Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (32): 5195-5202.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1462
Previous Articles Next Articles
Standardized treatment of infection around the prosthesis after joint replacement
Liu Sijie, E Xiaoqiang, Pan Qi, Yao Guijun
- First Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Online:2019-11-18Published:2019-11-18 -
Contact:E Xiaoqiang, MD, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, First Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Liu Sijie, Master candidate, Physician, First Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:the Youth Science Foundation Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81301530 (to EXQ)| the Science and Technology Research Project of Education Department of Heilongjiang Province, No. 12541334 (to EXQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Sijie, E Xiaoqiang, Pan Qi, Yao Guijun. Standardized treatment of infection around the prosthesis after joint replacement[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5195-5202.
share this article

2.1 诊断 2.1.1 背景 全髋关节置换和全膝关节置换后假体周围关节感染的诊断对治疗具有重要意义。虽然早期诊断和治疗可以明显改善结果,但明确诊断可能很困难,尤其是在病原体不易明确的情况下。及时诊断可以减少患者的痛苦,限制局部组织的破坏,降低全身并发症的风险[5]。尚缺乏一个金标准来诊断感染是无菌性感染或者是有菌性感染[6-7]。目前,关节假体周围感染诊断依赖于临床表现、外周血及滑膜液化验结果、微生物培养、假体周围组织组织学评价及术中表现[1,8]。血清红细胞沉降率和C-反应蛋白是诊断关节假体周围感染最广泛使用的辅助手段之一[5]。1921年当Westergren认识到红细胞沉降率在结核病中的作用时,认为红细胞沉降率在炎症条件下会升高。纤维蛋白原等血浆正常蛋白的增加、坏死组织来源的循环蛋白异常,可增强红细胞聚集,加速红细胞沉降,从而提高红细胞沉降率的检查值。C-反应蛋白是Tillett和Francis于1930年发现的一种典型的急性期蛋白,由肝脏产生,在炎症发生24-35 h后产生。肝组织培养研究表明,白细胞介素6是肝细胞C-反应蛋白microRNA的大量诱导物。C-反应蛋白结合革兰阳性菌和革兰阴性菌,刺激白细胞黏附和吞噬。它不是感染性炎症存在的具体参数,在类风湿关节炎等系统性自身免疫性疾病、创伤后或手术后及组织损伤中也时有升高。另一方面,它的浓度随着全身皮质类固醇药物的使用而降低。红细胞沉降率和C-反应蛋白临床应用广泛,因为它们成本低、可用性广、灵敏度较高。然而,4%关节假体周围感染患者表现为正常的红细胞沉降率和C-反应蛋白,红细胞沉降率和C-反应蛋白的作用在明确诊断关节假体周围感染中仍有争议,一些人提倡使用红细胞沉降率、C-反应蛋白用来明确排除关节假体周围感染,而另一些人则反对说,这将导致一个极高的假阴性结果,导致关节假体周围感染的诊断延误[5]。 2.1.2 症状、发病机制及常见病原菌 关节假体周围感染的临床症状表现多样,局部常表现为急性关节疼痛、伤口炎症(发热、红肿)、关节积液及功能丧失;全身表现为发热、不适、恶心等,虽不常见,但也可出现由金黄色葡萄球菌、革兰阴性杆菌等剧毒微生物引起的关节假体周围感染。在某些病例中还可能出现鼻内窦道和关节脓性分泌物,这是关节假体周围感染特异但不敏感的表现。慢性关节疼痛和假体松动是慢性关节假体周围感染的主要表现。目前人们一般认为关节假体周围感染是人体、细菌及假体三者相互作用的结果[7]。细菌生长的生物膜理论被认为在关节假体周围感染发病机制中起着重要作用。假体为细菌的最初附着和持续繁殖提供了温床。生物膜是由细胞外聚合物(如多糖、糖蛋白和DNA)组成的复杂基质,细菌在其中可以免受宿主免疫反应和抗菌药物的伤害。因此,尽管假体上存在大量的细菌,炎症反应仍然可以表现得很小。这使得细菌能够在假体表面长久生存而不受生物膜外环境的影响。此外,停留在生物膜上的细菌可以保持代谢静止状态,临床上表现为培养阴性的关节假体周围感染和耐药的关节假体周围感染。因此,针对生物膜成分(细胞外分子或寄存细菌)的诊断方法可以提高诊断关节假体周围感染的能力[6]。研究发现,多种细菌可引起关节假体周围感染。革兰阳性菌,特别是葡萄球菌(金黄色葡萄球菌、耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌和凝固酶阴性葡萄球菌)、链球菌和肠球菌,是大多数关节假体周围感染病例的病因。其他病原体包括革氏阴性菌、厌氧菌、真菌、分枝杆菌以及丙酸杆菌和不动杆菌等其他细菌也与关节假体周围感染的发生有关。革兰阴性感染较少见,据报道占感染的10%-20%。大约20%的关节假体周围感染是多微生物的[6]。关节假体周围感染可分为急性感染(发生在首次关节置换后6周内)、延迟感染(6周至6个月)或晚期感染(手术后大于6个月)。急性感染可能是围术期病原体直接感染关节,而延迟或晚期感染通常是血源性感染或病原体通过血液传播到关节[7]。 2.1.3 关节假体周围感染的生物标志物及诊断标准 见表1。"

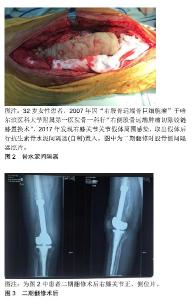
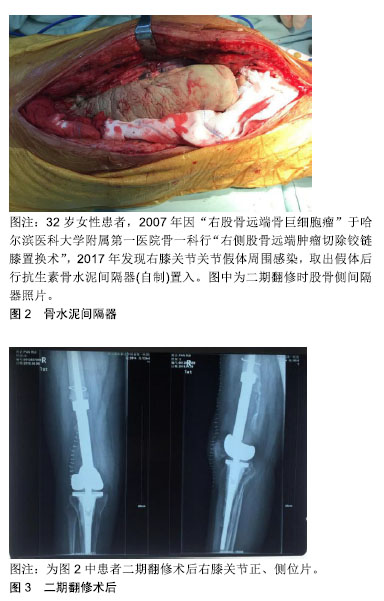
理想的生物标志物应该是准确、易于识别、分析迅速、检测有效的[8]。传统的血清标志物(红细胞沉降率和C-反应蛋白)通常是非特异性的,在炎症条件下可升高。因此,关节假体周围感染的明确诊断不能完全依赖于它们。使用蛋白质组学,滑液生物标志物如α-防御素、白细胞介素6已经被提议作为关节假体周围感染更精确的生物标志物[6]。Lee等[8]通过对滑膜液的13项指标[白细胞计数、多核白细胞百分比和C-反应蛋白、α-防御素、白细胞酯酶、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、白细胞介素10、白细胞介素1β、血管内皮生长因子和粒细胞集落刺激因子、培养及扩增的分子技术(PCR)]检测分析得出,滑膜白细胞计数、多核白细胞百分比、C-反应蛋白、α-防御素、白细胞酯酶、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8均表现为高灵敏度的关节假体周围感染诊断,α-防御素诊断假体周围感染的诊断优势比最高。但Shahi等[9]的研究表明白细胞酯酶诊断假体周围感染的诊断优势比最高。并表明血清D-二聚体是一种很有前途的关节假体周围感染诊断指标[10]。Wyatt等[11]就α-防御素和白细胞酯酶2种检查方法做了对比得出:2种试验对关节假体周围感染的诊断准确率均较高。鉴于研究数量有限,而且测试之间的成本差异很大,有必要对这些测试进行更独立的研究。血清生物标志物的未来可能会转向使用基因组学和蛋白质组学来识别在感染和脓毒症反应中通过信使RNA转录的蛋白质[10]。为了提高培养敏感性,最近研究了靶向生物膜的诊断方法。对生物膜概念的理解也促进了关节假体周围感染诊断新技术的发展,如荧光原位杂交生物膜的可视化和DNA微阵列检测细菌等。利用荧光原位杂交可以将生物膜及其物理结构可视化,荧光原位杂交利用荧光DNA或肽核酸探针与细菌中的特定靶点结合,包括核糖体RNA和负责抗生素耐药性的基因。最后,使用PCR来识别导致微生物培养阴性关节假体周围感染的特定细菌的种类的方法正在推广[6]。美国骨科医师学会(AAOS)提供了其诊断假体周围关节感染的指南中使用每种工具的证据。其中核成像包括标签白细胞成像、镓成像、F-18氟脱氧葡萄糖正电子发射断层扫描成像。在关节置换术后可以鉴别无菌性感染和有菌性感染关节疼痛,外科活检包括冷冻组织切片的组织学分析和假体周围组织的培养,窦道与关节相通可确认假体周围感染。长期以来,关节的化脓性感染被认为是假体周围关节感染的标志,但是不应该认为是感染存在的绝对指标和特异性的诊断标 志[1,4,12]。术中冷冻切片可显著提高血清红细胞沉降率和C-反应蛋白在关节假体周围感染诊断中的作 用[13]。Kwiecien等[14]研究表明术中冰冻切片组织学符合肌肉骨骼感染学会标准,特异度高,阳性预测值、阴性预测值、准确性高,敏感性适中。冰冻切片和永久切片之间的差异率很低,Parvizi等[15]在最新的关节假体周围感染诊断修订中讲到:关节假体周围感染的主要标准和诊断方法是2次及以上的培养物阳性或窦道的存在。血清C-反应蛋白(>10 mg/L)、D-二聚体(>860 μg/L)和血清红细胞沉降率(>30 mm/h)的计分分别为2分、2分和1分。此外,滑液的白细胞计数升高(>3×109 L-1)、α-防御素(信噪比>1)、白细胞酯酶(++)、多核白细胞百分比(>80%)和滑膜C-反应蛋白 (>6.9 mg/L)分别得到3,3,3,2和1分。总分≥6分的患者被认为是感染的,而2-5分的患者需要术中结果,以确认诊断结果。阳性组织学、化脓性和单一阳性培养的结果分别为3,3和2分。结合术前得分,总 分≥6分被认为感染,4-5分没有定论,≤3 分没有感染。与肌肉骨骼感染学会(79.3%)和国际共识会议定义(86.9%)相比,新标准的敏感性为97.7%,特异性为99.5%。微生物培养阴性的关节假体周围感染与培养阳性感染具有相同甚至更好的效果[16]。至于原本存在炎症性关节疾病的患者,炎症指标可能不会影响关节假体周围感染患者感染生物标志物的准确性[17]。 2.1.4 细菌培养阴性的常见原因 人工关节周围培养阴性感染的原因还没有得到明确。大概可以从以下几个方面考虑:①最常见的因素是取样前使用抗生素,这可能会降低常规实验室诊断的敏感性,因此建议在取样前至少2周停止抗菌治疗;②可能对分枝杆菌、真菌等稀有生物以及布鲁氏杆菌或伯氏杆菌等常规方法难以识别的生物使用了不合适的诊断方法或诊断工具;③低毒性的微生物可能因为采样较少,培养时间短,导致培养为阴性。为了提高低毒微生物的检出率,应多取样品(最少3份),并给予足够的生长时间,至少14 d;④诊断工具落后:假体超声治疗这种方法比传统的假体周围组织培养更敏感,尤其是在接受抗生素治疗的患者中。最常见的分子生物学技术是检测致病微生物的聚合酶链反应。即使是像真菌性假体周围关节感染这样不常见的物种,也可以通过选择性培养基和增加的潜伏期来检测[16]。 2.1.5 关节置换术前预防感染方法 在人工关节置换患者中,为了预防关节假体周围感染这一灾难性的并发症,需要采取多种措施,全身性抗生素能有效降低感染率。然而,抗生素的选择仍然存在争议。最常用的预防抗生素是头孢唑林和头孢呋辛。头孢唑林的剂量通常为体质量<80 kg为1 g或体质量>80 kg的患者2 g。体质量> 120 kg的患者可考虑3 g剂量。头孢呋辛剂量为1.5 g。这2种头孢菌素都是安全的,对最常见的微生物特别是革兰阳性菌和40%革兰阴性菌都是有效的。美国骨科医生学会关于抗生素预防的最新声明指出头孢唑林和头孢呋辛是首选抗生素。没有β-内酰胺过敏史的患者,第1代或第2代头孢菌素应作为常规预防的首选药物。当患者过敏而禁忌使用头孢菌素或患者已知携带耐药微生物(包括)的时候可使用克林霉素或万古霉素。目前的指南表明,万古霉素是β-内酰胺过敏患者和感染高危人群(如耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌高发地区的患者、住院患者、医护人员)抗生素的合理选择。2013年《人工关节周围感染国际共识》广泛支持在已知携带者、已知青霉素过敏者或感染高危人群中常规使用万古霉素。此外,一般不支持常规使用双抗生素。 2.2 治疗 关节假体周围感染的治疗最终目标是根除感染,重建一个功能性的,无痛的,稳定的关节[18]。治疗方法有抗生素治疗、冲洗、开放或关节镜清创、一期翻修和二期翻修、清创更换垫块假体保留、关节切除术、关节融合术、截肢[19]。抗生素治疗是为了控制感染而不是根除感染。抗生素治疗可用于年老体弱、无法承受外科手术治疗、关节功能要求不高的患者[20-21]。早期感染可通过积极清创、更换垫块和保留固定部件来治疗,也就是清创更换垫块假体保留[20]。一期关节翻修需要皮瓣和适当的软组织覆盖,否则应考虑二期翻修手术。二期翻修手术的适应证包括:①全身性感染的患者;②感染似乎很好诊断,但并未发现明确致病菌;③术前培养确定难以治疗和耐药的致病菌;④存在窦道;⑤软组织覆盖不足[22]。关节切除术可能适合需求较低的患者,他们只是需要舒服地坐着[20]。关节融合的适应证包括多次尝试重建失败,年轻活动量大的患者;以及由多种抗药性病原体引起的关节假体周围感染,这些病原体已经被证实是无法控制,和/或存在伸肌功能缺陷的患者。膝上截肢确实是膝关节置换后治疗关节假体周围感染的最后一种选择,很少有必要(0.1%)。截肢的适应证是广泛累及软组织,大量骨质丢失的持续感染;坏死性筋膜炎;控制感染的尝试失败,排除关节融合术(膝关节),软组织覆盖不足;多次翻修失败或切除关节成形术;血管疾病或神经与血管的损伤[20,22]。对于全膝关节置换两阶段再植术后失败持续感染的患者,膝关节融合优于膝关节截肢[23]。一期翻修和二期翻修、清创更换垫块假体保留在临床中较常用[21]。 2.2.1 一期翻修 一期翻修术有许多优点[20]。近期的研究表明,一期翻修可为部分患者提供更好的治疗效果,包括更低的再感染率和更好的功能。临床上,对于部分患者一期翻修可能是最佳治疗方法;然而,患者的选择、手术方法、术后抗菌治疗仍有待明确[24]。Kunutsor等[25]在回顾研究中报道,在一期翻修和二期翻修的修订策略中,总感染根除率分别为73%-100%和82%-100%,进一步评估以膝关节评分和活动范围的临床结果,2种策略之间没有显著差异。这种治疗方式在欧洲的38家医院和81家专业中心进行,高达85%,并且在北美越来越流行。对于大多数关节假体周围感染患者来说,这种方法是可行的。一期翻修的结果取决于合适的患者,主要是软组织覆盖,仔细的外科技术和严格的围术期多学科管理。这个过程在很大程度上取决于清创和减少生物膜的效率[20]。有研究将覆有特殊涂层的假体一期置入,与没有覆盖特殊涂层的二期翻修相比,感染复发率相似,整体住院时间和抗生素治疗时间缩短,但样本量较少[26]。 2.2.2 二期翻修 二期翻修是应用最为广泛的技术,被认为是治疗膝关节假体周围感染的首选方法及黄金标准[25,27-30]。Insall等[18]首次描述了两阶段的全膝关节置换感染的再植过程:第一阶段包括从关节中移除所有的假体和异物;接下来是对所有条件不佳的软组织和骨骼进行广泛清创、滑膜切除、冲洗和扩髓;关节准备好之后,置入混有抗生素的骨水泥占位器和/或静态连接垫片,然后闭合软组织和皮肤。Insall等首先描述了公认的两阶段再置入方案包括在2个手术阶段之间延长静脉注射抗生素(通常为6周)[18]。当关节被认为没有感染存在时,去除抗生素浸渍的水泥珠和/或间隔物,重复冲洗和清创,最后放入新的假体[20,30]。生物膜发病机制的主要因素是生物膜的形成。生物膜是一种复杂的结构,由包裹在糖酵母菌大分子和其他保护膜中的微生物组成[7]。在清创术中,所有的生物膜都必须彻底的切除,所有非出血的软组织都应该切除。膝关节后囊需要特别小心,因为它可能是再次感染的来源。为了进入膝关节后囊,必须取出内衬,最好更换内衬,应采集来自不同位置的多组织样本送去进行微生物检验,建议从股骨和胫骨的髓腔和膝关节后囊等区域取3-6个样本[20]。人们在使用低压或高压灌洗方面几乎没有达成共识。高压灌洗可迅速有效地清除坏死组织,但可能导致组织损伤或细菌侵入较深的软组织层,尽管文献中关于使用它的好处尚未得到确认,但清创后必须使用大量液体冲洗是达成一致的[20]。 (1)骨水泥间隔器:抗菌骨水泥垫片的作用是保持骨量和软组织张力、减少软组织挛缩、改善患者的功能,进而简化再植,同时提供额外的局部抗生素,进一步降低单阶段再感染率[2,20,31]。关节置换感染的过渡阶段中,常规使用抗生素骨水泥假体是安全和有效的[32-33]。使用何种类型的骨水泥间隔没有明确的禁忌证,没有证据表明一种间隔物比另一种能更好地控制感染,也没有证据表明预制骨水泥垫片比自制骨水泥垫片有任何优势。预制间隔器的优点在于它的表面更光滑,可以更好地连接,节省手术时间[20];氨基糖苷类抗生素庆大霉素和妥布霉素在骨水泥中的应用已被证实。对抗甲氧西林耐药细菌可使用万古霉素,因其对耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌和耐甲氧西林表皮葡萄球菌的有效性而广受欢迎[18]。建议在感染全髋关节和膝关节置换术中应用抗菌骨水泥间隔物时,每包骨水泥至少使用3.6 g妥布霉素和1 g万古霉素[34]。移动间隔器和静态间隔器再感染率、并发症发生率、再手术率均无差异[29,35],但移动间隔器提供了更好的运动范围,可能使二期手术在技术上更容易。移动间隔器包括水泥对水泥,水泥对聚乙烯和金属对聚乙烯垫片,是为了允许膝关节在第一阶段和第二阶段翻修过渡期间能够运动,这使得关节活动范围有了很大的改 善[36-37]。最近的研究表明,静态和移动的膝关节垫片有相似的感染根除率。研究表明在关节假体周围感染的二期翻修中,在水泥间隔物中加入糖肽可降低再置入时的微生物阳性培养率,并可降低凝血酶阴性葡萄球菌感染翻修的失败率[38]。典型病例见图2,3。"

(2)抗生素治疗:Insall等首先描述了公认的两阶段再置入方案包括在2个手术阶段之间延长静脉注射抗生素(通常为6周) [18]。虽然置入前通常使用6-8周的间隔时间,但最佳的假体游离间隔时间尚未确定。治疗应考虑到细菌种类和患者的情况,使其个性化。在最初的2周内,建议静脉注射,在此之后,根据机体的耐药情况和药物是否合适,可以继续口服治疗[20]。如果使用抗生素骨水泥间隔,长期(4-6周)使用抗生素可能并不一定是髋关节手术患者的常规做法[39]。延长的全身抗生素治疗可能不是必要的[30,40-41]。如果必要的话重复清创,并允许在软组织覆盖受损的情况下进行充分的软组织准备,C-反应蛋白和红细胞沉降率等血清学标志物在二期手术时机确认时并不可靠[22,42]。二期翻修前不建议再植前联合抽吸滑膜液、滑膜液白细胞计数和C-反应蛋白[43]。因此不能仅仅依靠红细胞沉降率和C-反应蛋白的结果确认第二阶段再植的时机,也不能依据金属腐蚀情况进行诊断。血清生物标志物的未来可能会转向使用基因组学和蛋白质组学来识别通过信使RNA转录的蛋白质, 以应对感染和败血症[44]。血清D-二聚体对于确定再种植的最佳时机也有很大的实用价值[10]。关于这2个阶段之间的最佳时间间隔,Bernard等[42]进行了一项前瞻性非随机研究,他发现6周的抗生素治疗足以治疗关节假体周围感染。有研究建议抗生素治疗时间应在6-12周[45]。Winkler等[46]采用高活性抗生素治疗时,短时间间隔(<4周)的两期交换与长时间间隔(4周)交换的结果相似。当采用短时间间隔的策略时,由于固定而造成的患者不便较少和护理费用较低。Vielgut等[47]认为第2阶段手术的最佳时机是4-11周。但是并没有得到一个明确的时间[48]。术后至少28 d的口服抗生素预防是否能降低再感染率。与非预防组相比,口服预防组患者的再感染率可能要低得多。口服抗生素的长期治疗可能有助于根除任何残留的潜伏致病菌,并减少同种致病菌再感染的发生率。与初次置换相比,翻修后的关节置换假体周围感染的风险更高,因此更积极的术后抗菌治疗可能减少再感染的发生率,在两阶段全膝关节置换术后,延长预防性口服抗生素治疗的疗程,可降低术后再感染的发生率[49-50]。"

| [1]Parvizi J, Adeli B, Zmistowski B, et al. Management of periprosthetic joint infection: the current knowledge: AAOS exhibit selection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(14): e104.[2]Hofmann AA, Goldberg TD, Tanner AM, et al. Ten-year experience using an articulating antibiotic cement hip spacer for the treatment of chronically infected total hip. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(7): 874-879.[3]Fu J, Ni M, Li H, et al. The proper timing of second-stage revision in treating periprosthetic knee infection: reliable indicators and risk factors. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1): 214.[4]Parvizi J, Della VC. AAOS Clinical Practice Guideline: diagnosis and treatment of periprosthetic joint infections of the hip and knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(12): 771-772.[5]Mcarthur BA, Abdel MP, Taunton MJ, et al. Seronegative infections in hip and knee arthroplasty: periprosthetic infections with normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level. Bone Joint J. 2015; 97-B(7): 939-944.[6]Patel R, Alijanipour P, Parvizi J. Advancements in Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infections after Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. Open Orthop J. 2016;10: 654-661.[7]Rasouli MR, Zmistowski B, Parvizi J. Diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. Curr Orthop Pract. 2013;24(1): 92-97.[8]Lee YS, Koo KH, Kim HJ, et al. Synovial fluid biomarkers for the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017; 99(24): 2077-2084.[9]Shahi A, Tan TL, Kheir MM, et al. Diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection: and the winner is? J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9S): S232-S235.[10]Shahi A, Kheir MM, Tarabichi M, et al. Serum D-Dimer test is promising for the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection and timing of reimplantation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(17): 1419-1427.[11]Wyatt MC, Beswick AD, Kunutsor SK, et al. The alpha-defensin immunoassay and leukocyte esterase colorimetric strip test for the diagnosis of periprosthetic infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(12): 992-1000.[12]Amanatullah D, Dennis D, Oltra EG, et al. Hip and Knee Section, Diagnosis, Definitions: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J Arthroplasty. 2019; 34(2S): S329-S337.[13]Xu C, Guo H, Chen JY. Intra-operative diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection can rely on frozen sections in patients without synovial fluid analyses. Int Orthop. 2018.[14]Kwiecien G, George J, Klika AK, et al. Intraoperative Frozen Section Histology: Matched for Musculoskeletal Infection Society Criteria. J Arthroplasty. 2017; 32(1): 223-227.[15]Parvizi J, Tan TL, Goswami K, et al. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(5): 1309-1314.[16]Reisener M, Perka C. Do culture-negative periprosthetic joint infections have a worse outcome than culture-positive periprosthetic joint infections? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2018, 2018: 6278012.[17]Tahta M, Simsek ME, Isik C, et al. Does inflammatory joint diseases affect the accuracy of infection biomarkers in patients with periprosthetic joint infections? A prospective comparative reliability study. J Orthop Sci. 2019;24(2): 286-289.[18]Kuzyk PR, Dhotar HS, Sternheim A, et al. Two-stage revision arthroplasty for management of chronic periprosthetic hip and knee infection: techniques, controversies, and outcomes. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014;22(3):153-164.[19]Qiu XS, Sun X, Chen DY, et al. Application of an articulating spacer in two-stage revision for severe infection after total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Surg. 2010; 2(4):299-304.[20]Gehrke T, Alijanipour P, Parvizi J. The management of an infected total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B (10 Suppl A): 20-29.[21]Rao N, Crossett LS, Sinha RK, et al. Long-term suppression of infection in total joint arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(414): 55-60.[22]Lichstein P, Gehrke T, Lombardi A, et al. One-stage versus two-stage exchange. J Orthop Res. 2014; 32 Suppl 1: S141-S146.[23]Rodríguez-Merchán EC, de la Corte-Rodriguez H, Román-Belmonte JM. Above Knee Amputation in the Treatment of Failed Septic Total Knee Arthroplasty. 2018: 181-191.[24]Nagra NS, Hamilton TW, Ganatra S, et al. One-stage versus two-stage exchange arthroplasty for infected total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(10): 3106-3114.[25]Kunutsor SK, Whitehouse MR, Lenguerrand E, et al. Re-infection outcomes following one- and two-stage surgical revision of infected knee prosthesis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016; 11(3): e151537.[26]Capuano N, Logoluso N, Gallazzi E, et al. One-stage exchange with antibacterial hydrogel coated implants provides similar results to two-stage revision, without the coating, for the treatment of peri-prosthetic infection. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(11): 3362-3367.[27]Ghanem E, Azzam K, Seeley M, et al. Staged revision for knee arthroplasty infection: what is the role of serologic tests before reimplantation? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(7): 1699-1705.[28]Ascione T, Pagliano P, Mariconda M, et al. Factors related to outcome of early and delayed prosthetic joint infections. J Infect. 2015; 70(1): 30-36.[29]Elsharkawy KA, Talmo CT. Use of an Antibiotic-Impregnated Spacer in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty. Rev Total Knee Arthroplasty. 2018:263-273.[30]Lee YS, Chen AF. Two-Stage Reimplantation in Infected Total Knee Arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2018;30(2): 107-114.[31]Joseph TN, Chen AL, Di Cesare PE. Use of antibiotic- impregnated cement in total joint arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003;11(1): 38-47.[32]Hsieh PH, Shih CH, Chang YH, et al. Two-stage revision hip arthroplasty for infection: comparison between the interim use of antibiotic-loaded cement beads and a spacer prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(9): 1989-1997.[33]Chalmers BP, Mabry TM, Abdel MP, et al. Two-stage revision total hip arthroplasty with a specific articulating antibiotic spacer design: reliable periprosthetic joint infection eradication and functional improvement. J Arthroplasty. 2018; 33(12): 3746-3753.[34]Masri BA, Duncan CP, Beauchamp CP. Long-term elution of antibiotics from bone-cement: an in vivo study using the prosthesis of antibiotic-loaded acrylic cement (PROSTALAC) system. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13(3): 331-338.[35]Pivec R, Naziri Q, Issa K, et al. Systematic review comparing static and articulating spacers used for revision of infected total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(3):553-557.[36]Kuzyk PR, Dhotar HS, Sternheim A, et al. Two-stage revision arthroplasty for management of chronic periprosthetic hip and knee infection: techniques, controversies, and outcomes. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014;22(3):153-164.[37]Ghanem M, Pempe C, Zajonz D, et al. Mid-term results of two-stage revision of total knee arthroplasty using a mobile (dynamic) cement spacer in the treatment of periprosthetic infections. GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg DGPW. 2018; 7: c2.[38]Wouthuyzen-Bakker M, Kheir MM, Moya I, et al. Failure after two-stage exchange arthroplasty for treatment of periprosthetic joint infection: the role of antibiotics in the cement spacer. Clin Infect Dis. 2018.[39]Hsieh PH, Huang KC, Lee PC, et al. Two-stage revision of infected hip arthroplasty using an antibiotic-loaded spacer: retrospective comparison between short-term and prolonged antibiotic therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009; 64(2): 392-397.[40]Hart W J, Jones RS. Two-stage revision of infected total knee replacements using articulating cement spacers and short-term antibiotic therapy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006; 88(8): 1011-1015.[41]Whittaker JP, Warren RE, Jones RS, et al. Is prolonged systemic antibiotic treatment essential in two-stage revision hip replacement for chronic Gram-positive infection? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009; 91(1): 44-51.[42]Bernard L, Legout L, Zurcher-Pfund L, et al. Six weeks of antibiotic treatment is sufficient following surgery for septic arthroplasty. J Infect. 2010;61(2):125-132.[43]Hoell S, Moeller A, Gosheger G, et al. Two-stage revision arthroplasty for periprosthetic joint infections: What is the value of cultures and white cell count in synovial fluid and CRP in serum before second stage reimplantation? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(4):447-452.[44]Saleh A, George J, Faour M, et al. Serum biomarkers in periprosthetic joint infections. Bone Joint Res. 2018; 7(1): 85-93.[45]Osmon DR, Berbari EF, Berendt AR, et al. Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of america. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(1): e1-e25.[46]Winkler T, Stuhlert M, Lieb E, et al. Outcome of short versus long interval in two-stage exchange for periprosthetic joint infection: a prospective cohort study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019;139(3): 295-303.[47]Vielgut I, Sadoghi P, Wolf M, et al. Two-stage revision of prosthetic hip joint infections using antibiotic-loaded cement spacers: When is the best time to perform the second stage? Int Orthop. 2015; 39(9): 1731-1736.[48]Minhas S, Odono R, Collins K, et al. The role and timing of treatment strategies during two-stage revision for periprosthetic joint infections. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2017;75(4): 246-247.[49]Zywiel MG, Johnson AJ, Stroh DA, et al. Prophylactic oral antibiotics reduce reinfection rates following two-stage revision total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2011; 35(1): 37-42.[50]Bosco JA, Bookman J, Slover J, et al. Principles of antibiotic prophylaxis in total joint arthroplasty: current concepts. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(8): e27-e35. |
| [1] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [2] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [3] | Zheng Li, Li Dadi, Hu Weifan, Tang Jinlong, Zhao Fengchao. Risk assessment of contralateral knee arthroplasty after unilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 374-379. |
| [4] | Ma Rui, Wang Jialin, Wu Mengjun, Ge Ying, Wang Wei, Wang Kunzheng. Relationship of pathogenic bacteria distribution with drug resistance and treatment cycle for periprosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 380-385. |
| [5] | Cheng Chongjie, Yan Yan, Zhang Qidong, Guo Wanshou. Diagnostic value and accuracy of D-dimer in periprosthetic joint infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3921-3928. |
| [6] | Fu Panfeng, Shang Wei, Kang Zhe, Deng Yu, Zhu Shaobo. Efficacy of anterolateral minimally invasive approach versus traditional posterolateral approach in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3409-3415. |
| [7] | Lin Haiqi, Chen Liang, Tang Lu, Weng Xiquan, Lin Wentao. Significance of urinary proteomics assessing pathological changes in the body [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3259-3266. |
| [8] | Hu Wandong, He Jialin, Zhang Longsheng, Liao Wenbo. Differential proteomics study of patients with sternal ossification of the ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2625-2629. |
| [9] | Liu Yongyu, Xu Jingli, Lin Tianye, Wu Feng, Shen Chulong, Xiong Binglang, Zou Qizhao, Lai Qizhong, Zhang Qingwen . Sensitivity and specificity of D-dimer in the diagnosis of chronic periprosthetic infection after hip replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1853-1857. |
| [10] | Song Min, Lu Chao, Chen Jin, Wu Gaoyi, Li Congcong, Li Anan, Ye Guozhu, Lin Wenzheng, Cai Yuning, Liu Wengang, Xu Weipeng. Application of tourniquet affects thickness of bone cement penetration in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1917-1923. |
| [11] | Li Shengqiang, Xie Bingying, Chen Juan, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, Ge Jirong. Interaction proteomics of long noncoding RNA uc431+ gene in postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1641-1646. |
| [12] | Zhao Chuntao, Qing Mingsong, Yu Langbo, Peng Jiachen . Meta-analysis of total knee arthroplasty guided by kinematic alignment and mechanical alignment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1435-1442. |
| [13] |
Zhang Cong, Zhao Yan, Du Xiaoyu, Du Xinrui, Pang Tingjuan, Fu Yining, Zhang Hao, Zhang Buzhou, Li Xiaohe, Wang Lidong.
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine and pelvis in adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis with lumbar major curve |
| [14] |
Cen Yanhui, Xia Meng, Jia Wei, Luo Weisheng, Lin Jiang, Chen Songlin, Chen Wei, Liu Peng, Li Mingxing, Li Jingyun, Li Manli, Ai Dingding, Jiang Yunxia.
Baicalein inhibits the biological behavior of hepatocellular
carcinoma stem cells by downregulation of Decoy receptor 3 expression |
| [15] | He Yujie, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Cai Yongqiang, Dai Lina, Xu Yangyang, Wang Yidan, Xu Xuebin. Digital measurements of the anatomical parameters of pedicle-rib unit screw fixation in thoracic vertebrae of preschoolers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 869-876. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||