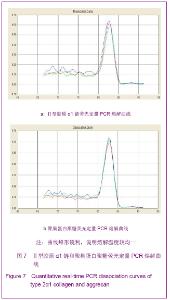
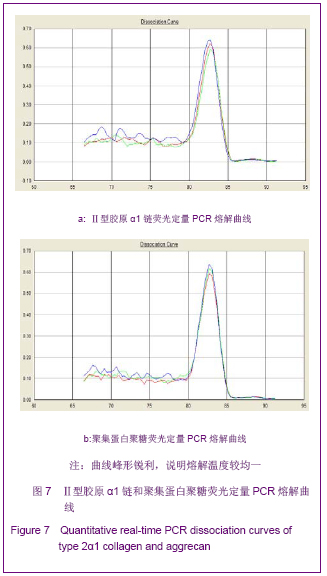
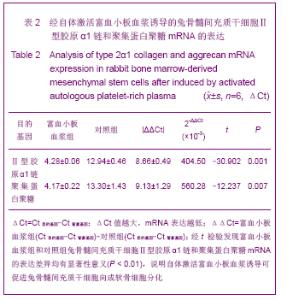
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (1): 1-8.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.01.001
Effect of activated autologous platelet-rich plasma on chondrogenic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro
Wang Shan-zheng, Wang Chen, Rui Yun-feng
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Zhongda Hospital of Southeast University, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2012-11-02Revised:2012-12-15Online:2013-01-01Published:2013-01-01 -
Contact:Wang Chen, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Zhongda Hospital of Southeast University, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu Province, China wangchen@ medmail.com.cn -
About author:Wang Shan-zheng★, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Zhongda Hospital of Southeast University, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu Province, China wshz2007@yahoo.com.cn -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, No. BK2012334*; Innovation Foundation of Southeast University, No. 3290002401*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Shan-zheng, Wang Chen, Rui Yun-feng. Effect of activated autologous platelet-rich plasma on chondrogenic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(1): 1-8.
share this article
| [1] Wearing SC, Hennig EM, Byrne NM, et al. Musculoskeletal disorders associated with obesity: a biomechanical perspective. Obes Rev. 2006;7(3):239-250.[2] Kock L, van Donkelaar CC, Ito K. Tissue engineering of functional articular cartilage: the current status. Cell Tissue Res. 2012;347(3):613-627.[3] Lim JY, Loiselle AE, Lee JS, et al. Optimizing the osteogenic potential of adult stem cells for skeletal regeneration. Orthop Res. 2011;29(11):1627-1633.[4] Tollervey JR, Lunyak VV. Adult stem cells: simply a tool for regenerative medicine or an additional piece in the puzzle of human aging? Cell Cycle. 2011;10(24):4173-4176.[5] Wang YT, Wu XT, Wang F. Regeneration potential and mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treating intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Sci. 2010;15(6):707-719.[6] Lee KS, Wilson JJ, Rabago DP, et al. Musculoskeletal applications of platelet-rich plasma: fad or future? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196(3):628-636.[7] Zhou HY, Wang C, Geng Z. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(24):4415-4418.周海洋,王宸,耿震.自体富含血小板血浆对兔骨折愈合的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(24):4415-4418.[8] Geng Z, Wang C, Zhou HY. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waikexue Zazhi. 2011;25(3):344-348.耿震,王宸,周海洋.富血小板血浆对肌腱愈合影响的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2011,25(3):344-348.[9] Morizaki Y, Zhao C, An KN, et al. The effects of platelet-rich plasma on bone marrow stromal cell transplants for tendon healing in vitro. J Hand Surg Am. 2010;35(11):1833-1841.[10] Xie X, Wang Y, Zhao C, et al. Comparative evaluation of MSCs from bone marrow and adipose tissue seeded in PRP-derived scaffold for cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials. 2012;33(29):7008-7018.[11] Torigoe I, Sotome S, Tsuchiya A, et al. Bone regeneration with autologous plasma, bone marrow stromal cells, and porous beta-tricalcium phosphate in nonhuman primates. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(7):1489-1499.[12] Ito K, Yamada Y, Nakamura S, et al. Osteogenic potential of effective bone engineering using dental pulp stem cells, bone marrow stem cells, and periosteal cells for osseointegration of dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011;26(5): 947-954.[13] Cenni E, Perut F, Ciapetti G, et al. In vitro evaluation of freeze-dried bone allografts combined with platelet rich plasma and human bone marrow stromal cells for tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009;20(1):45-50.[14] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30. [15] Zhang J, Wang JH. Platelet-rich plasma releasate promotes differentiation of tendon stem cells into active tenocytes. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(12):2477-2486.[16] Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402-408.[17] Sánchez-González DJ, Méndez-Bolaina E, Trejo-Bahena NI. Platelet-rich plasma peptides: key for regeneration. Int J Pept. 2012;2012:532519. [18] Atik OS. Is the evidence behind platelet-rich plasma therapies strong enough? Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2012;23(1):1.[19] Niemeyer P, Fechner K, Milz S, et al. Comparison of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue for bone regeneration in a critical size defect of the sheep tibia and the influence of platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials. 2010;31(13):3572-3579.[20] Hapa O, Cak?c? H, Kükner A, et al. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on tendon-to-bone healing after rotator cuff repair in rats: an in vivo experimental study. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2012;46(4):301-307.[21] Zhong W, Sumita Y, Ohba S, et al. In vivo comparison of the bone regeneration capability of human bone marrow concentrates vs. platelet-rich plasma. PLoS One. 2012; 7(7): e40833. [22] Kon E, Filardo G, Di Martino A, et al. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) to treat sports injuries: evidence to support its use. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(4):516-527. [23] Lacci KM, Dardik A. Platelet-rich plasma: support for its use in wound healing. Yale J Biol Med. 2010;83(1):1-9.[24] Conget PA, Minguell JJ. Phenotypical and functional properties of human bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells. J Cell Physiol. 1999;181(1):67-73.[25] Chen PM, Yen ML, Liu KJ, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of human adult and fetal multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Sci. 2011;18(1):49.[26] Jaiswal N, Haynesworth SE, Caplan AI, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of purified, culture-expanded human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 1997;64(2): 295-312.[27] Guo X, Huo R, Lü RR, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011,15(6):963-966.郭璇,霍然,吕仁荣,等.兔骨髓间充质干细胞培养及向成软骨细胞的诱导分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(6): 963-966.[28] Su JM, Jin Y, Qu Q, et al. Jichu Yixue yu Linchuang. 2010; 30(5):520-523.苏金梅,金晔,曲强,等.骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化过程中miR130a的表达[J].基础医学与临床,2010,30(5):520-523.[29] Fukumoto T, Sperling JW, Sanyal A, et al. Combined effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 and transforming growth factor-beta1 on periosteal mesenchymal cells during chondrogenesis in vitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003;11(1): 55-64.[30] Eleswarapu SV, Leipzig ND, Athanasiou KA. Gene expression of single articular chondrocytes. Cell Tissue Res. 2007;327(1):43-54. [31] Wei Y, Zeng W, Wan R, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells from osteoarthritic chondrocytes in alginate matrix. Eur Cell Mater. 2012;23:1-12. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [5] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [6] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [7] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [8] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [9] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [10] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [11] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [12] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [13] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [14] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [15] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||