Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (25): 4018-4024.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1784
Previous Articles Next Articles
Curcumin regulates odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells through Wnt signaling pathway
- 1Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2Department of Rehabilitation, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Revised:2019-04-15Online:2019-09-08Published:2019-09-08 -
Contact:Zhou Jianwei, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Rehabilitation, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Chen Dongmei, Attending physician, Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Project of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. 2014SZ0235 (to XLL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Dongmei, Xu Lili, Zhou Jianwei.
share this article
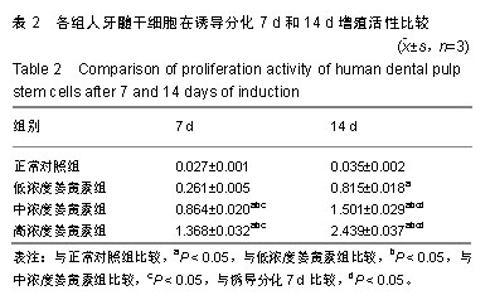
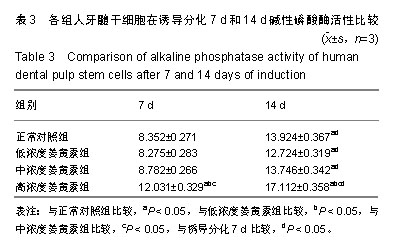
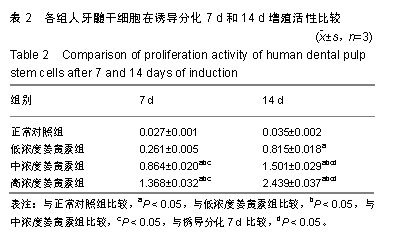
2.1 姜黄素对人牙髓干细胞增殖活力的影响 与正常对照组比较,诱导分化7 d后,中、高浓度姜黄素组细胞的增殖活性升高,诱导分化14 d后,低、中、高浓度姜黄素组细胞的增殖活性均升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与低浓度姜黄素组比较,诱导分化7 d和14 d后,中、高浓度姜黄素组细胞的增殖活性升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与中浓度姜黄素组比较,诱导分化7 d和14 d后,高浓度姜黄素组细胞的增殖活性升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与诱导分化7 d比较,诱导分化14 d低、中、高浓度姜黄素组细胞的增殖活性升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表2,提示姜黄素可提高人牙髓干细胞增殖活性,且作用呈时间和剂量依赖性。"
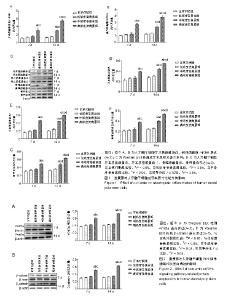
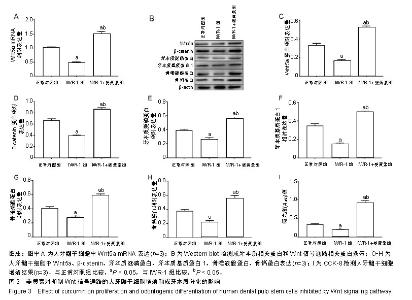
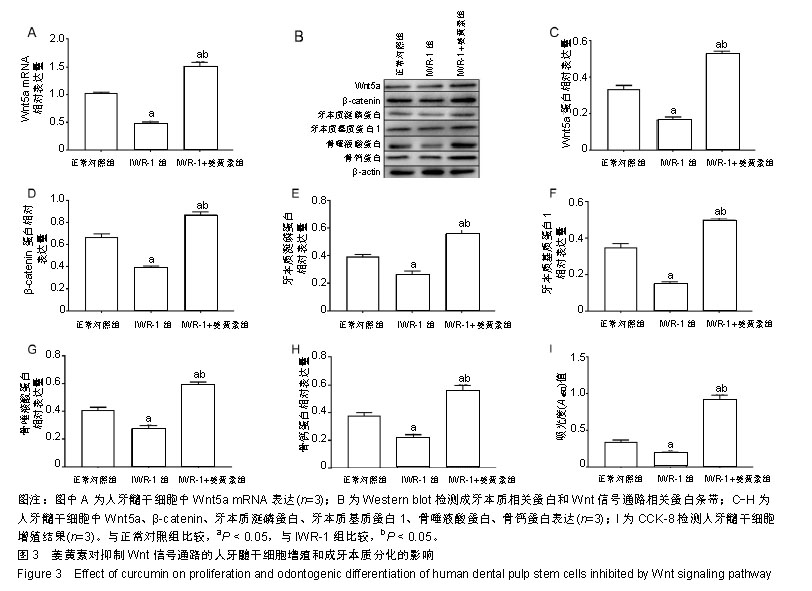
2.3 姜黄素对人牙髓干细胞成牙本质分化能力的影响 RT-qPCR检测结果显示,诱导分化7 d后,高浓度姜黄素组细胞的牙本质涎磷蛋白、碱性磷酸酶mRNA表达高于其他3组,诱导分化14 d后,中、高浓度姜黄素组细胞的牙本质涎磷蛋白、碱性磷酸酶mRNA表达高于其他2组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与诱导分化7 d比较,中、高浓度姜黄素组诱导分化14 d后牙本质涎磷蛋白、碱性磷酸酶mRNA表达升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 Western blot 检测结果也显示,诱导分化7 d后,高浓度姜黄素组细胞的牙本质涎磷蛋白、牙本质基质蛋白1、骨唾液酸蛋白和骨钙蛋白表达高于其他3组,诱导分化14 d后,中、高浓度姜黄素组细胞的牙本质涎磷蛋白、牙本质基质蛋白1、骨唾液酸蛋白和骨钙蛋白表达高于其他2组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与诱导分化7 d比较,中、高浓度姜黄素组细胞诱导分化14 d后牙本质涎磷蛋白、牙本质基质蛋白1、骨唾液酸蛋白和骨钙蛋白表达升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图1。以上结果提示姜黄素对人牙髓干细胞的成牙本质分化发挥促进作用。 2.4 姜黄素对人牙髓干细胞Wnt信号通路相关蛋白表达的影响 Western blot 检测结果显示,诱导分化7,14 d后,高浓度姜黄素组细胞中Wnt5a和β-catenin蛋白的表达高于其他3组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与诱导分化7 d比较,高浓度姜黄素组诱导分化14 d后细胞中Wnt5a和β-catenin蛋白的表达升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图2。以上结果提示姜黄素可促进人牙髓干细胞Wnt信号通路相关蛋白的表达。 2.5 姜黄素对抑制Wnt信号通路的人牙髓干细胞增殖和成牙本质分化的影响 为了进一步明确Wnt信号通路在姜黄素促进人牙髓干细胞增殖和成牙本质分化中的作用,应用Wnt信号通路抑制剂处理人牙髓干细胞,RT-qPCR和Western blot检测结果显示,与正常对照组比较,IWR-1组人牙髓干细胞中Wnt5a mRNA和Wnt5a、β-catenin、牙本质涎磷蛋白、牙本质基质蛋白1、骨唾液酸蛋白及骨钙蛋白的表达降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);IWR-1+姜黄素组人牙髓干细胞中Wnt5a mRNA和Wnt5a、牙本质涎磷蛋白、牙本质基质蛋白1、骨唾液酸蛋白及骨钙蛋白的表达高于IWR-1组和正常对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。CCK-8检测结果显示,与正常对照组比较,IWR-1组人牙髓干细胞增殖活性降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与IWR-1组比较,IWR-1+姜黄素组人牙髓干细胞增殖活性增高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图3。以上结果提示姜黄素通过激活Wnt信号通路促进人牙髓干细胞的增殖与成牙本质分化。"

| [1]Suneelkumar C, Subha A, Gogala D. Effect of Preoperative Corticosteroids in Patients with Symptomatic Pulpitis on Postoperative Pain after Single-visit Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Endod. 2018;44(9):1347-1354.[2]Shirvani A, Shamszadeh S, Eghbal MJ, et al. Effect of preoperative oral analgesics on pulpal anesthesia in patients with irreversible pulpitis-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig. 2017;21(1):43-52.[3]Yang X, Li L, Xiao L, et al. Recycle the dental fairy's package: overview of dental pulp stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):347.[4]Kaneko T, Gu B, Sone PP, et al. Dental Pulp Tissue Engineering Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells: a Review with a Protocol. Stem Cell Rev. 2018;14(5):668-676.[5]Graham CM, Kremer KL, Koblar SA, et al. Dental Pulp Stem Cells - Exploration in a Novel Animal Model: the Tasmanian Devil (Sarcophilus harrisii). Stem Cell Rev. 2018;14(4):500-509.[6]Hassan NT, AbdelAziz NA. Oral Mucosal Stem Cells, Human Immature Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Hair Follicle Bulge Stem Cells as Adult Stem Cells Able to Correct Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13(5):356-361.[7]Anitua E, Troya M, Zalduendo M. Progress in the use of dental pulp stem cells in regenerative medicine. Cytotherapy. 2018;20(4):479-498.[8]杨雪超,李晓宁,王伟东,等.牙本质支架促进人牙髓干细胞体外增殖与分化能力的研究[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2015,25(6):342-347.[9]杨鑫,李思洁,赵玮. Wnt信号通路在调控牙髓干细胞多向分化及炎症损伤修复中的作用[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2018,45(3):286-290.[10]陈婵婵,凌均棨. Wnt信号通路对牙齿发育和牙囊成骨向分化的调控作用[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2015,25(3):175-178.[11]Romanos GE. Biomolecular Cell-Signaling Mechanisms and Dental Implants: A Review on the Regulatory Molecular Biologic Patterns Under Functional and Immediate Loading. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31(4):939-951.[12]McCubrey JA, Lertpiriyapong K, Steelman LS, et al. Effects of resveratrol, curcumin, berberine and other nutraceuticals on aging, cancer development, cancer stem cells and microRNAs. Aging (Albany NY). 2017;9(6):1477-1536.[13]张庆美,李方正,姜忠玲,等.姜黄素对猪骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和成脂分化的影响[J].解剖学报, 2014,45(6):793-799.[14]陈飞,王皓香,向鑫,等.姜黄素对神经干细胞Wnt/β-catenin信号通路表达影响的离体研究[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2014,36(8):764-768.[15]顾巧丽,蔡燕,黄晨,等.姜黄素调控大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(27):5057-5061.[16]Chauhan S, 王盈. 用于治疗牙周炎的载姜黄素可生物降解交联明胶薄膜的研制[J].中国医药工业杂志,2018,49(5):593.[17]朱柯,潘芸,杨洋,等.姜黄素对牙周炎大鼠牙周支持组织炎症性破坏的保护作用[J].广东医学,2017,38(3):358-361.[18]刘明月,胡伟平,王晓芬,等.低浓度β-甘油磷酸钠培养牙髓干细胞向成牙本质细胞分化及相关因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(41): 6688-6693. [19]梁静,王君,唐传玲,等.低氧对H2O2预处理MC3T3-E1增殖和成骨分化功能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(4): 505-511. [20]Phan M, Conte F, Khandelwal KD, et al. Tooth agenesis and orofacial clefting: genetic brothers in arms. Hum Genet. 2016;135(12):1299-1327.[21]Mead B, Logan A, Berry M, et al. Concise Review: Dental Pulp Stem Cells: A Novel Cell Therapy for Retinal and Central Nervous System Repair. Stem Cells. 2017;35(1):61-67.[22]Nuti N, Corallo C, Chan BM, et al. Multipotent Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells: a Literature Review. Stem Cell Rev. 2016; 12(5):511-523.[23]Ledesma-Martínez E, Mendoza-Núñez VM, Santiago-Osorio E. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Dental Pulp: A Review. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:4709572.[24]Shehzad A, Lee YS. Molecular mechanisms of curcumin action: signal transduction. Biofactors. 2013;39(1):27-36.[25]席晅,任小琼.姜黄素通过PI3K/AKT信号通路调控神经干细胞增殖和凋亡实验研究[J].新中医,2016,48(3): 217-221.[26]马晓晓,王春满,张高龙,等.姜黄素通过抑制糖皮质激素受体促进大鼠神经干细胞增殖[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2015,29(02):202-207.[27]刘剑锋,朱平,马守原,等.姜黄素通过血红素加氧酶-1信号通路促进脂肪源干细胞增殖和旁分泌研究[J].中国心血管杂志, 2015,20(3):199-203.[28]邬培红,华子义,赵秀娟.姜黄素促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化中活性氧表达变化研究[J].中国医药导报, 2013,10(18):24-26,29.[29]陈飞,王皓香,向鑫,等.姜黄素对神经干细胞Wnt/β-catenin信号通路表达影响的离体研究[J].第三军医大学学报, 2014,36(8):764-768.[30]向鑫,袁继超,陈飞,等.姜黄素诱导内源性神经干细胞促进大鼠脊髓损伤后功能修复[J].第三军医大学学报, 2014,36(9):883-887.[31]Mah AT, Yan KS, Kuo CJ. Wnt pathway regulation of intestinal stem cells. J Physiol. 2016;594(17):4837-4847.[32]Yuan Z, Li Q, Luo S, et al. PPARγ and Wnt Signaling in Adipogenic and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;11(3):216-225.[33]Sun TJ, Tao R, Han YQ, et al. Therapeutic potential of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway pre-activated for the treatment of diabetic wounds. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(17):2460-2464.[34]Zhou Y, Kipps TJ, Zhang S. Wnt5a Signaling in Normal and Cancer Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:5295286.[35]Zhang X, Guo J, Zhou Y, et al. The roles of bone morphogenetic proteins and their signaling in the osteogenesis of adipose-derived stem cells. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014;20(1):84-92.[36]Katoh M, Katoh M. STAT3-induced WNT5A signaling loop in embryonic stem cells, adult normal tissues, chronic persistent inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis and cancer (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2007;19(2):273-278.[37]柳鑫,郭倩,肖燕,等.Wnt5a对牙髓干细胞成骨/成牙本质向分化的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2018,28(6):311-320.[38]包幸福,倪宇昕,李莹,等. Wnt5a在小鼠牙骨质发育中的表达特点及其对成牙骨质细胞分化的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2018,44(3): 461-465,693. |
| [1] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [2] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [3] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [4] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [5] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [6] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [7] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [8] | Ye Haimin, Ding Linghua, Kong Weihao, Huang Zutai, Xiong Long. Role and mechanism of hierarchical microchanneled bone scaffolds in promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 621-625. |
| [9] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [10] | Zhou Wu, Wang Binping, Wang Yawen, Cheng Yanan, Huang Xieshan. Transforming growth factor beta combined with bone morphogenetic protein-2 induces the proliferation and differentiation of mouse MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3630-3635. |
| [11] | Li Xinping, Cui Qiuju, Zeng Shuguang, Ran Gaoying, Zhang Zhaoqiang, Liu Xianwen, Fang Wei, Xu Shuaimei. Effect of modification of β-tricalcium phosphate/chitosan hydrogel on growth and mineralization of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3493-3499. |
| [12] | Li Zhen, Huang Yonghui, Sun Jifu, Sun Haitao. Role and mechanism of focal adhesion kinase in inducing osteogenic differentiation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 165-171. |
| [13] | Yu Chengshuai, Du Gang, Pang Shenning, Lao Shan. Chemerin, a pro-inflammatory adipokine, regulates chondrocyte proliferation and metabolism by increasing production of nitric oxide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 258-263. |
| [14] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [15] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||