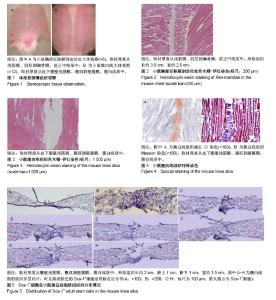
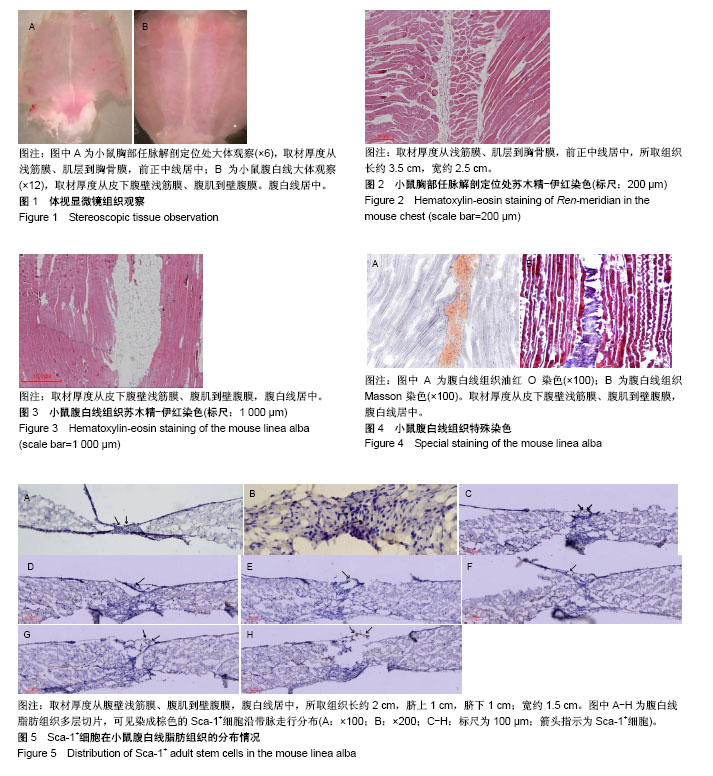
| [1] 温昊天,隋华,李琦,等.干细胞与中医理论关系的思考[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2017,32(4):1422-1424.[2] 袁红豆,王勇.论中医先天之精的生生之用基础(元气、经络)的微观形 式——干细胞调控[J]. 四川中医,2017,35(3):25-27.[3] 赵春华,赵洋洋,韩钦,等. 从亚全能干细胞角度解读远古医学[J]. 医学争鸣, 2013,4(2):1-5.[4] 张建新. 经络是干细胞系——兼论物种的起源与干细胞系的进化[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志,2001,7(4):17-20.[5] 张建新.不同种类干细胞巢的有序分布构成中医经络系统[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2006,10(21):189-192.[6] 张建新.待验证的揭示人体干细胞分布与分类的中医经络学说[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志,2004,10(6):13-15.[7] 张建新. 从进化论角度探讨干细胞分化及其干细胞巢分布规律[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(50):7571-7578.[8] 陈军德.经络“营阴阳”作用与生命活动连续性的运行及调控[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2011,17(9):1024-1027.[9] 陈军德.经络运行气血作用的机制与医学模型创建[J].中国针灸, 2010, 30(4): 296-300.[10] 林泰骄,叶声,林超岱.任脉与“腹白线”关系研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2012,27(7):1750-1752.[11] 薄智云.腹针疗法[M]. 北京:中国中医药出版社,2010:38.[12] 李鼎,肖少卿,杨介宾,等.经络学[M].上海:上海科学出版社, 1984: 78-83.[13] 胡元亮,刘钟杰.小动物针灸技法手册[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2009: 239-242.[14] 马迎民,徐德成,范吉平.中医“肾精化生元气和脏腑之气”的现代医学机制[J]. 中医杂志,2016,57(12):1000-1004.[15] 徐德成,马迎民,范吉平. 中医“肾精”的现代医学内涵[J].中医杂志, 2017, 58(22):1891-1897.[16] 张金生,张宝霞.“肾精”与“干细胞”的同一性认识[J].中华中医药学刊, 2018, 36(2):326-328.[17] 黄中迪,高建东. 中医肾精与干细胞关系辨识[J].山东中医杂志, 2014, 33(12):957-959.[18] 牛溪苑. 肾藏象现代研究的理论总结[D].咸阳:陕西中医学院, 2014: 1-23.[19] 王志同,乔玉秋,李壮,等.干细胞循经穴位法移植治疗糖尿病足临床研究[J].中国中医急症,2011,20 (9):1384-1386.[20] 李晓滨,曾园山,陈土玲.督脉电针与神经+细胞移植联合应用促进脊髓全横断大鼠后肢运动功能的恢复[J].解剖学报, 2004,35(6) :58-60.[21] 杨军,褚春,谭芳.干细胞心肌移植和气血经络的关系[C]. 广州:第五届国际络病学大会论文集,2009.[22] 杨军,褚春,谭芳.骨髓间充质干细胞心脏移植微环境和经络气血的关系[J]. 医学信息(内•外科版) ,2009,22(11):1024-1027.[23] 孙洁. 电针结合人胚胎间充质干细胞移植对酒精性肝纤维化模型大鼠干预的研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2012:1-15.[24] 饶晓丹.电针任脉对脑缺血大鼠神经干细胞增殖与分化的影响[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2006:1-25.[25] 杨卓欣,于海波,饶晓丹,等.任脉电针对脑缺血大鼠侧脑室下区神经干细胞增殖与分化的影响[J]. 中医杂志,2006,47(6):429-432.[26] 刁利红,于海波,皮敏,等. 电针任脉和肌肉注射碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对脑缺血模型大鼠侧脑室下区原位神经干细胞增殖的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(8):1435-1439.[27] 刘明发,庄明华,骆健明,等. 缺血缺氧性脑损伤对新生鼠脑内神经干细胞的影响[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2006,4(3):216-218.[28] 庄明华,骆健明,刘明发,等. 针刺任脉、督脉及膀胱经促进新生儿缺血缺氧性脑病鼠模型脑内神经干细胞增殖[J].中华神经医学杂志,2006,5(7): 686-688.[29] 王居易. 经络医学概要[M]. 北京:中国中医药出版社, 2016:1-12.[30] 高爽.关于我国现行中、西医学现状与发展的几点浅见[J].中华中医药杂志, 2016,31(10):3878-3880.[31] 高黎.基于概念隐喻与数据挖掘的中医人体之气研究[D]. 北京:北京中医药大学, 2018:1-24.[32] 王睿.任脉腧穴命名文化与临床意义[D]. 沈阳:辽宁中医药大学, 2015: 1-20.[33] 马宁.任脉、督脉的胚胎发生学探讨[J].山东中医药大学学报, 2017, 41(5): 412-416.[34] 孙春全,李金玲,杨继国.任脉灸疗法初探[J]. 山东中医杂志, 2017, 36(8): 669-671.[35] 王君琳.任脉的古今文献研究[D]. 南宁:广西中医药大学, 2017:1-32.[36] 赵春华.干细胞原理技术与临床[M].北京:化学化工出版社, 2006:10-200.[37] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12):4279-4295.[38] 陈盼盼,张丽华,董为人,等.脂肪组织源性干细胞分步诱导分化为神经元样细胞[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2011,31(3):512-517.[39] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2): 211-228.[40] Safford KM, Hicok KC, Safford SD, et al. Neurogenic differentiation of murine and human adipose-derived stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;294(2):371-379.[41] Cousin B, André M, Arnaud E, et al. Reconstitution of lethally irradiated mice by cells isolated from adipose tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;301(4):1016-1022.[42] Chai Y, Liu F, Li Q, et al. BMP-9 induces rabbit adipose-derived stem cells to differentiation into osteoblasts via BMP signaling pathway. Anal Quant Cytopathol Histpathol. 2013;35(3):171-177.[43] Ogawa R, Mizuno H, Watanabe A, et al. Adipogenic differentiation by adipose-derived stem cells harvested from GFP transgenic mice-including relationship of sex differences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;319(2):511-517.[44] Ong WK, Tan CS, Chan KL, et al. Identification of specific cell-surface markers of adipose-derived stem cells from subcutaneous and visceral fat depots. Stem Cell Reports. 2014;2(2):171-179.[45] 张文韬,尼茹帕玛•舍弗德.富有潜力的干细胞[J].世界科学, 2012,5(15): 24-29.[46] Welm BE, Tepera SB, Venezia T, et al. Sca-1(pos) cells in the mouse mammary gland represent an enriched progenitor cell population. Dev Biol. 2002;245(1):42-56.[47] 刘达,陈平.干细胞抗原-1(Sca-1)在干/祖细胞自我更新和分化中的作用研究[J].医学信息(中旬刊),2011,24(9):4640-4641. |