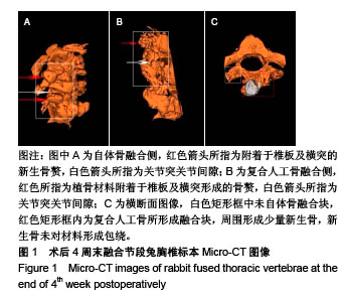
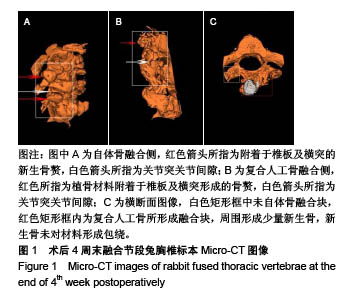
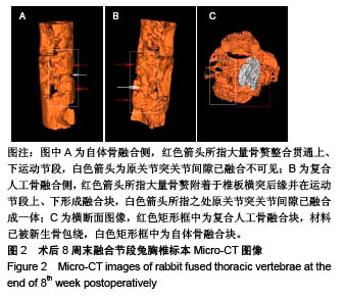
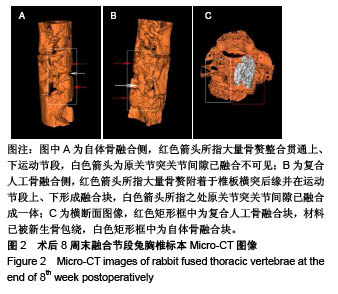
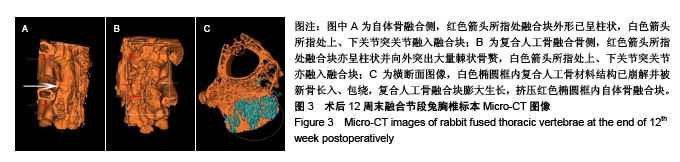
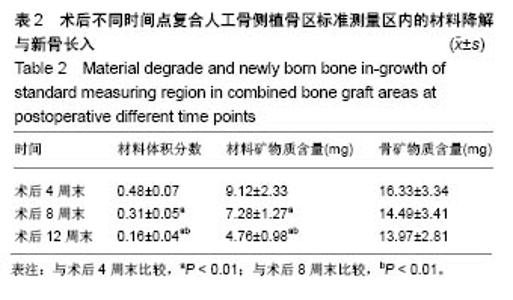
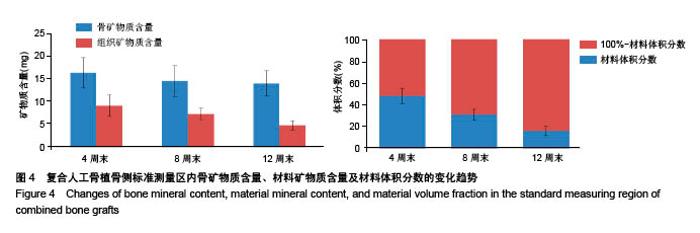
| [1]Bohner M,Tadier S,van Garderen N,et al.Synthesis of spherical calcium phosphate particles for dental and orthopedic applications.Biomatter.2013;3(2):e25103. doi:10.4161/biom.25103.[2]Abdullah KG,Steinmetz MP,Benzel EC,et al.The state of lumbar fusion extenders. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(20): E1328-1334. [3]Kadam A,Millhouse PW,Kepler CK,et al.Bone substitutes and expanders in Spine Surgery: A review of their fusion efficacies. Int J Spine Surg.2016;10:33. [4]Fillingham Y,Jacobs J.Bone grafts and their substitutes. Bone Joint J.2016;98-B(1 Suppl A):6-9. [5]张志达,江晓兵,沈耿杨,等.磷酸钙及硫酸钙支架在骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(8):1203-1209. [6]López-Álvarez M,Pérez-Davila S,Rodríguez-Valencia C,et al.The improved biological response of shark tooth bioapatites in a comparative in vitro study with synthetic and bovine bone grafts. Biomed Mater.2016;11(3):035011. [7]Buser Z,Brodke DS,Youssef JA,et al.Synthetic bone graft versus autograft or allograft for spinal fusion: a systematic review.J Neurosurg Spine.2016;25(4):509-516.[8]Barbanti BG,Griffoni C,Nataloni A,et al.Biomaterials as bone graft substitutes for spine surgery: from preclinical results to clinical study.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents.2017;31(4 suppl 1):167-181. [9]Pulyala P,Singh A,Dias-Netipanyj MF,et al.In-vitro cell adhesion and proliferation of adipose derived stem cell on hydroxyapatite composite surfaces.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;75:1305-1316. [10]Oliveira HL,Da Rosa WLO,Cuevas-Suárez CE,et al. Histological Evaluation of Bone Repair with Hydroxyapatite: A Systematic Review.Calcif Tissue Int.2017;101(4):341-354. [11]Fathima H,Harish.Osteostimulatory effect of bone grafts on fibroblast cultures.J Nat Sci Biol Med.2015;6(2):291-294. [12]Dahabreh Z,Panteli M,Pountos I,et al.Ability of bone graft substitutes to support the osteoprogenitor cells: An in-vitro study.World J Stem Cells.2014;6(4):497-504.[13]Seebach C,Schultheiss J,Wilhelm K,et al.Comparison of six bone-graft substitutes regarding to cell seeding efficiency, metabolism and growth behaviour of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in vitro.Injury.2010;41(7):731-738. [14]Barradas AM,Monticone V,Hulsman M,et al.Molecular mechanisms of biomaterial-driven osteogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stromal cells.Integr Biol(Camb). 2013;5(7):920-931. [15]Van Hoff C,Samora JB,Griesser MJ,et al.Effectiveness of ultraporous β-tricalcium phosphate (vitoss) as bone graft substitute for cavitary defects in benign and low-grade malignant bone tumors. Am J Orthop(Belle Mead NJ). 2012; 41(1):20-23. [16]Hernigou P,Dubory A,Pariat J,et al. Beta-tricalcium phosphate for orthopedic reconstructions as an alternative to autogenous bone graft.Morphologie.2017;101(334):173-179. [17]Ofluoglu AE,Erdogan U,Aydogan M,et al.Anterior cervical fusion with interbody cage containing beta-tricalcium phosphate: Clinical and radiological results.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2017;51(3):197-200. [18]Lechner R,Putzer D,Liebensteiner M,et al.Fusion rate and clinical outcome in anterior lumbar interbody fusion with beta-tricalcium phosphate and bone marrow aspirate as a bone graft substitute. A prospective clinical study in fifty patients.Int Orthop.2017;41(2):333-339.[19]Yamagata T,Naito K,Arima H,et al.A minimum 2-year comparative study of autologous cancellous bone grafting versus beta-tricalcium phosphate in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion using a rectangular titanium stand-alone cage.Neurosurg Rev.2016;39(3):475-482.[20]Kong S, Park JH, Roh SW. A prospective comparative study of radiological outcomes after instrumented posterolateral fusion mass using autologous local bone or a mixture of beta-tcp and autologous local bone in the same patient.Acta Neurochir(Wien).2013;155(5):765-770. [21]Feng SW,Chang MC,Chou PH,et al.Implantation of an empty polyetheretherketone cage in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: a prospective randomised controlled study with 2 years follow-up. Eur Spine J.2018;27(6):1358-1364. [22]周骁,钱玉芬.组织工程骨修复骨缺损的稳定性:材料降解与新骨形成[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(12):1938-1942. [23]Tanaka T,Komaki H,Chazono M,et al.Basic research and clinical application of beta-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP). Morphologie.2017;101(334):164-172. [24]Kato E,Lemler J,Sakurai K,et al.Biodegradation property of beta-tricalcium phosphate-collagen composite in accordance with bone formation: a comparative study with Bio-Oss Collagen® in a rat critical-size defect model.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2014;16(2):202-211. [25]Chen G,Li J,Li X,et al.Giant cell tumor of axial vertebra: surgical experience of five cases and a review of the literature. World J Surg Oncol.2015;13:62. [26]李熙,施毅,俞维川,等.β-磷酸三钙在跟骨塌陷性骨折手术治疗中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(8):885-886. [27]Rolvien T,Barvencik F,Klatte TO,et al.ß-TCP bone substitutes in tibial plateau depression fractures.Knee. 2017;24(5): 1138-1145.[28]Eder C,Meissner J,Bretschneider W,et al.Analysis of a β-TCP bone graft extender explanted during revision surgery after 28 months in vivo.Eur Spine J.2014;23 Suppl 2:157-160. [29]毛文文,茹江英.羟基磷灰石类陶瓷在骨组织工程中的研究与更广泛应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(30):4855-4863. [30]Matsunaga A,Takami M,Irié T,et al.Microscopic study on resorption of β-tricalcium phosphate materials by osteoclasts. Cytotechnology.2015;67(4):727-732. [31]Pförringer D,Harrasser N, Mühlhofer H, et al. Osteoinduction and -conduction through absorbable bone substitute materials based on calcium sulfate: in vivo biological behavior in a rabbit model. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2018;29(2):17. |