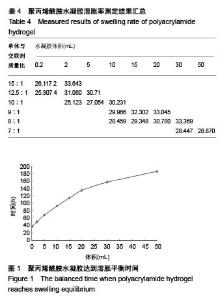
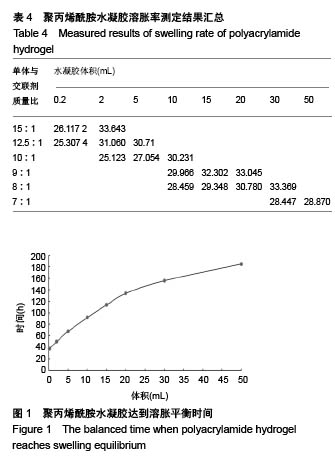
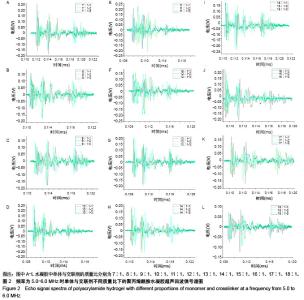
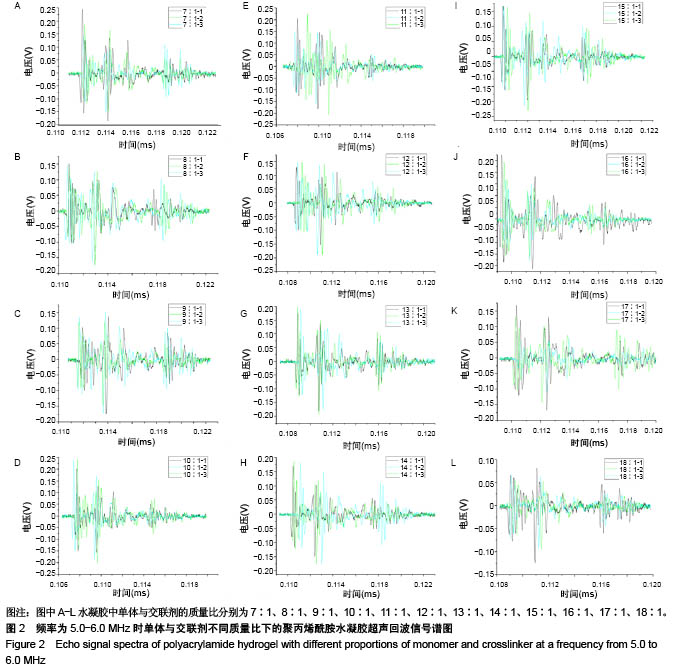
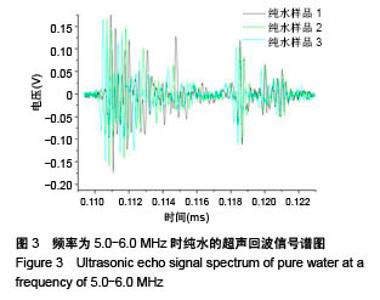
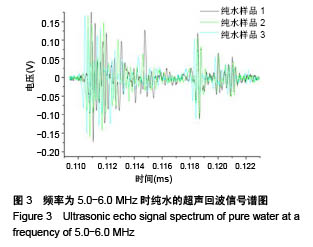
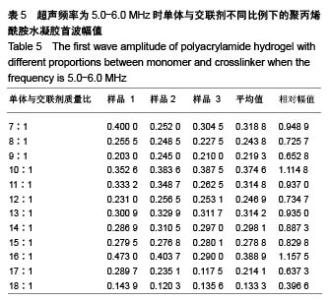
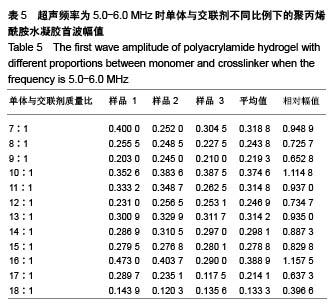
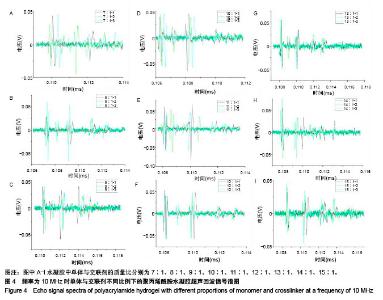
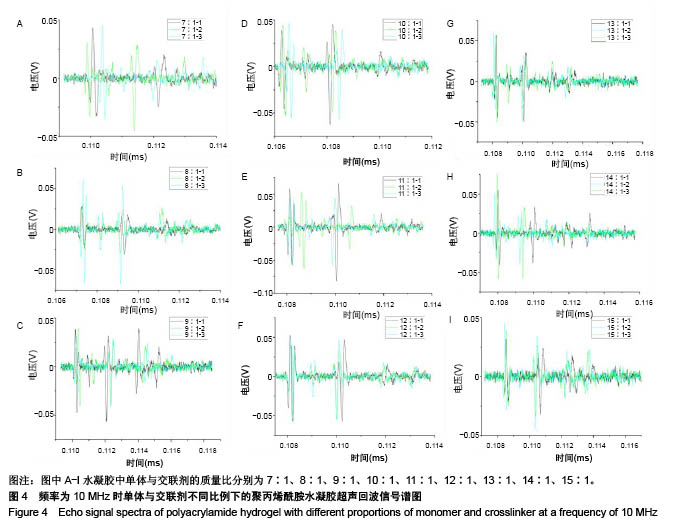
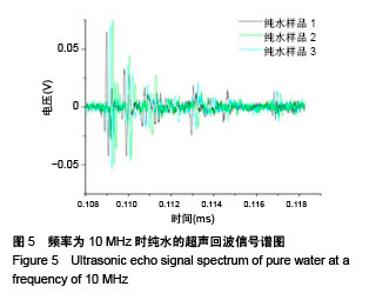
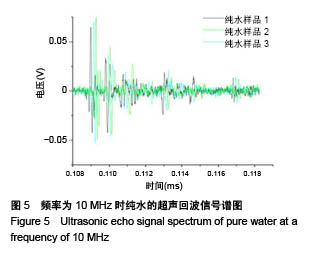
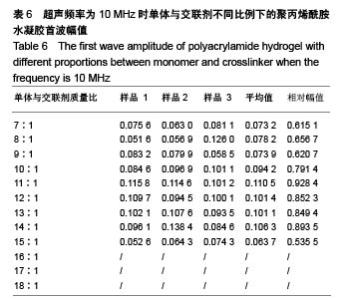
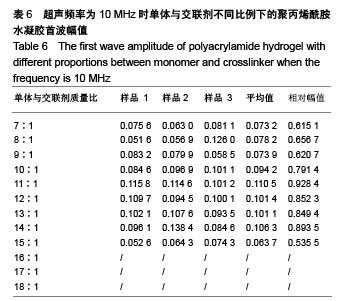
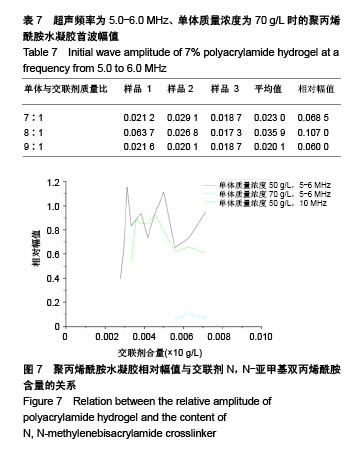
| [1] Silverman RH.High-resolution ultrasound imaging of the eye-a review.Clin Exp Ophthalmol.2010;37(1):54-67.[2] Cui A,Qianqian LI,Ding X,et al.Applications of endoscopic ultrasound elastographic imaging in diagnosis of digestive system diseases.Chin J Int Imaging Ther.2016. DOI:10.13929/ j.1672-8475.2016.11.013[3] Viereck V,Pauer HU,Bader W,et al.Ultrasound imaging of the lower urinary tract in women before andafter colposuspension: a 6-month follow-up.Ultraschall Med.2003;24(5):340.[4] Baba K,Kobayashi K,Hayashi M,et al.Extended field-of-view ultrasound imaging in obstetrics and gynecology: preliminary experience.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2000;15(2):157-159.[5] Doherty JR,Dumont DM,Trahey GE.The development of a combined b-mode, ARFI, and spectral Doppler ultrasound imaging system for investigating cardiovascular stiffness and hemodynamics[C]// SPIE Medical Imaging. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2011:2155-2157.[6] 张国栋,郭玉军.超声医学超声成像技术的探讨[C]//中华医学会医学工程学分会全国医疗器械应用技术评价暨医学影像技术研讨会论文集,2003.[7] 卞加聪,胡文祥,周八妹.多匹配层空气耦合压电超声换能器[J].应用声学,2018,37(1):96-100.[8] 匡泓锦,郭永强,杜斌.压电超声换能器匹配层的数值分析研究[J].科技视界,2017,7(25):40-41.[9] 李德来,杨金耀.医学超声成像换能器的研究与应用进展[J].中国医疗器械信息,2011,17(7):6-8.[10] 熊贵.医学超声成像压电换能器探头的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2010.[11] Li X. Progress in the Synthesis of Polyacrylamide(PAM). Shandong Chemical Industry,2016.[12] Zell K,Sperl J,Vogel MR,et al.Acoustical properties of selected tissue phantom materials for ultrasound imaging.Phys Med Biol. 2007;52(20):475-484.[13] Kumar K,Andrews ME,Jayashankar V,et al.Measurement of Viscoelastic Properties of Polyacrylamide-Based Tissue-Mimicking Phantoms for Ultrasound Elastography Applications.IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. 2010;59(5):1224-1232.[14] Park SK,Guntur SR,Kang IL,et al.Reusable ultrasonic tissue mimicking hydrogels containing nonionic surface-active agents for visualizing thermal lesions.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2010; 57(1):194-202.[15] Park CH,Jeong SH.A study on acoustic characteristics of couplants in HIFU for extracorporeal non-invasive treatment of CTO[C]//International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems.IEEE,2014:1551-1553.[16] Kandadai MA,Raymond JL,Shaw GJ.Comparison of electrical conductivities of various brain phantom gels: Developing a 'Brain Gel Model'.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2012;32(8): 2664-2667.[17] Mishra S,Mukul A,Sen G,et al.Microwave assisted synthesis of polyacrylamide grafted starch (St-g-PAM) and its applicability as flocculant for water treatment.Int J Biol Macromol. 2011; 48(1):106-111.[18] 安玉林,周锡明,沙宪政.医用超声探头的研究进展[J].医用医疗设备, 2015,30(3):71-73.[19] Chebli R,Kassem A,Sawan M.Integrated front-end preamplifier dedicated to ultrasonic receivers[C]// The, IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems. IEEE, 2001; (3):1103-1106.[20] Zakerhamidi MS,Tajalli H,Ghanadzadeh A,et al.Effect of polyacrylamide hydrophilic gel composition on photo-physical behavior of Oxazine 750.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2010;77(1):164-169. |