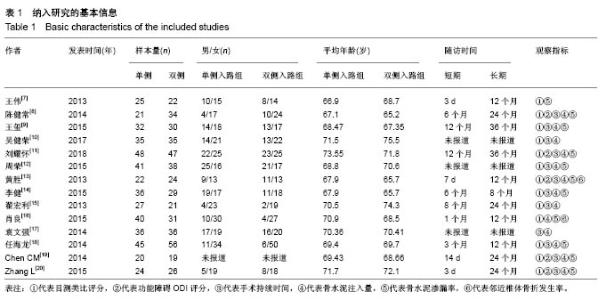
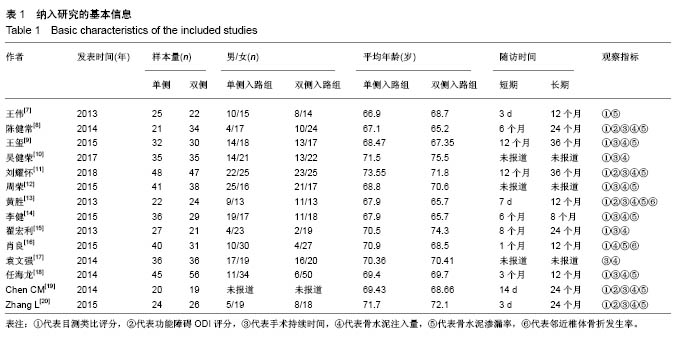
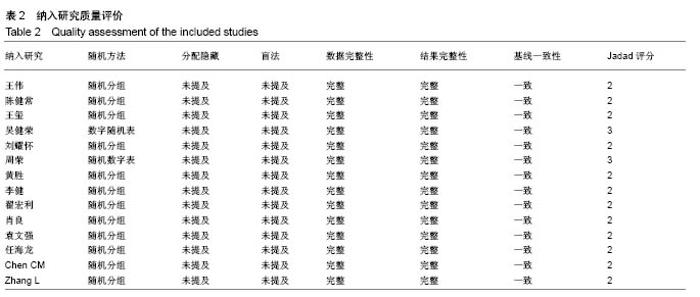
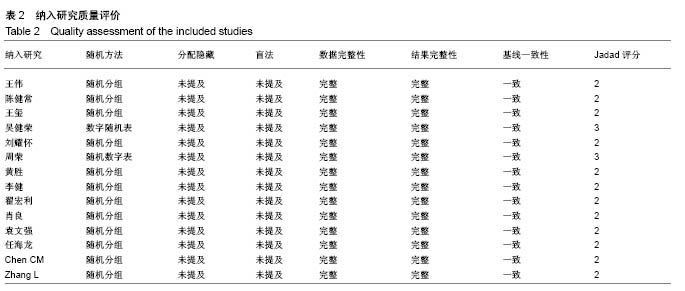
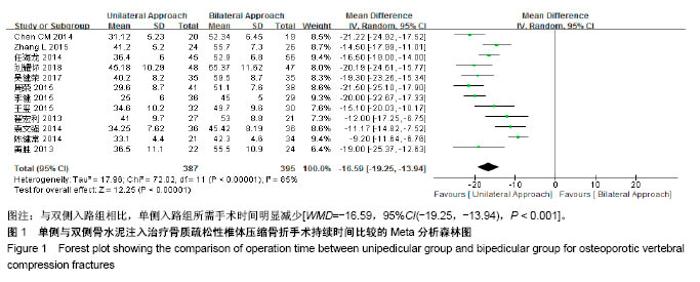
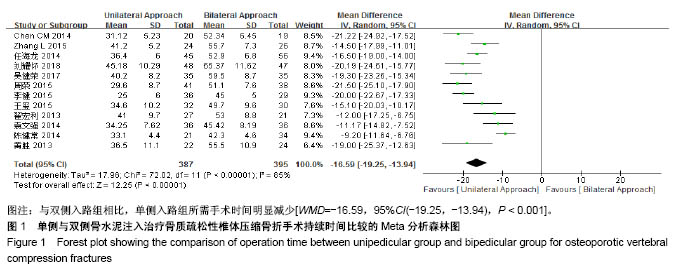
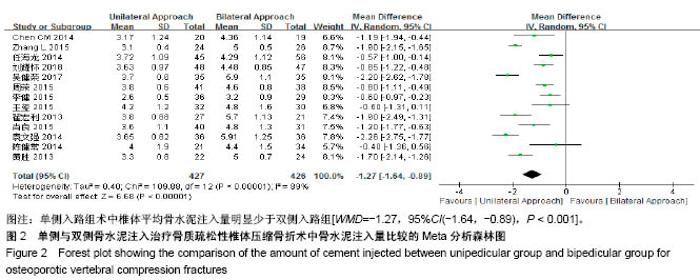
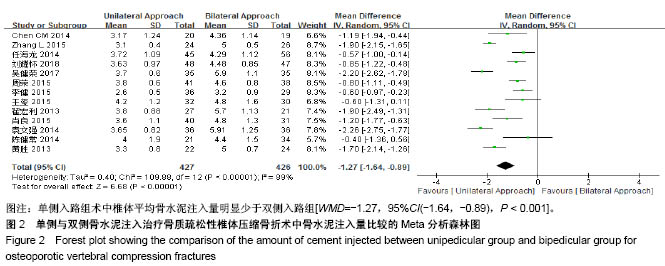
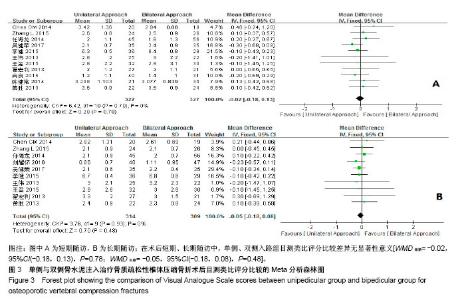
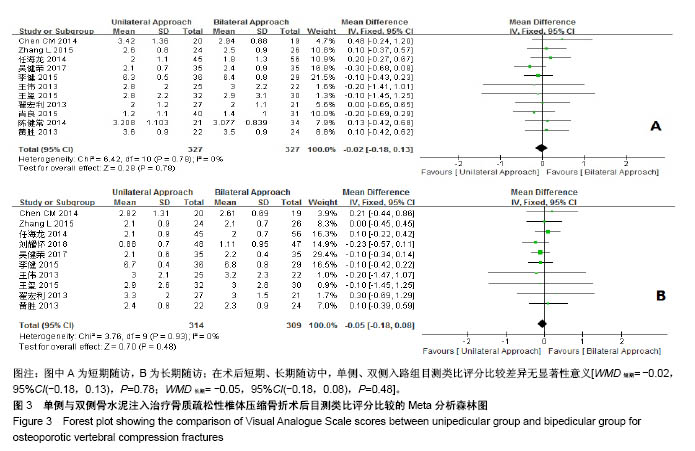
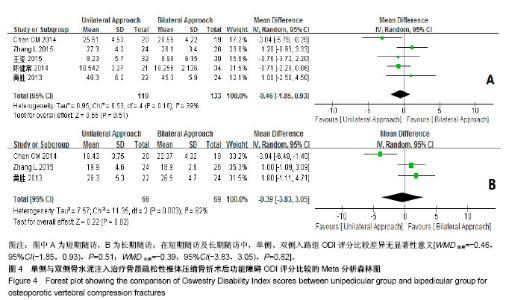
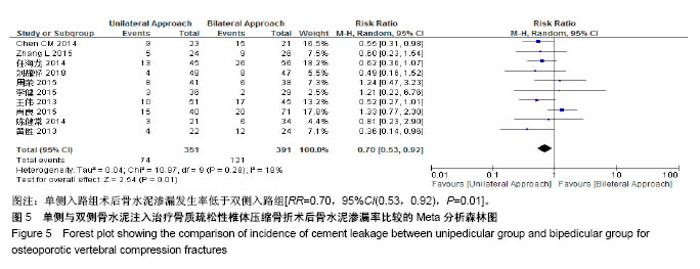
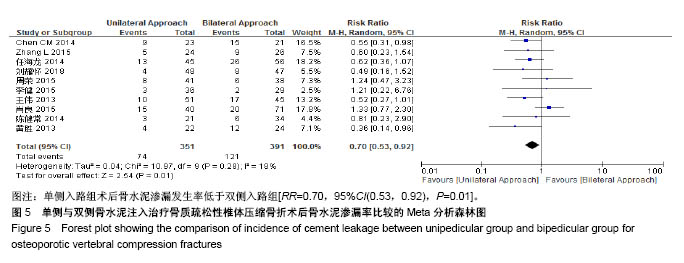
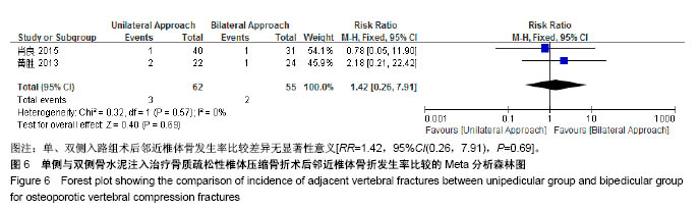
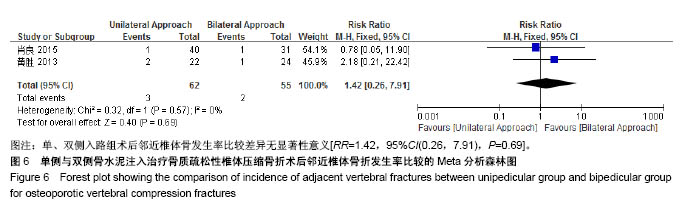
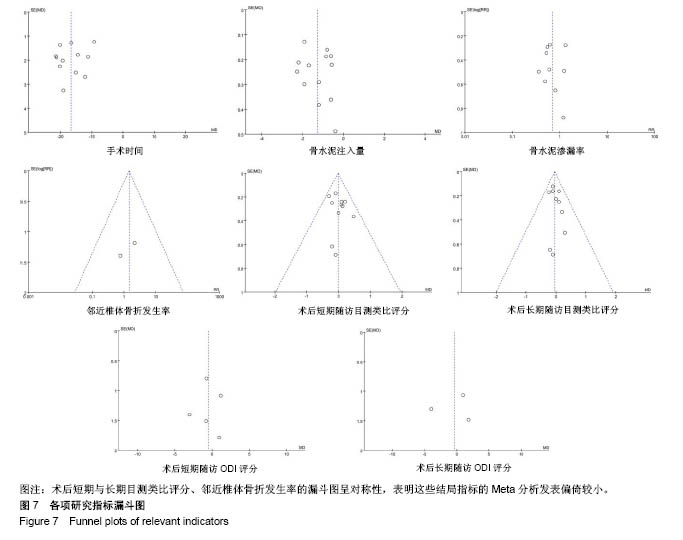
| [1] Mattia C, Coluzzi F, Celidonio L, et al.Bone pain mechanism in osteoporosis: a narrative review. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab.2016;13(2):97-100. [2] Boyce-Fappiano D,Elibe E,Schultz L,et al.Analysis of the Factors Contributing to Vertebral Compression Fractures After Spine Stereotactic Radiosurgery.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;93(3):S56-S57.[3] Galibert P,Deramond H,Rosat P,et al.Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty.Neurochirurgie.1987;33(2):166-168.[4] 赵俊强,陈琼,黄志坚,等.单侧与双侧经皮椎体成形术治疗椎体压缩性骨折的前瞻性研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2011,26(3): 229-230.[5] Mattie R,Laimi K,Yu S,et al. Comparing Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Conservative Therapy for Treating Osteoporotic Compression Fractures in the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2016;98(12):1041-1051.[6] Yang LY,Wang XL,Zhou L,et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of unilateral versus bilateral kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Pain Physician.2013;16(4):277-290.[7] 王伟,王成文,朱世华.单、双侧经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2013, 19(8):690-692.[8] 陈建常,梁景灏,马在松,等.单、双侧入路椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的疗效比较[J].临床军医杂志, 2014, 42(07):704-706,725. [9] 王玺,寇剑铭,贾学军,等.单、双侧椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的临床疗效比较[J].中国老年学, 2016,36(16): 4012-4014.[10] 吴建荣.单侧与双侧经皮椎体成形及椎体后突成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效比较[J].浙江创伤外科, 2017,22(3): 517-518.[11] 刘耀怀,马兴.单侧与双侧入路行椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的效果[J].临床医学研究与实践, 2018,3(22): 58-59.[12] 周荣,范华侨,周秩华,等.单侧与双侧入路经皮穿刺椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩性骨折[J].临床骨科杂志, 2015,18(6): 667-669.[13] 黄胜,许靖,项禹诚,等.单侧与双侧入路经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松压缩性骨折的比较研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013,21(2): 115-118.[14] 李健,沈文龙,常兴华.单侧与双侧椎弓根入路椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的临床疗效比较[J].大连医科大学学报, 2015,37(2):145-147.[15] 翟宏利,张飞.单侧与双侧椎弓根入路椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].内蒙古医学杂志,2013, 45(12):1501-1502.[16] 肖良,徐宏光,刘平,等.单双侧入路经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效比较[J].皖南医学院学报, 2015,34(6): 533-537.[17] 袁文强,邹蕾.局麻下单侧与双侧PVP治疗老年OVCF的效果观察[J].白求恩医学杂志,2014,12(6):582-582.[18] 任海龙,王吉兴,陈建庭,等.单侧与双侧经椎弓根入路经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(8):684-689.[19] Chen C,Bian J,Zhang W,et al.Unilateral versus bilateral vertebroplasty for severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech.2014;27(8):E301-304.[20] Zhang L,Liu Z,Wang J,et al. Unipedicular versus bipedicular percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a prospective randomized study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:145.[21] 汪呈,曹宇,顾永清,等.骨质疏松治疗药物的研究进展[J].科学通报,2014,59(13):1209-1214.[22] 董继胜,董力军,闫兵勇,等.经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(8):748-751.[23] 王翀,李京,田征,等.经皮椎体成形术与非手术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(6): 493-498.[24] 李祖国,扈佐鸿,刘浩,等.单侧经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性上胸椎骨折的临床疗效观察[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2015, 9(15):2820-2823.[25] 程才,王路,李书奎.经皮椎体成形术中注入不同剂量骨水泥治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的对比研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(5):460-461.[26] 郭小伟,潘玉林,焦云龙,等.单侧经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折的疗效分析和技术总结[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2015,7(1):24-28. |