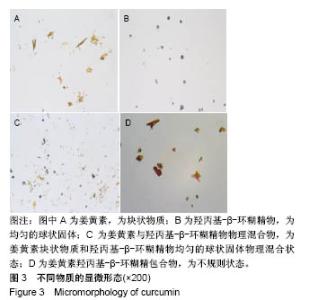
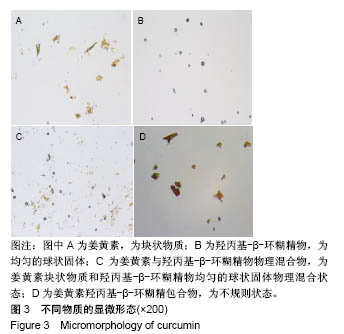
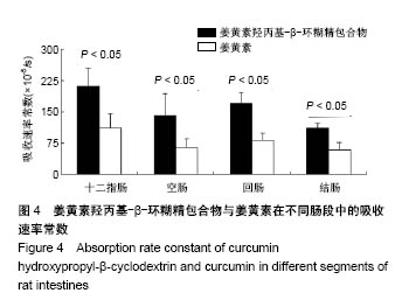
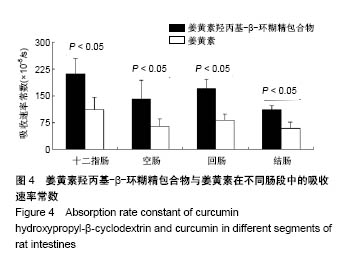
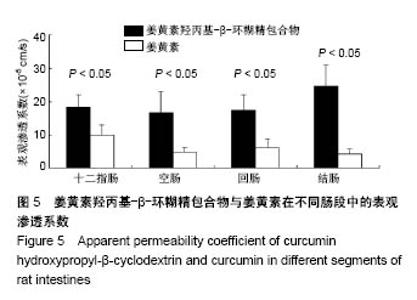
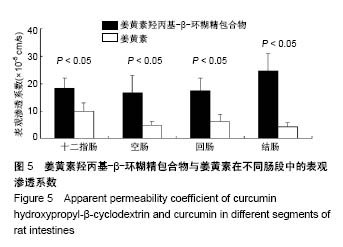
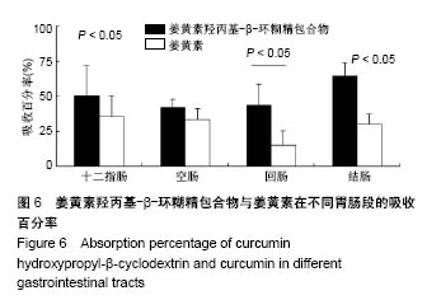
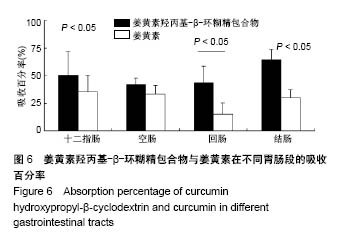
| [1] Lin CC, Lin HY, Chi MH, et al. Preparation of curcumin microemulsions with food-grade soybean oil/lecithin and their cytotoxicity on the HepG2 cell line. Food Chem. 2014;154: 282-290. [2] Garrido-Armas M, Corona JC, Escobar ML, et al. Paraptosis in human glioblastoma cell line induced by curcumin. Toxicol In Vitro. 2018;51:63-73. [3] Chen M, Du ZY, Zheng X, et al. Use of curcumin in diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(4):742-752. [4] Koo BB, Calderazzo S, Bowley BGE, et al. Long-term Effects of Curcumin in the Non-human Primate Brain. Brain Res Bull. 2018;142:88-95. [5] Jurenka JS. Anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin, a major constituent of Curcuma longa: a review of preclinical and clinical research. Altern Med Rev. 2009;14:141-153. [6] 孙永,彭明利.姜黄素及其衍生物在肝脏相关疾病中防治作用的研究进展[J].药学学报,2014,49(11):1483-1490.[7] Bai X, Oberley-Deegan RE, Bai A, et al. Curcumin enhances human macrophage control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Respirology. 2016;21(5):951-957. [8] 张继芬,唐勤,莫婷,等.姜黄素磷脂载体的表征及肠吸收研究[J].中国药学杂志,2012,47(21):1736-1740.[9] Maiti K, Mukherjee K, Gantait A, et al. Curcumin-phospholipid complex: Preparation, therapeutic evaluation and pharmacokinetic study in rats. Int J Pharm. 2007;330(1-2): 155-163. [10] Lu PS, Inbaraj BS, Chen BH. Determination of oral bioavailability of curcuminoid dispersions and nanoemulsions prepared from Curcuma longa Linnaeus. J Sci Food Agric. 2018;98(1):51-63. [11] 赵会娟,刘红星,黄初升,等.姜黄色素3种主要成分的分离纯化研究进展[J].化工技术与开发,2012,41(7):41-46.[12] 闫文丽,黄兆胜,曾晓会,等.单向灌流法研究姜黄素的大鼠在体肠吸收[J].今日药学,2012,3(12):137-141.[13] Tan Q, Wu J, Li Y, et al. A supermolecular curcumin for enhanced antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities: molecular characteristics, computer modeling and in vivo pharmacokinetics. Nanotechnology. 2013;24(3):035102. [14] Hu J, Chen D, Jiang R, et al. Improved absorption and in vivo kinetic characteristics of nanoemulsions containing evodiamine-phospholipid nanocomplex. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:4411-4420. [15] Kunnumakkara AB, Bordoloi D, Padmavathi G, et al. Curcumin, the golden nutraceutical: Multitargetingfor multiple chronic diseases. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(11):1325-1348. [16] Andrew R, Izzo AA. Principles of pharmacological research of nutraceuticals. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(11):1177-1194. [17] Ganjali S, Blesso CN, Banach M, et al. Effects of curcumin on HDL functionality. Pharmacol Res. 2017;119:208-218. [18] Rahmani S, Asgary S, Askari G, et al. Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Curcumin: A Randomized Placebo-controlled Trial. Phytothe Res. 2016; 30(9):1540-1548. [19] Banik U, Parasuraman S, Adhikary AK, et al. Curcumin: the spicy modulator of breast carcinogenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36(1):98. [20] Davatgaran-Taghipour Y, Masoomzadeh S, Farzaei MH, et al. Polyphenol nanoformulations for cancer therapy: experimental Evidence and clinicalperspective. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:2689-2702. [21] 何瑶,徐晓玉,陈红,等.卡前列甲酯-羟丙基-β-环糊精包合物的制备和评价[J].中国新药杂志,2018,27(6):637-643.[22] Merisko-Liversidge E, Liversidge GG, Cooper ER. Nanosizing: a Formulation Approachfor poorly-water-soluble compounds. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2003;18(2):113-120. [23] Gidwani B, Vyas A. A Comprehensive Review on Cyclodextrin-Based Carriers for Delivery of ChemotherapeuticCytotoxic Anticancer Drugs. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:198268. [24] 邓少东,张鹏,林励,等.单向灌流法研究巴戟天低聚糖的大鼠肠吸收特性[J].中国中药杂志,2015,40(1):134-140.[25] 刘诗雨,柏希慧,董林娟,等.基于单向灌流法的葛根素羧甲基壳聚糖微球肠吸收特性研究[J].中草药,2016,47(14):2488-2491.[26] 罗轶凡,任利翔,李晓红,等.药物肠道吸收研究方法概述[J].药物评价研究,2017,40(5):706-710.[27] 邓少东,林靖然,林励,等.巴戟甲素的大鼠在体肠吸收动力学[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2015,21(4):89-93.[28] 李万玉,晏子俊,孙立力.姜黄素固体脂质纳米粒在大鼠体肠中吸收的研究[J].食品与生物技术学报,2017,36(7):733-737.[29] 张雪,刘宏明,雷婷婷,等.吴茱萸碱羟丙基-β-环糊精包合物大鼠在体肠吸收特征[J].第二军医大学学报, 2016,11(37): 1387-1391.[30] 罗见春,胡雪原,吴建勇,等.姜黄素羟丙基-β-环糊精磷脂复合物在大鼠体内药代动力学研究[J].中药材,2015,38(3):572-575.[31] 罗见春,何丹,尹华峰,等.姜黄素磷脂复合物的药代动力学评价[J].第二军医大学学报,2014,35(7):754-757.[32] 徐伟良,詹怡飞,杨岚.NL-101-羟丙基倍他环糊精包合物的制备及其特性研究[J].中国现代应用药学,2017,34(11):1568-1571.[33] 赵孝先,高玲,梁园园,等.丁苯酞-磺丁基-β-环糊精包合物的制备与表征[J].中国现代应用药学,2016,33(6):762-767.[34] 高振珅,王兰.姜黄素-羟丙基-β-环糊精包合物的制备及其理化性质研究[J].中国药房,2007,13(18):999-1000.[35] 周云,符旭东,毕诗涛.盐酸奈必洛尔-羟丙基-β-环糊精包合物的制备及表征[J].中国新药杂志,2018,27(8):954-959. |