Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (32): 5188-5194.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1496
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of three different fixation methods for distal tibial fracture
Jia Junfeng, Tang Chengjie, Yue Jintao, Li Feng
- Sichuan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital, Chengdu 610040, Sichuan Province, China
-
Online:2019-11-18Published:2019-11-18 -
Contact:Yue Jintao, Chief physician, Sichuan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital, Chengdu 610040, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Jia Junfeng, Master, Sichuan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital, Chengdu 610040, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jia Junfeng, Tang Chengjie, Yue Jintao, Li Feng. Finite element analysis of three different fixation methods for distal tibial fracture[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5188-5194.
share this article
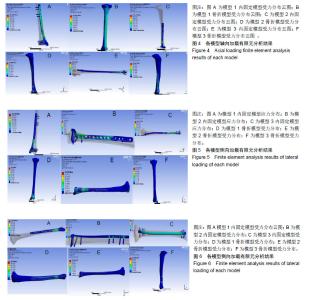
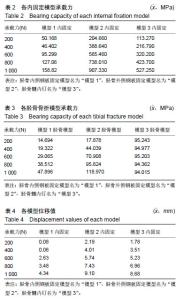
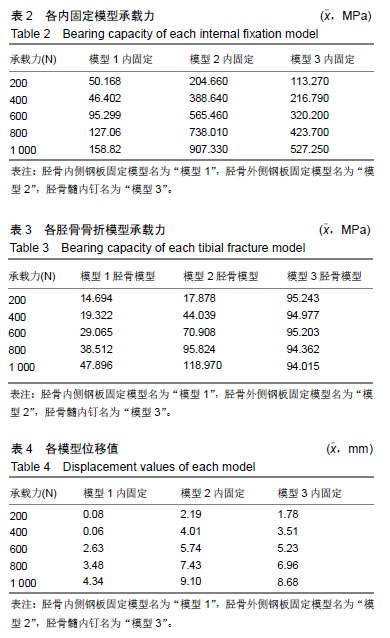
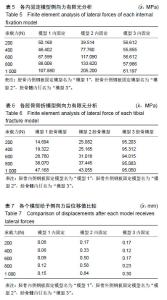
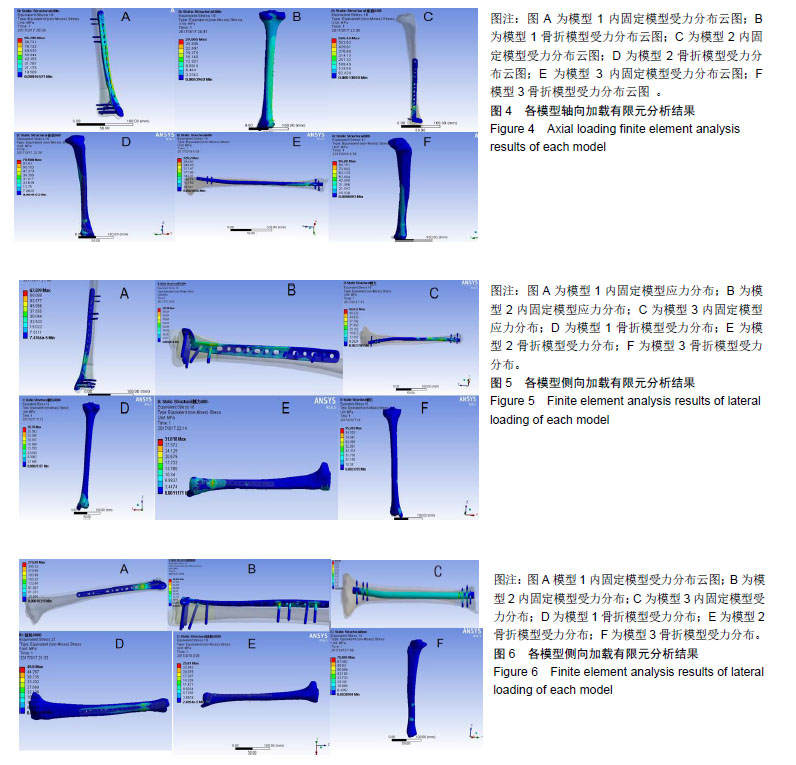
2.1 轴向加载各固定模型系统实验结果 在模型1中,其内固定系统承担的承载力为95.54 MPa,见图4A,胫骨模型平均承载力为29.89 MPa,见图4B。而在模型2中,内固定系统承载力约为560.82 MPa,见图4C,胫骨模型平均应力为69.52 MPa,见图4D。在模型3中,内固定系统承载力约为320.24 MPa,见图4E,胫骨模型平均应力为94.70 MPa,见图4F。 模型1,2,3的内固定受力3者差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表2;即给予轴向力时模型1的内固定受力最小,模型2的内固定受力最大。模型1,2,3差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表3;但模型2与模型3骨折模型受力差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),模型1,2,3的位移均值分别为:2.11,5.69,5.23 mm。3个模型位移值差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表4;即模型1位移较小,模型2的位移最大。 2.2 侧向弯曲加载各固定模型系统实验结果 模型1内固定系统与胫骨骨折模型中,其内固定系统承担的承载力为72 MPa,见图5A,胫骨模型平均承载力为29.6 MPa,见图5B。而在模型2中,内固定系统承载力约为 114.63 MPa,见图5C,胫骨模型平均应力为32 MPa,见图5D。在模型3中,内固定系统承载力约为57.65 MPa,见图5E,胫骨模型平均应力为94.93 MPa,见图5F。 模型1,2,3的内固定受力3者差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表5。模型1,2骨折模型无显著性意义(P > 0.05);但模型3与模型1,2骨折模型差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.05),见表6;模型3较模型1,2的胫骨骨折模型承担较多的压力;即模型1位移较小,模型2的位移最大。从模型1,2,3的位移分别为:0.1,0.48,0.19 mm。位移3者模型差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表7;模型2在给予侧向力时的位移最大。 "
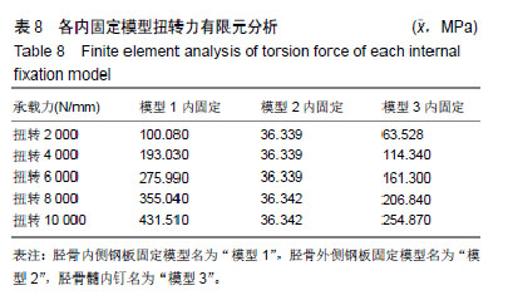
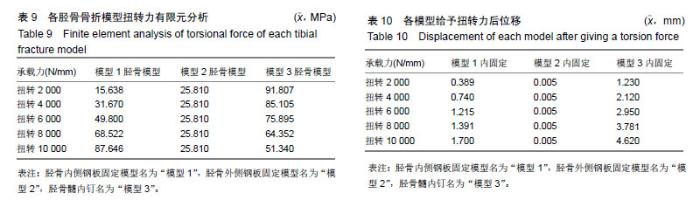
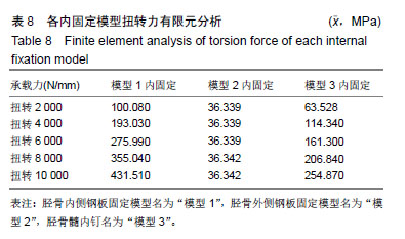
2.3 扭转力加载各固定模型系统实验结果 模型1内固定系统与胫骨骨折模型中,其内固定系统承担的承载力为271.13 MPa,见图6A,胫骨模型平均承载力为50.65 MPa,见图6B。而在模型2中,内固定系统承载力约为36.34 MPa,见图6C,胫骨模型平均应力为25.81 MPa,见图6D。在模型3中,内固定系统承载力约为160.17 MPa,见图6E,胫骨模型平均应力为73 MPa,见图6F。 模型1,2,3的内固定受力3者差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表8;模型1内固定承受最大的扭转力,模型2内固定承受最小的扭转力;模型1与模型2,3骨折模型差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);但模型2,3骨折模型受力差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表9;模型3的胫骨模型受力最大。模型1,2,3位移3者差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表10;模型1,2,3位移均值分别为:1.05,0.05,2.94 mm,模型3的位移最大。"
| [1]Wai IH, Ui Gani N,Yaseen M, et al. Operative management of distal tibial extra-articalar fractures-intramedul lary nail versus minmally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2017;19(6):537-541.[2]Vaienti E, Schiavi P, Ceccarelli F, et al. Treatment of distal tibial fractures: prospective comparative study evaluating two surgical procedures with investigation for predictive factors of unfavourable outcome. Int Orthop. 2019;43(1):201-207. [3]Daolagupu AK, Mudgal A, Agarwala V, et al. A Comparative study of intramedullary interlocking nailling and minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis inextra articular distal tibial fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2017;51(3):292-298.[4]Maredza M, Petrou S, Dritsaki M, et al. Acomparison of the cost-effectiveness of in tramedullary nail fixation and locking plate ication in the treatment of adult patients with anextra-articular fracture of the dital tibia. Bone Joint J. 2018;100B(5):624-633.[5]Costa ML, Achten J, Griffin J, et al. Effect of locking plate fixations vs intramedullary nail fixation on 6-month disability among adult with displaced fracture of the distal tibia the UK FixDT randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318(18): 1767-1776. [6]钟华,朱智敏,刘立华.MIPPO技术下LCP锁定和加压固定后应力遮挡的有限元研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(3): 213-216.[7]李赞罡,陈为坚,李贵涛.不同运动步态下锁定加压钢板固定胫骨干骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(4): 612-619.[8]刘易军,宫赫,刘百奇,等.胫骨上端外部形状及内部结构的模拟[J].中国生物医学工程学,2006,25(5):563-579.[9]Sitthiseripratip K, Van Oosterwyck H, Vander Sloten J, et al. Finite element study of trochanteric gamma nail for trochanteric fracture. Med Eng Phys. 2003;25(2):99-106.[10]李维新,袁斌云.跟骨骨折锁定钢板内固定与普通钢板内固定的有限元分析[J].中医正骨,2013,25(4):10-11.[11]Galloway F, Kahnt M, Ramm H, et al. A Large scale finite element study of a cementless ossointegrated tibial tray. J Biomech. 2013;46(11):1900-1906.[12]Wong C, Mikkelsen P, Hansen LB, et al. Finite element analysis of tibial fractures. Dan Med Ball. 2010;57(5):A4148.[13]Chen FC, Huang XW, Ya YS, et al. Finite element analysis of intramedullary nailing and double locking plate for treating extra-articular proximal tibial fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):2-8.[14]Atmaca H, Ozkan A, Matla I, et al. The effect of proximal tibial corrective osteotomy on menisci tibia and tarsal bones: a finit element model study of tibia vara. Int J Med Robot. 2014; 10(1):93-97.[15]Sawatari T, Tsamura H, Iesaka K, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty the influence of tibial component inclination. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(3):541-554.[16]Sowmianarayanan S, Chandrasekaran A, Kumar RK. Finite element analysis of a subtrochanteric fractured femur with dynamic hip screw, dynamic condylar screw, and proximal femur nail implants a comparative study. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008;222(1):117-127.[17]马童,蔡珉巍,涂意辉,等.经皮微创钢板固定技术Meta接骨板治疗胫骨远端干骺端骨折[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2011,8(3): 30-34. [18]赵勇,申才佳,李勇,等.胫骨远端前外侧解剖型钢板治疗不稳定性Pilon骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2013,15(6):666-667. [19]Kuo LT, Chi CC, Chuang CH. Surgical interventions for treating distal tibial metaphyseal fractures in adultes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(3):CD010261.[20]Beytemur O, Barl A, Albay C, et al. Comparison of intramedullary nailing and minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis in the treatment of simple intra-articular fractures of the distal tibia (AO-OTA type43C1-C2). Acta orthop Traumatol Turc. 2017;51(1):12-16.[21]Guo C, Ma J, Ma X, et al. Comparing intramedullary nailing and plate fixation for treating distal tibail fractures: ameta-analysis of randomizedcontroll edtrials. Int J Surg. 2018;53:5-11. [22]Lai TC, Fleming JJ. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal tibia fractures. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2018;35(2): 223-232.[23]Redfern DJ, Syed SU, Davies SJ. Fractures of the distal tibia:minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 2004; 35(6):615-620.[24]Park KC, Oh CW, Kim JW, et al. Minimally invasive plate augmentation in the treatment of long bone non unions. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(11):8-18.[25]Nork SE, Schwartz AK, Agel J, et al. Intramedullary nailing of distal meta physeal tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(6):1213-1221.[26]Shukla R, Jain N, Jain RK, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using locking plates for AO 43-type fractures lessons learnt from a prospective study. Foot Ankle Spec. 2018;11(3):1-5.[27]Bisaccia M, Cappiello A, Meccariello L, et al. Nail orplate in the management of distal extra-articular tibial fracture, what is better? Valutation of out comes. SICOT J. 2018;4:2.[28]Guo C, Ma J, Ma X, et al. Comparing intramedullary nailing and plate fixation for treating distal tibail fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg. 2018;53:5-11.[29]Wang Z, Cheng Y, Xin D, et al. Expert tibial nails for treating distal tibial fractures with soft tissue damage: apatient series. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;56(6):1232-1235.[30]Oken OF, Yildirim AO, Asilturk M, et al. Finite element analysis of the stability of AO/OTA 43-C1 type distal tibial fractures treated with distal tibia medial anatomic plate versus anterolateral anatomic plate. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2017;51(5):1-5.[31]Garg S, Khanna V, Goyal MP, et al. Comparative prospective study between medial and lateral distal tibial locking compression plates for distal third tibia fractures. Chin J Traumatol. 2017;20(3):151-154.[32]Choudhari P, Padia D. Minimally invasive osteosynthesis of distal tibia fractures using anterolateral locking plate. Malays Orthop J. 2018;12(3):38-42.[33]Muzaffar N, Bhat R, Yasin M. Complications of minmally invasive percutaneous plating for distal tibail fractures. Trauma Mon. 2016;21(3):e22131.[34]Akra GA, Lazarides S, Nanu AM. Early results of minimally invasive percutaneou splate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia; aretrospective case series and review of the literature. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;10:1179544117701724.[35]Kim JW, Kim HU, Oh CW, et al. A prospective randomized study on operative treatment for simple distal tibial fractures-minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis versus minimal open reduction and inter nail fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32(1):e19-e24. |
| [1] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [2] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [3] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [4] | Chai Le, Lü Jianlan, Hu Jintao, Hu Huahui, Xu Qingjun, Yu Jinwei, Quan Renfu. Signal pathway variation after induction of inflammatory response in rats with acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1218-1223. |
| [5] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [6] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [7] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [8] | Yuan Xinping, Shao Yanbo, Wu Chao, Wang Jianling, Tong Liangcheng, Li Ying. Accuracy of target bone segments in personalized differential modeling and simulation of CT scanning parameters at fracture end [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 912-916. |
| [9] | Zhang Jing, Wang Bin, Lü Xin. Application of anatomic intramedullary nail in tubular bone fractures of limbs: stronger holding force and anti-rotation ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 917-922. |
| [10] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [11] | Liu Zhao, Xu Xilin, Shen Yiwei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Lü Hang, Zhao Jun, Wang Zhengchun, Liu Xuzhuo, Wang Haitao. Guiding role and prospect of staging and classification combined collapse prediction method for osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| [12] | Zhang Mi, Wu Saixuan, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Expression of interleukin-24 in a mouse model of periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 679-684. |
| [13] | Li Chenjie, Lü Linwei, Song Yang, Liu Jingna, Zhang Chunqiu. Measurement and statistical analysis of trabecular morphological parameters of titanium alloy peri-prosthesis under preload [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 516-520. |
| [14] | Xiang Feifan, Ye Junwu, Zhang Xihai, Ge Jianhua, Tang Lian, Yang Yunkang. Comparison of three different internal fixation methods in treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 403-408. |
| [15] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||