Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (29): 4722-4727.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1802
Previous Articles Next Articles
Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Xie Jingchun1, 2, Yao Guanping3, Yu Limei1, 2, 4
- 1Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering in Guizhou Province, 2Talent Base of Biological Treatment in Guizhou Province, 3Reproductive Center, 4Zunyi Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Engineering Research Center, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China
-
Revised:2019-05-14Online:2019-10-18Published:2019-10-18 -
Contact:Yu Limei, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, 1Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering in Guizhou Province, 2Talent Base of Biological Treatment in Guizhou Province, 4Zunyi Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Engineering Research Center, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Xie Jingchun, Master, 1Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering in Guizhou Province, 2Talent Base of Biological Treatment in Guizhou Province, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81460136 (to YGP); Guizhou Province Science and Technology Major Project, No. Qian ke he zhong da zhuan xiang zi [2011] 6002 (to YLM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Jingchun, Yao Guanping, Yu Limei. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(29): 4722-4727.
share this article

2.1 间充质干细胞治疗类风湿性关节炎的效果 细胞共培养实验发现脂肪来源间充质干细胞能显著下调类风湿性关节炎患者外周血单个核细胞中的肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素17A和白细胞介素21水平,并促进转化生长因子β1水平显著增加[13],且在间充质干细胞影响下Th17降低,CD4+CD25+FoxP3+显著增加[14],说明脂肪间充质干细胞产生的分泌因子能下调Th17并增加类风湿性关节炎患者外周血单个核细胞中的Treg细胞数量。 动物实验发现骨髓和羊膜间充质干细胞也可以明显减少类风湿性关节炎动物血清和关节液中白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α等促炎细胞因子水平,上调白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10等抗炎细胞因子水平,诱导Treg细胞的表达来阻止类风湿性关节炎的发展,上调局部组织转化生长因子β和骨保护素水平,下调基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13等,减少滑膜炎性增生,减轻骨侵蚀、软骨破坏和骨赘形成[2,15];脐血间充质干细胞不仅可以抑制成熟树突状细胞的功能,也可通过调控Treg来下调Th1和Th17细胞,并通过转化生长因子β1抑制成纤维样滑膜细胞增生[16]。 此外,在难治性类风湿性关节炎患者Ⅰb/Ⅱa期临床试验中也发现脂肪间充质干细胞静脉输注具有良好的耐受性,并观察到临床疗效的趋势在所研究的剂量范围和时间段没有剂量相关毒性的证据[17];同时伊朗9例接受骨髓间充质干细胞治疗的难治性类风湿性关节炎患者也在12个月的随访中发现白细胞介素17A的Th17百分比呈显著下降趋势,且1个月和12个月时基于血沉的类风湿关节炎患者疾病活动度评分(DAS28-ESR)显著下降,目测类比评分表现显著下降趋势[18];不仅如此,一项在甲氨喋呤治疗后仍有中度疾病活动的Ⅰa期临床试验表明,单次脐带间充质干细胞静脉输注对类风湿性关节炎患者是安全的,4周后平均类风湿关节炎患者疾病活动度评分(DAS28)降低[19];另一项1/2期试验也证实膝关节内移植骨髓间充质干细胞有助于改善类风湿性关节炎患者临床效应,但这种改善不能持续超过12个月,此外,间充质干细胞似乎有助于减少甲氨蝶呤和强的松龙的使用[20],见图1。"
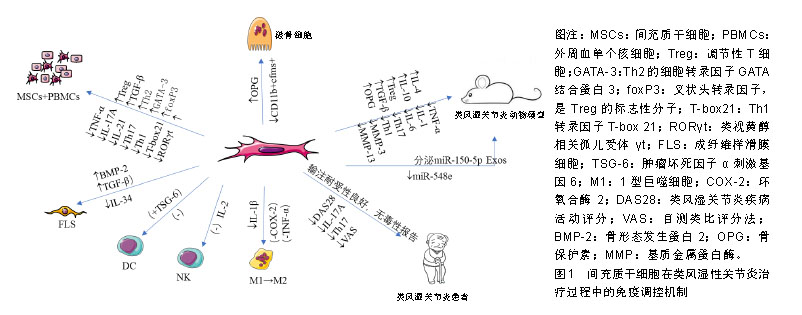
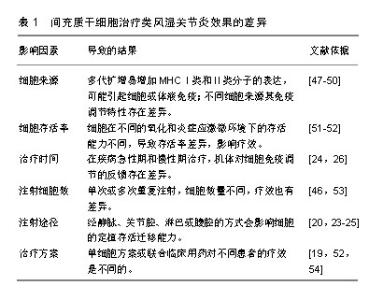
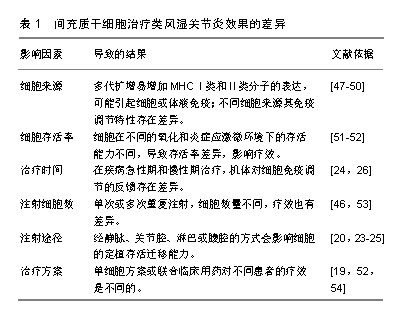
2.2 间充质干细胞治疗类风湿性关节炎的作用机制 2.2.1 免疫调节 间充质干细胞在类风湿性关节炎治疗中的免疫调节作用突出表现在抑制T细胞增殖与功能,诱导Treg细胞产生, 抑制B细胞增殖、分化、免疫球蛋白的产生;同时间充质干细胞也可抑制树突状细胞成熟,促进巨噬细胞极化到抗炎表型和抑制NK细胞功能[21],进而减缓炎症和防止关节损伤。但间充质干细胞在类风湿性关节炎中对Treg细胞和炎症细胞因子网络的调控作用仍十分复杂,还可能涉及miRNA等表观遗传学机制[22]。 (1)间充质干细胞调节T、B细胞:动物实验表明,骨髓、羊膜、脂肪来源间充质干细胞静脉或关节腔内移植,对弗氏佐剂诱发的类风湿性关节炎和胶原诱导的关节炎均具有减轻炎症损伤的良好疗效[23]。然而有研究报道,静脉注射脂肪来源间充质干细胞后,在关节处未检测到注射的间充质干细胞,表明间充质干细胞预防关节损伤的作用主要是通过抑制机体免疫系统来实现[24]。也有研究发现腹腔内注射骨髓间充质干细胞治疗胶原抗体诱导的关节炎小鼠,间充质干细胞可诱导基质细胞衍生因子1α的过表达促进间充质干细胞迁移到炎症损伤的足爪关节部位,也可通过直接诱导CD4+ T细胞分化成Treg细胞,而抑制免疫炎症反应[25]。 Treg细胞在维持类风湿性关节炎机体的自身免疫耐受中发挥关键作用。有研究发现,Treg细胞产生的白细胞介素10通过抑制Th1细胞的活化而对胶原诱导的关节炎具有明显保护作用[26];最近发现脂肪间充质干细胞对类风湿性关节炎患者T细胞亚群的免疫调节作用还体现在能上调Th2和Treg细胞转录因子GATA结合蛋白3和叉头盒P3,并且下调Th1和Th17转录因子T-box 21和类视黄醇相关孤儿受体γt[27],这些结果表明,脂肪间充质干细胞可通过抑制促炎T细胞和诱导调节表型的Terg而产生免疫抑制环境。 此外,间充质干细胞与类风湿性关节炎患者外周血分离的T细胞、B细胞或Treg细胞共培养,发现间充质干细胞可明显改变T、B细胞和Treg细胞的比例及其所释放因子的产生,如Treg水平增加了2倍,CD3+T细胞介导的肿瘤坏死因子α分泌被抑制,白细胞介素10水平上调,由B细胞针对瓜氨酸化蛋白抗原产生的自身抗体也被明显抑制[28]。不仅如此,研究还显示脐带间充质干细胞在体外和体内均能抑制脾脏中分离的Tfh细胞分化和数量,进而抑制B淋巴细胞增殖、分化[29],且研究也认为间充质干细胞对B细胞的抑制作用依赖于间充质干细胞和T细胞之间的相互作用[30]。 (2)间充质干细胞调节DC、NK细胞:正常情况下体内未成熟的树突状细胞低表达MHCⅡ类分子,但在摄取抗原或炎性刺激下,未成熟树突状细胞开始分化成熟。研究发现间充质干细胞可通过释放肿瘤坏死因子刺激基因6来减少成熟树突状细胞上CD80和CD86刺激分子的表达,促使成熟树突状细胞趋向一种未成熟状态,从而抑制树突状细胞成熟和功能[31];其次,间充质干细胞也能够抑制白细胞介素2导致的NK细胞增殖发挥免疫抑制功能[32]。此外,脐带间充质干细胞可通过抑制肿瘤坏死因子α介导的环氧合酶2和TSG-6的活化来诱导M2型巨噬细胞的产生,抑制M1型巨噬细胞的活化,并抑制NLRP3炎症小体介导的白细胞介素1β分泌,有效调节类风湿性关节炎患者循环中的巨噬细胞极化状态[33]。 2.2.2 调节炎症因子分泌 炎症递质与关节损伤的严重程度和类风湿性关节炎进展息息相关,而间充质干细胞所分泌的大量抗炎因子、miRNA及外泌体等都可能直接参与了类风湿性关节炎相关的炎症因子调控[22,34],所以探索触发炎症因子级联效应的靶点,可更好地提高类风湿性关节炎的治疗效果。 最近有研究发现类风湿性关节炎患者骨髓间充质干细胞中的A20(肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白3)含量减少,白细胞介素6分泌增加,Th17/Treg平衡被打破;同时也发现胶原诱导的关节炎小鼠间充质干细胞A20mRNA和蛋白水平下降,白细胞介素6表达升高,但经脐带间充质干细胞处理后,A20、白细胞介素6表达量得到明显改善[35]。结果表明间充质干细胞中A20在促炎因子白细胞介素6生成过程中的调控作用可能是类风湿性关节炎治疗中的潜在靶点。不仅如此,早期研究就发现白细胞介素1β拮抗剂IL-1Ra敲除的BALB/c小鼠在13周龄时多可发展为关节炎[36],将骨髓间充质干细胞腹腔注射到白细胞介素1Ra敲除小鼠后,降低了白细胞介素1β等多种促炎因子水平以及Th17/Treg的比率[37]。这些结果都表明,间充质干细胞抑制相关可能性炎症靶点是有效的。 不仅如此,间充质干细胞似乎通过激活转化生长因子β受体信号来降低胶原诱导的关节炎小鼠关节组织中NF-κB信号传导的活性,并降低miR-548e水平来减轻类风湿性关节炎小鼠的关节炎症与损伤症状,因为miR-548e可与IκB mRNA的3'-UTR结合,抑制NF-κB抑制剂IκB的蛋白质翻译,而与携带miR-548e的腺病毒共移植的间充质干细胞却消除了间充质干细胞对胶原诱导性关节炎的治疗作用[22]。 前期研究发现中性粒细胞衍生的外泌体可传递到血清中,使诱导性关节炎小鼠在膝关节中表达抗炎特性,防止软骨退化,还可穿透无血管的软骨细胞外基质向软骨细胞递送生物活性分子而有利于软骨合成代谢[38]。近期研究发现间充质干细胞释放的外泌体也可介导组织再生和免疫调节。如在胶原诱导性关节炎小鼠中发现间充质干细胞衍生的miR-150-5p外泌体能通过靶向基质金属蛋白酶14和血管内皮生长因子降低类风湿性关节炎中成纤维样滑膜细胞的迁移和侵袭,也能通过抑制滑膜细胞增生和血管生成来减少关节破坏,其作用可能与外泌体中所含的miRNA在细胞与细胞间直接转移作用有关[39]。最新的研究又发现来自间充质干细胞的外泌体和微粒以剂量依赖性方式抑制T淋巴细胞增殖,并降低CD4+和CD8+ T细胞亚群的百分比,有效降低炎症反应;而且与间充质干细胞相似,外泌体也可增加Treg细胞比例,间充质干细胞、外泌体或微粒都可以降低浆母细胞分化,外泌体的有益作用与淋巴结中更少的浆母细胞和更多Breg样细胞相关[40]。由此推测间充质干细胞介导的相关信号分子或阻断炎症因子级联放大效应的关键信号分子表达水平,都可能在类风湿性关节炎的炎症因子网络调控中发挥重要治疗作用。 2.2.3 抑制破骨细胞功能 在类风湿性关节炎病程中,关节腔内成纤维样滑膜细胞的异常活化、增殖及基质金属蛋白酶分泌引起的组织水肿增生进一步诱导了骨破坏;其次,破骨细胞的激活与活性增加又引起过度骨吸收。 由于关节内无营养血管存在,损伤关节组织的自身修复能力明显减弱,但间充质干细胞分泌的转化生长因子β、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和外泌体等可能直接或间接调节局部基质组分,进而促进损伤关节组织修复[41];而Zhang等[26]为了跟踪脂肪间充质干细胞在稳态宿主中的生物分布,将荧光标记的间充质干细胞静脉注射到胶原诱导性关节炎小鼠中,24 h后可以在小鼠踝关节中检测到主要的荧光信号,说明了间充质干细胞可以归巢到炎症损伤部位发挥疗效;其次,间充质干细胞在抑制破骨细胞过度激活及其促炎因子的释放方面,也显著降低了骨吸收作用[42]。有证据表明,间充质干细胞对破骨细胞生成的直接抑制作用可能是通过产生NF-κB受体活化因子配体诱导骨保护素而发挥作用的[43];也可通过CD200/CD200R依赖性地抑制破骨细胞前体的相互作用而实现[44]。此外,向胶原诱导性关节炎小鼠注射脂肪来源间充质干细胞可预防局部和全身性骨丢失,其作用机制与减少骨髓中CD11b+cfms+破骨细胞前体细胞有关[45]。近来发现类风湿性关节炎患者成纤维样滑膜细胞表达的促炎因子还包括白细胞介素34,它能促进单核细胞增殖和存活以及破骨细胞分化,其表达水平高低与炎症反应程度、白细胞数量和滑膜炎的严重程度密切相关,在肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β存在时,白细胞介素34水平明显上调;研究发现活化素受体样激酶1、活化素受体样激酶5下游的转化生长因子β1和骨形态发生蛋白2可分别通过剂量和时间依赖性方式降低成纤维样滑膜细胞或鼠源性间充质干细胞中白细胞介素34的表达来减轻类风湿性关节炎的关节损伤,间接促进损伤修复[46]。 2.3 间充质干细胞治疗类风湿性关节炎效果的差异性 见表1。然而,一些研究却未能证明间充质干细胞治疗类风湿性关节炎的效果,有些研究甚至还报告了更差的结果。首先这种相互矛盾的结果可能与间充质干细胞的来源、细胞存活率、治疗时间、注射细胞数、注射途径和治疗方案等有关。间充质干细胞经多代扩增、向终末功能细胞分化,会一定程度地增加MHCⅠ类和Ⅱ类分子的表达[47],进而在同种异体间充质干细胞移植时可能在体内引起体液或细胞免疫;且不同来源间充质干细胞具有的免疫调节特性也不完全一样,导致间充质干细胞所发挥的临床效力也有差异。与来自骨髓、骨膜和脂肪的间充质干细胞相比,人滑膜来源间充质干细胞在体外研究中显现出更强的软骨形成能力[48],而它们在体内骨形成能力方面不如骨膜来源间充质干细胞[49];与骨髓间充质干细胞相比,脂肪间充质干细胞对T细胞和单核细胞具有更强的免疫抑制能力[50];更有研究显示,与造血干细胞和甲氨蝶呤治疗相比,间充质干细胞在改善爪水肿、类风湿性关节炎评分、类风湿因子、抗氧化状态、NF-κB、基质金属蛋白酶3和软骨寡聚基质蛋白方面效果更佳[51]。此外,移植后细胞存活率低归因于受伤部位的氧化和炎症应激。有研究发现间充质干细胞与具有抗氧化和抗炎活性橙皮苷联合使用可以降低类风湿性关节炎中的白细胞介素9水平,减轻氧化应激,增强干细胞的免疫调节作用[52]。最近还有研究指出长时间多次重复静脉注射脐血间充质干细胞对改善胶原诱导性关节炎小鼠模型的类风湿性关节炎症状具有剂量依赖性作用[53]。而在治疗方案上也证实低甲基化剂和组蛋白脱乙酰基酶抑制剂的联合可以增强间充质干细胞对类风湿性关节炎患者Th17细胞的免疫抑制作用[54]。 有些研究没有充分考虑到类风湿性关节炎所处的病理环境,已有文献报道脂肪间充质干细胞的存活和生物分布依赖于机体的免疫状态,而不受炎症程度轻重的影响[24]。另外有研究观察到间充质干细胞的治疗效果差异可以用高血清干扰素γ水平来预测,因为在间充质干细胞移植治疗类风湿性关节炎改善患者血清干扰素γ(> 2 ng/L)水平短暂增加,并发现随后两三周出现白细胞介素10水平和Treg/Th17比率增加以及白细胞介素6水平降低[55],所以间充质干细胞治疗类风湿性关节炎的差异好坏可能与当时类风湿性关节炎本身所处的免疫炎症状态时相关。"
| [1]Niu X, Chen G. Clinical biomarkers and pathogenic-related cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:698192.[2]肖瑶,方宁,陈代雄,等.人羊膜间充质干细胞对大鼠胶原性关节炎的疗效及免疫调节作用[J].免疫学杂志,2013,29(6):461-466. [3]Fiehn C, Holle J, Iking-Konert C,et al.S2e guideline:treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with disease-modifying drugs.Z Rheumatol. 2018; 77(Suppl 2):35-53.[4]McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(23):2205-2219.[5]McInnes IB, Buckley CD, Isaacs JD. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis - shaping the immunological landscape. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016; 12(1):63-68.[6]Chastek B, Becker LK, Chen CI, et al. Outcomes of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor cycling versus switching to a disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug with a new mechanism of action among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Med Econ. 2017;20(5):464-473.[7]Bongartz T, Sutton AJ, Sweeting MJ, et al. Anti-TNF antibody therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of serious infections and malignancies: systematic review and meta-analysis of rare harmful effects in randomized controlled trials.JAMA. 2006;295(19):2275-2285.[8]Salliot C, Gossec L, Ruyssen-Witrand A, et al. Infections during tumour necrosis factor-alpha blocker therapy for rheumatic diseases in daily practice: a systematic retrospective study of 709 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007;46(2):327-334.[9]Castro-Manrreza ME, Montesinos JJ. Immunoregulation by mesenchymal stem cells: biological aspects and clinical applications. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:394917.[10]刘荣霞,杨炳,余丽梅,等.不同来源间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰的作用及机制研究进展[J].山东医药,2018,58(40):106-110. [11]罗欣,余丽梅.外泌体在间充质干细胞治疗骨性关节炎中的作用:新策略与新思路[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(1):140-145. [12]Munir H, McGettrick HM. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Disease: Risks and Rewards. Stem Cells Dev. 2015; 24(18):2091-2100.[13]Baharlou R, Ahmadi-Vasmehjani A, Faraji F, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in rheumatoid arthritis: Regulatory effects on peripheral blood mononuclear cells activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;47:59-69.[14]Vasilev G, Ivanova M, Ivanova-Todorova E, et al. Secretory factors produced by adipose mesenchymal stem cells downregulate Th17 and increase Treg cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatol Int. 2019;39(5):819-826.[15]Park KH, Mun CH, Kang MI, et al. Treatment of Collagen-Induced Arthritis Using Immune Modulatory Properties of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(6):1057-1072.[16]Greish S, Abogresha N, Abdel-Hady Z, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells as treatment of adjuvant rheumatoid arthritis in a rat model. World J Stem Cells. 2012;4(10):101-109.[17]Álvaro-Gracia JM, Jover JA, García-Vicuña R, et al. Intravenous administration of expanded allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in refractory rheumatoid arthritis (Cx611): results of a multicentre, dose escalation, randomised, single-blind, placebo- controlled phase Ib/IIa clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(1): 196-202.[18]Ghoryani M, Shariati-Sarabi Z, Tavakkol-Afshari J, et al. Amelioration of clinical symptoms of patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis following treatment with autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: A successful clinical trial in Iran. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:1834-1840.[19]Park EH, Lim HS, Lee S, et al. Intravenous Infusion of Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Phase Ia Clinical Trial. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7(9):636-642.[20]Shadmanfar S, Labibzadeh N, Emadedin M, et al. Intra-articular knee implantation of autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients with knee involvement: Results of a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1/2 clinical trial. Cytotherapy. 2018;20(4):499-506.[21]Uccelli A, de Rosbo NK. The immunomodulatory function of mesenchymal stem cells: mode of action and pathways. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1351:114-126.[22]Yan X, Cen Y, Wang Q. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experimental rheumatoid arthritis through microRNA-regulated IκB expression. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28915.[23]MacDonald GI, Augello A, De Bari C. Role of mesenchymal stem cells in reestablishing immunologic tolerance in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(9):2547-2557.[24]Toupet K, Maumus M, Luz-Crawford P, et al. Survival and biodistribution of xenogenic adipose mesenchymal stem cells is not affected by the degree of inflammation in arthritis. PLoS One. 2015;10(1):e0114962.[25]Nam Y, Jung SM, Rim YA, et al. Intraperitoneal infusion of mesenchymal stem cell attenuates severity of collagen antibody induced arthritis. PLoS One. 2018;13(6):e0198740.[26]Zhang L, Wang XY, Zhou PJ, et al. Use of immune modulation by human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to treat experimental arthritis in mice. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(5):2595-2607.[27]Baharlou R, Rashidi N, Ahmadi-Vasmehjani A, et al. Immunomodulatory Effects of Human Adipose Tissue-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on T Cell Subsets in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019;18(1):114-119.[28]Usha Shalini P, Vidyasagar JV, Kona LK, et al. In vitro allogeneic immune cell response to mesenchymal stromal cells derived from human adipose in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Immunol. 2017;314:18-25.[29]Liu R, Li X, Zhang Z, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells inhibited T follicular helper cell generation in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:12777.[30]Rosado MM, Bernardo ME, Scarsella M, et al. Inhibition of B-cell proliferation and antibody production by mesenchymal stromal cells is mediated by T cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(1):93-103.[31]Liu Y, Yin Z, Zhang R, et al. MSCs inhibit bone marrow-derived DC maturation and function through the release of TSG-6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;450(4):1409-1415.[32]Spaggiari GM, Moretta L. Cellular and molecular interactions of mesenchymal stem cells in innate immunity. Immunol Cell Biol. 2013; 91(1):27-31.[33]Shin TH, Kim HS, Kang TW, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-stem cells direct macrophage polarization and block inflammasome activation to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(12): e2524.[34]Zhang S, Chu WC, Lai RC, et al. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(12):2135-2140.[35]Feng Z, Zhai Y, Zheng Z, et al. Loss of A20 in BM-MSCs regulates the Th17/Treg balance in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):427. [36]Horai R, Saijo S, Tanioka H, et al. Development of chronic inflammatory arthropathy resembling rheumatoid arthritis in interleukin 1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 2000;191(2):313-320.[37]Lee K, Park N, Jung H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental arthritis via expression of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. PLoS One. 2018;13(2):e0193086.[38]Headland SE, Jones HR, Norling LV, et al. Neutrophil-derived microvesicles enter cartilage and protect the joint in inflammatory arthritis. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7(315):315ra190. [39]Chen Z, Wang H, Xia Y, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Cell-Derived miRNA-150-5p-Expressing Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mediated by the Modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J Immunol. 2018;201(8):2472-2482.[40]Cosenza S, Toupet K, Maumus M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells- derived exosomes are more immunosuppressive than microparticles in inflammatory arthritis. Theranostics.2018;8(5):1399-1410.[41]张中原,余丽梅,王信. 膝骨关节炎再生修复治疗新方法研究进展[J]. 实用医学杂志,2018,34(9):1561-1564. [42]Zaiss MM, Frey B, Hess A, et al. Regulatory T cells protect from local and systemic bone destruction in arthritis.J Immunol. 2010;184(12): 7238-7246.[43]Oshita K, Yamaoka K, Udagawa N, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit osteoclastogenesis through osteoprotegerin production. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(6):1658-1667.[44]Varin A, Pontikoglou C, Labat E, et al. CD200R/CD200 inhibits osteoclastogenesis: new mechanism of osteoclast control by mesenchymal stem cells in human. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e72831.[45]Garimella MG, Kour S, Piprode V, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prevent Systemic Bone Loss in Collagen-Induced Arthritis. J Immunol. 2015;195(11):5136-5148.[46]Chemel M, Brion R, Segaliny AI, et al. Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 and Transforming Growth Factor β1 Inhibit the Expression of the Proinflammatory Cytokine IL-34 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts. Am J Pathol. 2017;187(1):156-162.[47]Le Blanc K, Tammik C, Rosendahl K, et al. HLA expression and immunologic properties of differentiated and undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Hematol. 2003;31(10):890-896.[48]Sakaguchi Y, Sekiya I, Yagishita K, et al. Comparison of human stem cells derived from various mesenchymal tissues: superiority of synovium as a cell source. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(8):2521-2529.[49]De Bari C, Dell'Accio F, Karystinou A, et al. A biomarker-based mathematical model to predict bone-forming potency of human synovial and periosteal mesenchymal stem cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(1):240-250.[50]Melief SM, Zwaginga JJ, Fibbe WE, et al. Adipose tissue-derived multipotent stromal cells have a higher immunomodulatory capacity than their bone marrow-derived counterparts. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(6):455-463.[51]Abdelmawgoud H, Saleh A. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of mesenchymal and hematopoietic stem cells in a rheumatoid arthritis rat model. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2018;27(7):873-880.[52]Abd Elhalem SS, Haggag NZ, El-Shinnawy NA. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppress IL-9 in adjuvant-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity. 2018;51(1):25-34.[53]Yu Y, Yoon KA, Kang TW, et al. Therapeutic effect of long-interval repeated intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in DBA/1 mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019 Apr 8. doi: 10.1002/term.2861. [Epub ahead of print][54]Kim KW, Kim HJ, Kim BM, et al. Epigenetic modification of mesenchymal stromal cells enhances their suppressive effects on the Th17 responses of cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):208.[55]Yang Y, He X, Zhao R, et al. Serum IFN-γ levels predict the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in active rheumatoid arthritis. J Transl Med. 2018;16(1):165. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [5] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [6] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [7] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [8] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [9] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [10] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [11] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [12] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [13] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [14] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [15] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||