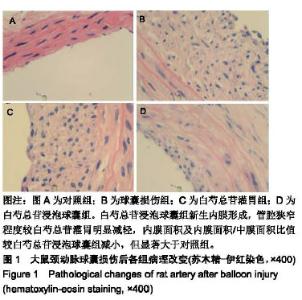
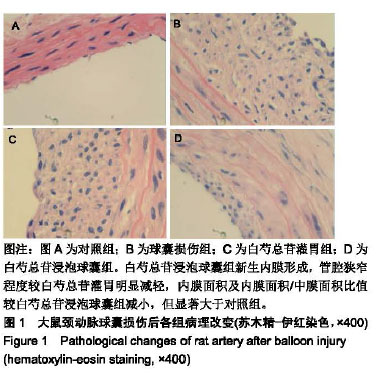
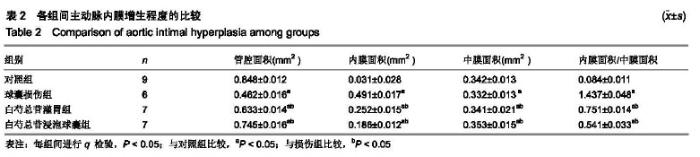
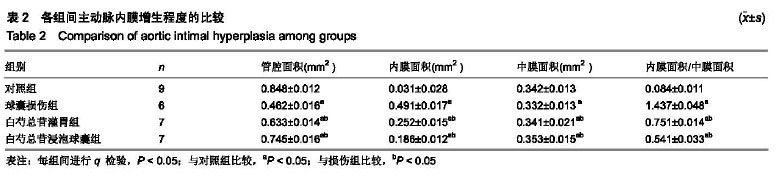
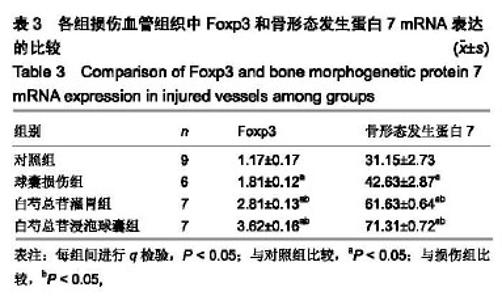
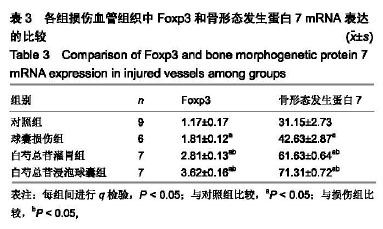
| [1]林欣,杨滨,王晔玲.冠脉支架植入术后炎症反应对再狭窄影响的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(1):233-236. [2]王萍,叶登美,窦德宇,等.白芍总苷对 EAT小鼠Th1/Th2型细胞因子表达的影响[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2016,21(8):894-898.[3]王晓,玉魏伟,唐丽琴,等.芍药苷对佐剂性关节炎大鼠腹腔巨噬细胞吞噬功能及其产生细胞因子的影响[J].安徽医科大学学报,2007, 42(2):189-191.[4]梁小红.白芍总苷对系统性红斑狼疮患者IL-8?TNF-α和INF-α表达的影响[J].中国现代药物应用,2008,2(24):64-66. [5]孙美珠,刘宏斌,黄党生,等.紫杉醇涂层球囊与第二代药物洗脱支架治疗支架内再狭窄患者的临床分析[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2018,10(9):1095-1098.[6]董少红,刘华东,廖玉华,等.Medtronic导管建立动脉损伤模型及对内膜增生的观察[J].广州医学院学报,2008,36(3):17-20.[7]Meng LB,Chen K,Zhang YM,et al. Common Injuries and Repair Mechanisms in the Endothelial Lining. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018; 131(19):2338-2345.[8]Wang F,Li C,Ding FH,et al.Increased serum TREM-1 level is associated with in-stent restenosis, and activation of TREM-1 promotes inflammation, proliferation and migration in vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. 2017;267(12):10-18.[9]Khattri R,Cox T,Yasayko SA,et al. An essential role for Scurfin in CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4(4): 337-342. [10]Milkova L,Voelcker V,Forstreuter I,et al. The NF-kappaB signalling pathway is involved in the LPS/IL-2-induced upregulation of FoxP3 expression in human CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells. Exp Dermatol. 2010;19(1):29-37.[11]Zhang W,Zhao L,Su SQ,et al.Total glucosides of paeony attenuate renal tubulointerstitial injury in STZ-induced diabetic rats: role of Toll-like receptor 2.J Pharmacol Sci. 2014;125(1): 59-67.[12]Capucha T,Koren N,Nassar M,et al.Sequential BMP7/TGF-β1 signaling and microbiota instruct mucosal Langerhans cell differentiation.J Exp Med.2018;215(2):481-500.[13]Zhu C,Cao C,Wang X,et al. UCN enhances TGF-beta- mediated mitoinhibition of VSMCs via counteracting TGF-beta-induced cPLA2 expression and activation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.2016; 80(11):98-108.[14]Midgley AC,Duggal L,Jenkins R,et al. Hyaluronan regulates bone morphogenetic protein-7-dependent prevention and reversal of myofibroblast phenotype. J Biol Chem.2015; 290(18):11218-11234.[15]任静,黄启丽,黄翠雯,等.过表达BMP7对TGF-β1诱导肾小管上皮细胞功能的影响[J].广东医学,2018,39(10):1454-1459.[16]郑琳颖,潘竞锵,吕俊华,等.白芍总苷药理作用研究[J].广州医药, 2011,42(3):66-69.[17]王治校,林静,陈彬,等.FOXP3基因对ApoE-knockout小鼠动脉粥样硬化的影响[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2011, 27(2):154-157.[18]王志强. BMP7?TGF-β在cGNHD狼疮样小鼠肾组织的表达及雷公藤多苷联合白芍总苷的干预作用[D].石家庄:河北医科大学. 2009.[19]Shateri H,Fadaei R, Najafi M,et al.Circulating Levels of IL-35 and Gene Expression of FoxP3 in Coronary Artery Disease:Is There Any Interplay Between Them and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3? Clin Lab. 2018;64(4):483-490.[20]Huang L,Zheng Y,Yuan X,et al.Decreased frequencies and impaired functions of the CD31+ subpopulation in Treg cells associated with decreased FoxP3 expression and enhanced Treg cell defects in patients with coronary heart disease. Clin Exp Immunol.2017;187(3):441-454. [21]Freedman BI,Bowden DW,Ziegler JT,et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 7(BMP7) gene polymorphisms are associated with inverse relationships between vascular calcification and BMD: the Diabetes Heart Study. J Bone Miner Res.2009;24(10):1719-1727.[22]Duranay M,Segall L,Sen N,et al. Bone morphogenic protein-7 serum level decreases significantly in patients with contrast- induced nephropathy. Int Urol Nephrol.2011;43(3):807-812.[23]Singla DK,Singla R,Wang J. BMP-7 Treatment Increases M2 Macrophage Differentiation and Reduces Inflammation and Plaque Formation in Apo E-/- Mice.PLoS One.2016;11(1): e0147897.[24]Lin H,Zhang W,Jiang X,et al.Total glucosides of paeony ameliorates TNBS?induced colitis by modulating differentiation of Th17/Treg cells and the secretion of cytokines.Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(6):8265-8276.[25]余欣然,向楠,李家园,等.白芍总苷胶囊对自身免疫性甲状腺炎模型大鼠Treg细胞的影响[J].云南中医学院学报,2017,40(6):5-8.[26]Chen Y,Wang Y,Xu L,et al.Influence of total glucosides of paeony on PD-1/PD-L1 expression in primary Sjögren's syndrome. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019;22(2):200-206.[27]吴亚军.药物涂层支架在冠心病介入治疗中的应用效果观察[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2018,5(41):33-36.[28]刘志涛,何国祥.冠状动脉支架内血栓与药物洗脱支架的安全性[J].心血管病学进展, 2009, 30(2):246-249.[29]翟洪发.抗肿瘤药紫杉醇的不良反应及临床合理用药评价[J].临床医药文献电子杂志, 2017,4(76):15018-15020. [30]陈将飞,马雪,盖增鑫,等.雷帕霉素(RAP)对斑马鱼胚胎的发育?运动行为和免疫毒性的影响[J].环境化学,2014,99(4):556-561. |