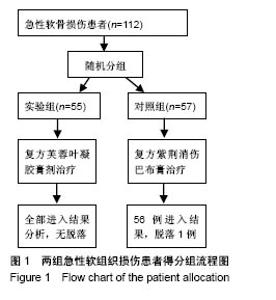
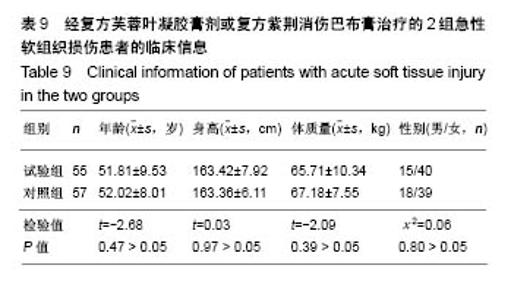
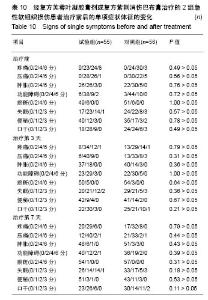
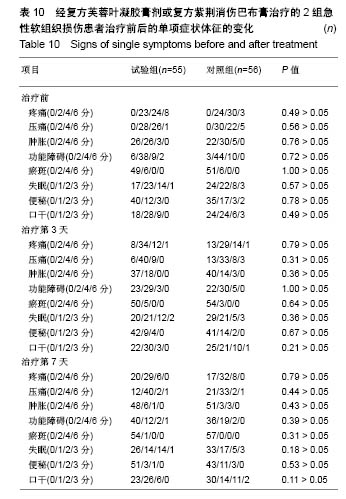
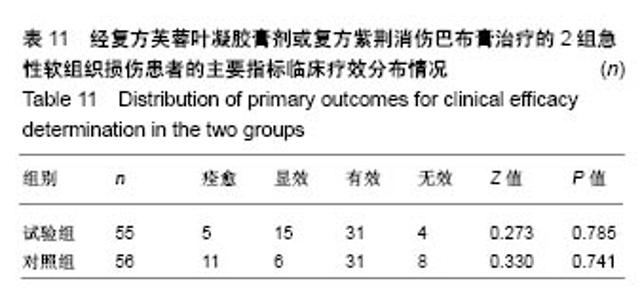
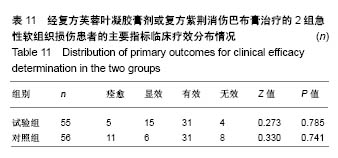
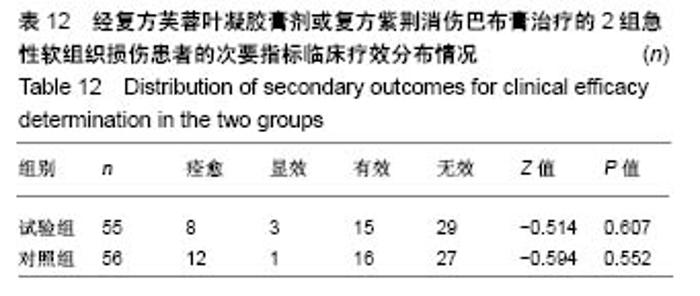
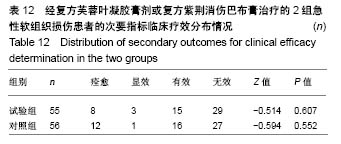
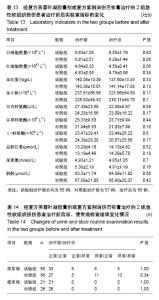
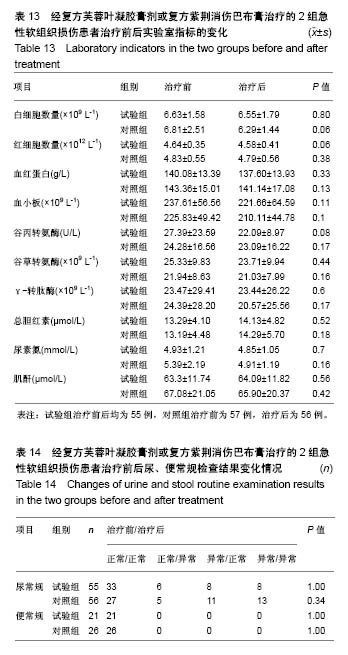
| [1] 孙树椿.中医筋伤学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1990:25-26.[2] 杨春恒,刘德春,韩士鼎.伤痛膏外敷治疗急性软组织损伤疗效观察[J].中医药临床杂志,2017,29(2):270-272.[3] 滕忠,李茂,周军,等.济民风湿王抗炎?镇痛和对急性软组织损伤作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(24):176.[4] 李飞跃,奚小冰,傅文彧,等.改良消肿散(巴布剂)治疗急性软组织损伤的临床研究[J].中成药,2005,27(3):312-314.[5] 宋立华,刘淑芝.中药凝胶膏剂的研究进展分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2015,21(22):133-136.[6] 董礼,徐希明,余江南.中药凝胶膏剂研究概述[J].中国药师, 2011, 14(1):129-132.[7] 李智勇.中药复方经皮给药制剂—癌痛巴布剂的研制[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2010.[8] 窦鹏.中药经皮给药系统新型基质材料的合成?制备与性能研究[D].北京:北京化工大学,2013.[9] 吕琳,王国杰,何晓明,等.生物黏附给药系统黏附性能的体外评价方法的研究进展[J].中国药师,2016,19(9):1752-1755.[10] 孟舒.玄丹巴布剂治疗乳腺增生的药学研究[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2007.[11] 郑兴荣,冯丽娟,刘伟伟.沸石/聚丙烯酸钠调湿材料的制备与特性分析[J].实验室研究与探索,2018,37(1):13-15,32.[12] 王丽梅.散结止痛巴布剂药学及初步药效学的研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2010.[13] 朱法根.半夏?掌叶半夏中凝集素蛋白促炎作用及矾制解毒机理研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2012.[14] 王景红,郑金凤,夏坤,等.宣痹凝胶剂提取纯化及成型工艺研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2016,22(8):1111-1114.[15] 杨春蓉.交联对胶原生物学和物理性能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(3):521-524.[16] 李朝辉,刘艳芝,黄剑萍,等.加味黄柏散治疗急性软组织损伤的疗效研究[J].中医临床研究,2013,5(5):1-3.[17] 张波,范家伟,贾树范,等.金骨莲胶囊治疗急性软组织损伤84例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2014,22(11):45-46.[18] 郑筱萸.中药新药临床研究指导原则(试行)[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2002:342-343.[19] 杨莉娅,谢松,吴云鸣,等.巴布剂复方紫荆消伤膏质量标准研究[J].中草药,2000,31(11):28-30.[20] 王丽伟,于跃,王伟.药品不良事件数据挖掘研究进展[J].中国医院药学杂志,2013,33(22):1880-1883.[21] 冯宇,信维伟,李鹤.疼痛方外敷治疗踝关节骨折后急性软组织损伤的临床研究[J].上海中医药杂志,2017,51(9):68-71.[22] 缪定国.依托芬那酯超声透入治疗急性软组织损伤疗效观察[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2016,22(1):80.[23] Hung KKC, Graham CA, Lo RSL, et al. Oral paracetamol and/or ibuprofen for treating pain after soft tissue injuries: Single centre double-blind, randomised controlled clinical trial. PLoS One. 2018;13(2):e0192043. [24] 李蜀平,刘冬平,董莹.中药化瘀止痛胶囊疼痛药效学的实验研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2009,24(S1):156-157.[25] 余兆仲,万小明,丁雪勇,等.跌打软膏治疗急性闭合性软组织损伤27例[J].江西中医药大学学报,2017,29(6):28-31.[26] 蒋国鹏,谢兴文,顾玉彪,等.急性软组织损伤的中医药治疗进展[J].中国中医急症,2015,24(7):1209-1211.[27] 王曙东,刘文雅.凝胶剂的研究进展及应用概况[J].中国药业, 2010, 19(21):1-4.[28] 何琪莹.局部药用凝胶剂的研究新进展和新应用[J].中国药物与临床,2006,6(5):384-387.[29] 胡劲松,奚小冰.复方芙蓉叶巴布膏治疗膝骨关节炎的临床疗效观察[J].老年医学与保健,2015,21(2):77-79.[30] 刘秀丽,滕蔚然.新型外用敷贴制剂治疗膝骨关节炎的研究进展[J].医学综述,2014,20(13):2420-2422. |