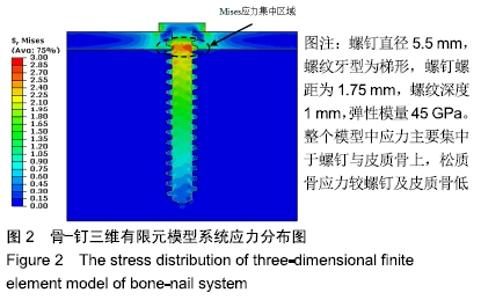
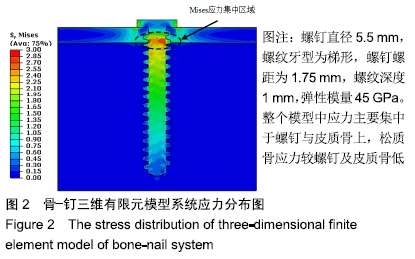
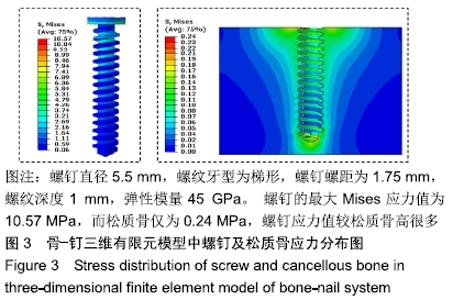
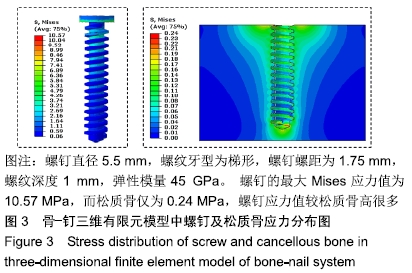
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 1574-1579.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1887
Previous Articles Next Articles
Orthopedic screw parameters in the orthogonal test: biocompatibility evaluation
Long Dengyan1, Ji Aimin1, Zhao Zhonghang1, Fang Runxin1, Chen Changsheng1,2
- 1College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Hohai University, Changzhou 213022, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Changzhou Orthmed Medical Instrument Co., Ltd., Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2019-04-30Revised:2019-05-07Accepted:2019-06-22Online:2020-04-08Published:2020-02-17 -
Contact:Ji Aimin, Professor, College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Hohai University, Changzhou 213022, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Long Dengyan, Master candidate, College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Hohai University, Changzhou 213022, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Central University's Basic Research Business Expenses Special Fund, No. 2019B63914; Jiangsu Provincial Graduate Research and Practice Innovation Project, No. SJKY19_0435
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Long Dengyan, Ji Aimin, Zhao Zhonghang, Fang Runxin, Chen Changsheng. Orthopedic screw parameters in the orthogonal test: biocompatibility evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1574-1579.
share this article
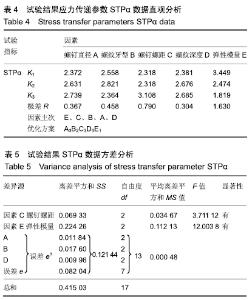
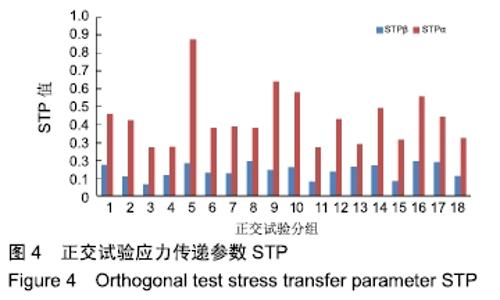
对图4数据进行简要分析可知,STPα值远高于STPβ值,最大差值出现在第5组,STPα值比STPβ值高近4倍。以上数据表明松质骨-螺钉之间的应力遮挡效应较皮质骨-螺钉的严重。 2.2.1 试验结果STPα数据分析 通过对皮质骨-螺钉的应力传递参数STPα直观分析表明:极差RE>RC>RB> RA>RD,可见各因素对试验指标STPα的影响主次顺序为接骨螺钉弹性模量(E)、螺钉螺距(C)、螺纹牙型(B)、螺钉直径(A)、螺纹深度(D)。STPα值越大应力遮挡程度越轻,接骨螺钉的生物相容性能越好。A因素下K3>K2>K1,可知A3为因素A的最佳方案;同理分析可知B2、C3、D3、E1分别为因素B、C、D、E的最佳方案,见表4,5。 "
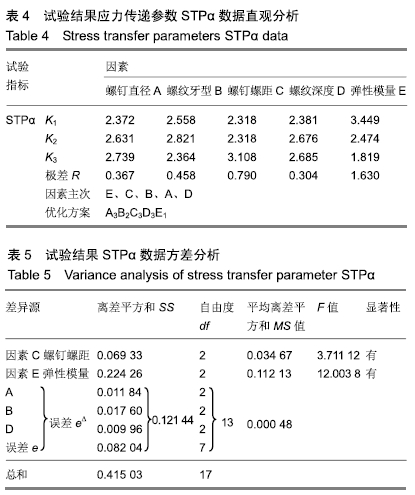
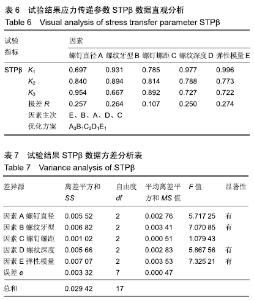
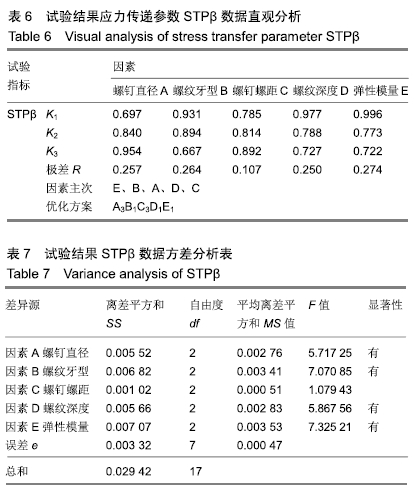
由于MSA<MSe、MSB<MSe、MSD<MSe,所以因素A、B、D对试验结果影响较小,将其归入误差中。查得临界值F0.10(2,13)=2.763 2,F0.05(2,13)=3.805 6,F0.01(2,13)=6.701,由于F0.10(2,13)<FC<F0.05(2,13),FE>F0.10(2,13)可见因素C对于考察指标STPα有一定影响;因素E对考察指标STPα有非常显著的影响。 2.2.2 试验结果STPβ数据分析 通过对松质骨-螺钉的应力传递参数STPβ直观分析表明:RE>RB>RA>RD>RC,可见各因素对试验指标STPβ的影响主次顺序为接骨螺钉弹性模量(E)、螺纹牙型(B)、螺钉直径(A)、螺纹深度(D)、螺钉螺距(C)。STPβ值越大,应力遮挡程度越轻,接骨螺钉的生物相容性能越好。A因素下K3>K2>K1,可知A3为因素A的最佳方案;同理分析可知B1、C3、D1、E1分别为因素B、C、D、E的最佳方案,见表6,7。 "

查得临界值F0.10(2,7)=3.257 4,F0.05(2,7)=4.737 4,F0.01(2,7)=9.546 6,F0.05(2,7)<FA、FB、FD、FE、F0.01(2,7)FC< F0.10(2,7),可见因素A、B、D、E对考察指标STPα均有显著影响,只有因素C对考察指标STPα无显著影响。 2.2.3 权矩阵法综合评价 分析试验数据可知,因素E即接骨螺钉弹性模量的影响高度显著,其余不同因素对于皮质骨-螺钉的应力传递与松质骨-螺钉的应力传递的影响程度不一样。因此,需要对上述两指标进行综合考量。权矩阵法可以计算出影响试验结果的考察指标权重,根据权重大小可快速有效的得出试验的最佳方案以及各因素对于正交试验指标值影响的主次顺序,因此采用权矩阵法来确定因素的主次顺序及最佳方案。 根据文献[22]计算方法,对权函数ω进行求解。第一个试验考察指标为皮质骨-螺钉的应力传递参数STPα,其值越大越好,权矩阵ω1计算结果如下: ω1T=[0.031 673,0.035 123,0.036 57,0.042 616,0.047 011,0.039 383,0.066 637—0.066 634,0.089 348,0.026 354,0.029 613,0.029 719,0.204 629,0.146 755,0.107 934] 第二个实验考察指标为松质骨-螺钉的应力传递参数STPβ,其值越大越好,权矩阵ω2计算结果如下: ω2T=[0.062 422,0.075 163,0.085 408,0.085 627,0.082 278,0.061 335,0.029 311—0.030 391,0.033 31,0.085 074,0.068 595,0.063 311,0.095 059,0.073 79,0.068 925] 正交试验考察指标的总权矩阵为2个指标值的权矩阵的平均值,计算如下: ωT=[0.047 048,0.055 143,0.060 989,0.064 122,0.064 645,0.050 359,0.047 974—0.048 512,0.061 329,0.055 714,0.049 104,0.046 515,0.149 844,0.110 273,0.088 429] =[A1,A2,A3,B1,B2,B3,C1,C2,C3,D1,D2,D3,E1,E2,E3] 综合计算上述可知,因素A的3个水平对试验结果的影响权重分别为:A1=0.047 048,A2=0.055 143,A3=0.060 989,A3权重最大;同理,因素B中B2权重最大,因素C中C3权重最大,因素D中D1权重最大,因素E中E1权重最大。由此可知,本正交试验的最优方案为A3B2C3D1E1,即大径为6.5 mm、梯形螺纹、螺距为2.75 mm、螺纹深度为0.5 mm、弹性模量为45 GPa的接骨螺钉生物力学性能表现最佳。同时可得出各个因素对于试验考察指标影响的主要次序为E、B、C、A、D,即弹性模量对试验指标的影响最大,其次是螺纹牙型、螺距和螺纹直径并且其影响程度相近,而螺纹深度影响最小。 "

| [1] 王江泽,丁真奇.影响松质骨螺钉固定强度的相关因素[J].中国现代医生,2012,50(12):26-28. [2] 张克玉,华子恺.接骨螺钉的失效分析与强度测试[J].医用生物力学,2018,33(3):280-284. [3] ZHANG QH, TAN SH, CHOU SM.Investigation of fixation screw pull-out strength on human spine. J Biomech. 2004; 37(4):479-485. [4] ZHANG QH, TAN SH, CHOU SM.Effects of bone materials on the screw pull-out strength in human spine.Med Eng Phys. 2006;28(8):795-801. [5] SCHLIEMANN B, RISSE N, FRANK A, et al. Screws with larger core diameter and lower thread pitch increase the stability of locked plating in osteoporotic proximal humeral fractures.Clin Biomech (Bristol,Avon).2019;63:21-26. [6] ERASLAN O, INAN O.The effect of thread design on stress distribution in a solid screw implant: a 3D finite element analysis.Clin Oral Investig.2010;14(4):411-416. [7] 肖玲,岳云,程文杰,等.不同螺纹形态的圆柱状2D种植体的即刻力学分析[J].西安科技大学学报, 2017,37(2):292-298. [8] 周绍波.骨螺钉稳定性影响因素研究[D].广州:广东工业大学, 2018. [9] 祝联,崔磊,曹谊林,等.骨制松质骨螺钉的生物力学性能实验研究[J].医用生物力学,2001,16(2):99-104. [10] 张其美.基于有限元分析的Mg-Zn-Y-Nd合金骨螺钉的结构优化[D].郑州:郑州大学,2017. [11] ROUHI G, TAHANI M, HAGHIGHI B, et al. Prediction of Stress Shielding Around Orthopedic Screws: Time-Dependent Bone Remodeling Analysis Using Finite Element Approach.J Med Biol Eng.2015;35(4): 545-554. [12] UHTHOFF HK.Bone reaction around screw threads.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1975;111:305. [13] UHTHOFF HK, JAWORSKI ZF.Bone loss in response to long-term immobilisation.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1978;60-B(3): 420-429. [14] VAN LENTHE GH, DE WAAL MALEFIJT MC, HUISKES R.Stress shielding after total knee replacement may cause bone resorption in the distal femur.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(1):117-122. [15] OKUYAMA K ,ABE E, SUZUKI T, et al.Can insertional torque predict screw looseningand related failures? An in vivo study of pedicle screw fixationaugmenting posterior lumbar interbody fusion.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2000;25(7):858-864. [16] GEFEN A.Computational simulations of stress shielding and bone resorption around existing and computer-designed orthopaedic screws.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2002;40(3): 311-322. [17] HAASE K, ROUHI G.Prediction of stress shielding around an orthopedic screw: Using stress and strain energy density as mechanical stimuli.Comput Biol Med.2013;43(11):1748-1757. [18] 李志西,杜双奎.试验优化设计与统计分析[M].北京:科学出版社, 2010:130-143. [19] 李云雁,胡传荣.试验设计与数据处理[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2008:229-230. [20] GEFEN A.Optimizing the biomechanical compatibility of orthopedic screws for bone fracture fixation.Med Eng Phys. 2002;24(5):337-347. [21] HOSSEINITABATABAEI S, ASHJAEE N, TAHANI M. Introduction of Maximum Stress Parameter for the Evaluation of Stress Shielding Around Orthopedic Screws in the Presence of Bone Remodeling Process.J Med Biol Eng. 2017; 37(5):703-716. [22] 周玉珠.正交试验设计的矩阵分析方法[J].数学的实践与认识, 2009,39(2):202-207. [23] TURNER CH.Three rules for bone adaptation to mechanical stimuli.Bone(New York).1998; 23(5):400-407. [24] ROUHI G.Biomechanics of Osteoporosis: The Importance of Bone Resorption and Remodeling Processes.Osteoporosis. InTech,2012. [25] ASHJAEE N, HOSSEINITABATABAEI S, TAHANI M.Design optimization of an orthopedic screw based on stress stimulus using Taguchi method and finite element analysis.National Conference on Applied Researches in Electrical,2015. [26] ER MS, VERIM O, EROGLU M, et al.Biomechanical evaluation of syndesmotic screw design via finite element analysis and Taguchi's method.J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2015;105(1):14-21. [27] MUHAMAD N, DAUD R, ARIFFIN AK, et al.Finite Element Analysis of Stress Shielding between Orthopedic Screw and Cortical-Cancellous Bone: A pilot study.Symposium on Damage Mechanics in Materials and Structures,2016. [28] UHTHOFF HK, BARDOS DI, LISKOVA-KIAR M.The advantages of titanium alloy over stainless steel plates for the internal fixation of fractures. An experimental study in dogs.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1981;63-B(3):427-484. [29] WOO SL, SIMON BR, AKESON WH, et al. A new approach to the design of internal fixation plates. J Biomed Mater Res. 2010;17(3):427-439. |
| [1] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [2] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [3] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [4] | Liu Zhao, Xu Xilin, Shen Yiwei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Lü Hang, Zhao Jun, Wang Zhengchun, Liu Xuzhuo, Wang Haitao. Guiding role and prospect of staging and classification combined collapse prediction method for osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| [5] | Chen Lu, Zhang Jianguang, Deng Changgong, Yan Caiping, Zhang Wei, Zhang Yuan. Finite element analysis of locking screw assisted acetabular cup fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 356-361. |
| [6] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [7] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| [8] | Liu Jinyu, Ding Yiwei, Lu Zhengcao, Gao Tianjun, Cui Hongpeng, Li Wen, Du Wei, Ding Yu. Finite element biomechanical study of full endoscopic fenestration decompression for cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3850-3854. |
| [9] | Qin Wan’an, Cai Zhouyu, Wei Gejin, Lin Zhoudan. Finite element analysis of absorbable screws and ethibond sutures for the treatment of humerus shaft fractures caused by grenade throwing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3855-3859. |
| [10] | Li Xinping, Cui Qiuju, Zeng Shuguang, Ran Gaoying, Zhang Zhaoqiang, Liu Xianwen, Fang Wei, Xu Shuaimei. Effect of modification of β-tricalcium phosphate/chitosan hydrogel on growth and mineralization of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3493-3499. |
| [11] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| [12] | Ma Qing, Shi Liyan, Huang Sixue, Zheng Zhangbowen, Zhang Aihua, Zhan Desong, Fu Jiale. Research status and prospect of zirconia ceramics in dental prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3597-3602. |
| [13] | Wen Zhijing, Gu Pengzhen, He Xijing, Li Jialiang, Wang Yibin, Wang Yiqun. Development of high molecular polymer polyetherketoneketone and its prospects in medical applications [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3603-3608. |
| [14] | Cai Qunbin, Yang Lijuan, Li Qiumin, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei . Feasibility of internal fixation removal of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients based on fracture mechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3313-3318. |
| [15] | Wei Yuanbiao, Guo Huizhi, Zhang Shuncong. Finite element analysis of cortical bone trajectory screw fixation on adjacent segments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2799-2804. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||