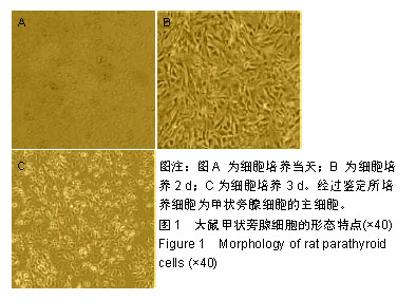
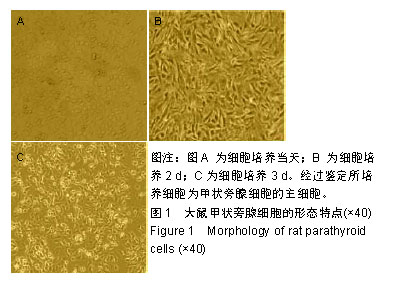
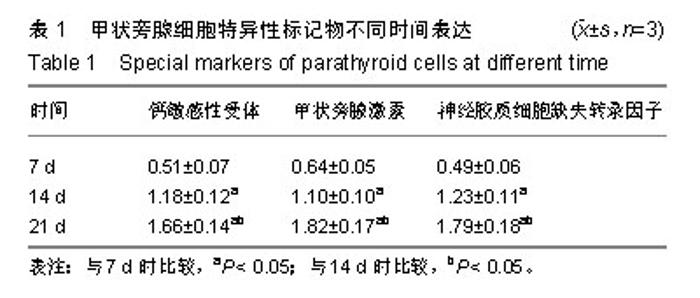
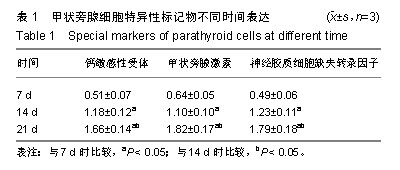
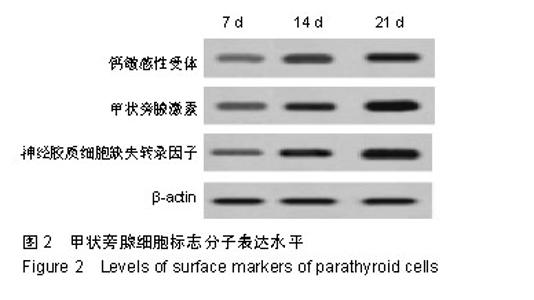
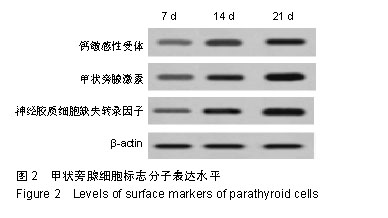
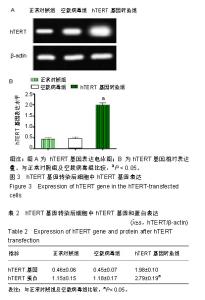
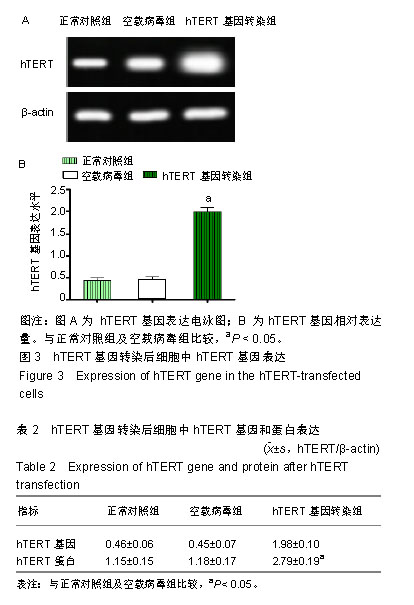
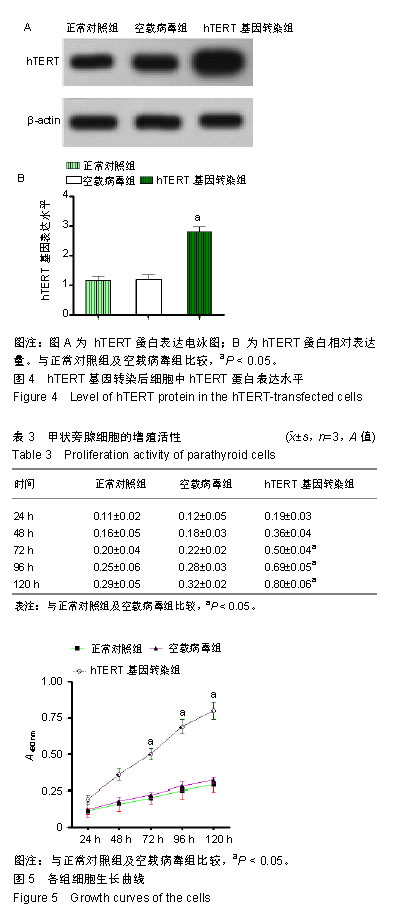
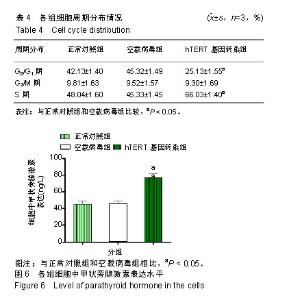
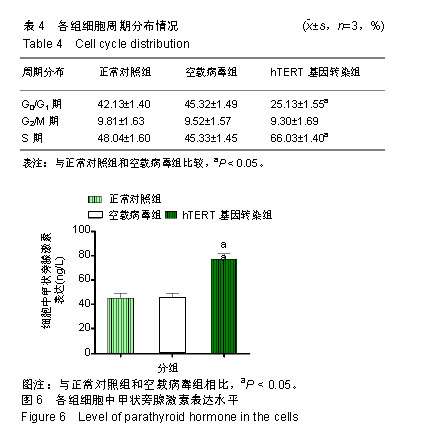
| [1]陈佳,霍景山.甲状旁腺功能减退症的非手术治疗进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2014,8(19):81-85.[2]全婷婷,王鸥,聂敏,等.甲状旁腺功能减退症发病机制的遗传学进展[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2017,10(2):186-193.[3]张凯凯,刘晋闽.甲状腺功能减退致骨质疏松症的机制及治疗进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(6):837-840.[4]刘洋.甲状腺癌全切术后甲状旁腺功能减退及血钙变化规律[D].吉林大学, 2015.[5]Lourida I,ThompsoncoonJ,Dickens CM,etal. ParathyroidHormone, Cognitive Function and Dementia:A Systematic Review.Plos One. 2015;10(5):e0127574.[6]Russo R,Ruospo M,Cozzolino M,et al.Effects of vitamin D on parathyroid hormone and clinical outcomes in peritoneal dialysis:a narrative review. J Nephrol. 2014 Oct; 27(5):483-494.[7]Kakava K,Tournis S,Papadakis G,et al. Postsurgical Hypoparathyroidism: A Systematic Review. Vivo. 2016;30(3):171.[8]徐德全,代文杰.甲状旁腺激素替代疗法治疗甲状旁腺功能减退研究进展[J].中国实用外科杂志,2014,34(5):459-461.[9]孙海晨,刘爽,崔叶青,等.成人甲状旁腺细胞的培养方法及其分泌功能研究[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2014,21(9):1120-1123.[10]赵越,王晓辉,刘爽,等.成人甲状旁腺细胞的培养和鉴定[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2017,24(1):32-36.[11]赵越.甲状旁腺功能减退症的治疗现状[J].医学研究生学报, 2016, 29(1):104-108.[12]Choi MJ,Cho KH,Lee S,et al.hTERT mediates norepinephrine- induced Slug expression and ovarian cancer aggressiveness. Oncogene.2015; 34(26):3402-3412.[13]Guo W,Lu J,Dai M,etal.Transcriptionalcoactivator CBP upregulateshTERT expression and tumor growth and predicts poor prognosis in human lung cancers.Oncotarget. 2014;5(19): 9349-9361.[14]Schneiderstock R,Emrich T,Peters B,etal.Analysis of human telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA (hTERT) expression in myxoidliposarcomas using Light Cycler real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase- polymerase chain reaction. Electrophoresis. 2015;22(6):1098-1101.[15]Zhao Q,Zhai YX,LiuH Q,et al.MicroRNA-491-5p suppresses cervical cancer cell growth by targeting hTERT.Oncology Reports. 2015;34(2):979.[16]于宏建,赵杨,赵世铭,等.hTERT基因沉默对乳腺癌细胞生物学特性及COX-2表达的影响[J].中国实验诊断学, 2016,20(11):1817-1821.[17]秦玲.hTERT基因修饰神经干细胞移植修复大鼠脊髓损伤[J].医学研究杂志,2016,45(2):99-104.[18]Mitsui T,Narumi S,Inokuchi M,et al.Comprehensive next-generation sequencing analyses of hypoparathyroidism: identification of novel GCM2 mutations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Nov;99(11): E2421-2428.[19]阮莹,侯佳宁,刘仁斌,等.条件重编辑共培养技术体外培养人甲状旁腺细胞的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2018,35(9):1641-1643.[20]李佳丽,赵瑞力.干细胞向甲状旁腺细胞的分化及在甲状旁腺功能减退中的研究进展[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版), 2018,8(3): 168-171.[21]陈宇嘉.补脾肾活血方对慢性肾衰鼠甲状旁腺细胞增生及凋亡影响[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2015:1-41.[22]赵越,罗斌.水凝胶化成人甲状旁腺细胞形态和功能的观察[J].国际外科学杂志,2016,43(2):85-87,封3.[23]Li SH,Wang DD,Xu YJ,et al.ExogenoushTERT gene transfected endothelial progenitor cells from bone marrow promoted angiogenesis in ischemic myocardium of rats.Int J ClinExp Med. 2015;8(8):14447-14453.[24]Liu AQ,GeL Y,Lu XL,et al.Silencing of the hTERT Gene by shRNA Inhibits Colon Cancer SW480 Cell Growth In Vitro and In Vivo. Plos One.2014;9(9):e107019.[25]刘志平,沙翔垠,王智崇,等.转染hTERT基因对人角膜内皮细胞增殖及功能维持的影响[J].广东医学,2016,37(7):965-969.[26]尹博文.慢病毒介导转染hTERT基因建立永生化树鼩小肠上皮细胞系[D].北京协和医学院中国医学科学院,2017:1-71.[27]莫霄.hTERT基因转染大鼠雪旺细胞的实验研究[D].大连:大连医科大学, 2013.[28]吴灵芝,李水彬,程刚卫,等.hTERT基因转染对人神经元活力的影响[J].赣南医学院学报,2014,34(2):170-173.[29]Ling-Zhao MO,De-Quan LI,Yu X,et al.Effect of hTERT Gene Expression on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Cervical Cancer Caski Cells by Lentivirus-Mediated Small Interfering RNA.J Int Transl Med 2016;4(2):114-120.[30]李佳丽,赵瑞力.干细胞向甲状旁腺细胞的分化及在甲状旁腺功能减退中的研究进展[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版), 2018,8(3): 168-171. |