Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 619-624.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1434
Previous Articles Next Articles
The role and mechanism of graphene and its derivatives-related composites in cartilage repair
Tang Jingfeng1, Zhang Jun2, You Qi2, Liu Yi2
- 1Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2First Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2019-04-04Revised:2019-04-13Accepted:2019-05-05Online:2020-02-08Published:2020-01-07 -
Contact:Liu Yi, Professor, Master’s supervisor, First Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Tang Jingfeng, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Program of Guizhou Province, No. qiankehe-LH-[2017]7105
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Jingfeng, Zhang Jun, You Qi, Liu Yi. The role and mechanism of graphene and its derivatives-related composites in cartilage repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 619-624.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
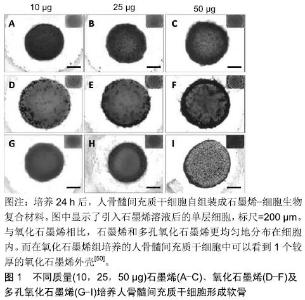
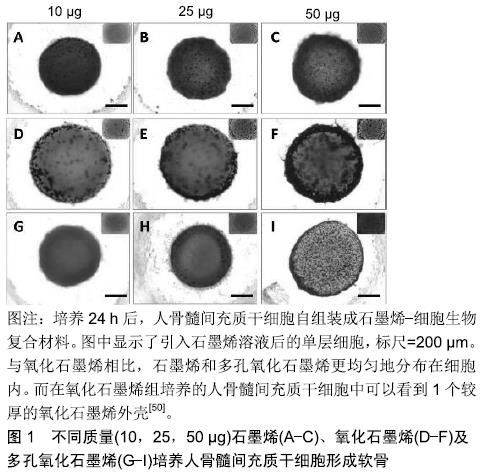
2.1 石墨烯及其衍生物的一般性质及其生物相容性 2.1.1 石墨烯及其衍生物 石墨烯可以通过化学气相沉积、石墨的机械切割及石墨的电化学剥离等多种方法制备[22-24]。石墨烯薄片分为单层和多层,每增加一层其性质都会有所改变,随着层数的增多,其性质会越来越接近于石墨[25]。多层石墨烯最初是作为单层石墨烯制备的副产品产生的[2],然而由于单层石墨烯很难悬浮在溶剂中,多层石墨烯在生物领域的应用越来越受到人们的关注[13]。由于其原子结构,结合石墨烯的电子分布,让它拥有了许多优异的物理性能,例如硬度比钻石高,弹性模量高达1 TPa[25],热传导性为铜的13倍以上[26],在室温下的电子迁移率大于15 000 cm2/(V)[27],表面积高达2 630 m2/g,因此,石墨烯与合成或天然聚合物等其他材料混合后,能增强其机械应力及导电性能等物理特性,另外高表面积能使相邻的碳原子间生成π键进一步提高其结构稳定性。 氧化石墨烯是石墨烯的衍生物,氧化石墨烯薄片可以从高锰酸钾和硫酸处理石墨时获得[28]。氧化石墨烯的结构由单层原子厚度的石墨烯和羧酸、环氧及羟基等官能团组成,这些官能团可以使氧化石墨烯具有两亲性[29-30]。氧化石墨烯平面上的羧基使其具有胶体稳定性和pH依赖性负电荷[31],其他基团可以通过物理吸附或化学结合的方式DNA,多肽或蛋白质作用,但同时由于其他基团的影响,其力学、电学和热性能较石墨烯降低了[32]。 还原氧化石墨烯可以通过加热、化学反应或紫外线照射氧化石墨烯来产生。此外,用肼在100 ℃下处理 24 h后可生成还原氧化石墨烯[33]。由于还原氧化石墨烯表面的氧含量减少,使其疏水性增强,同时它具有更大的电子迁移率(大于400 S/cm)[34],即更好的导电性。 2.1.2 石墨烯的生物相容性 用于组织工程的材料,评估其生物相容性与细胞毒性是使用该材料的前提。生物相容性是指材料与细胞组织相互接触时,不会对材料周围细胞组织造成损害的能力[35]。大量石墨烯复合材料已被证明对原核细胞和真核细胞都具有毒性。一方面,石墨烯复合材料可因其对原核细胞良好的抗菌活性用于抗菌及抗感染;另一方面,合理的表面修饰可以降低材料对真核细胞的毒性,提高在真核细胞中的生物相容性。对于原核细胞的毒性,有研究表明石墨烯和氧化石墨烯是通过损伤破坏细胞膜结构而表现出明显的抗菌作用[36]。在另一项研究中,石墨烯衍生物已经被充分证明可以通过氧化应激和破坏生物膜增强金属和金属氧化物纳米结构的抗菌活性[37]。对于真核细胞,有多种机制被认为是产生细胞毒性的原因,包括氧化应激、基因毒性、自噬、细胞凋亡及免疫应答等[38]。将石墨烯或氧化石墨烯与靶细胞(肺上皮细胞与成纤维细胞)相互作用的研究中,结果表明体内的单层石墨烯或氧化石墨烯薄片被肺上皮细胞或成纤维细胞包裹、隔离从而进一步降解。但随着石墨烯的剂量增加,毒性渐渐表现出来。体外结果表明,当单层氧化石墨烯的剂量在20 mg/L以上时,24 h后可诱导毒性产生[39-40]。另外,石墨烯毒性也与材料体积有关,在用新鲜兔血研究石墨烯与氧化石墨烯的血液相容性实验中发现,氧化石墨烯表面氧含量较高,其与红细胞外膜之间的静电相互作用增强了溶血作用,小体积的氧化石墨烯的溶血反应更加明显。 然而,过大的氧化石墨烯由于不容易被巨噬细胞吞噬,会很难降解并引起炎症反应[41]。还原氧化石墨烯具有比氧化石墨烯更大的细胞毒性,其生物学和分子机制不同,这与氧化石墨烯表面氧化状态不同有关[38]。同时,表面改性已被证明可以改变石墨烯生物相容性,羧基化石墨烯的毒性比氧化石墨烯或纯石墨烯小[42],除此之外,有研究制备了壳聚糖/还原氧化石墨烯薄膜[15],并将(50±15)岁女性患者的软骨薄片种植在薄膜上,发现软骨细胞能随时间不断增殖,这可能是通过屏蔽静电相互作用消除细胞毒性,提高生物相容性[43]。有研究构建的牛血清白蛋白修饰氧化石墨烯纳米薄片(GO-g-BSA)研究显示,材料对红细胞的溶血反应降低,且未观察到有血红蛋白释放[44]。 2.2 用于软骨的石墨烯及其衍生物相关的复合材料 目前石墨烯应用于软骨修复的材料主要分为2大类:一类是充当一种支架,能促进软骨下包的分化、成熟以及软骨组织的形成,且自身拥有一定程度的降解率,修复缺损软骨后能被代谢出去;另一类则是一种材料,能尽量模拟软骨组织结构,且拥有基本的软骨组织特性,用于代替缺损的软骨。 2.2.1 促进软骨修复的石墨烯相关复合材料 石墨烯材料被用作各种类型细胞生长、分化的培养支架,包括骨、神经、肌肉及脂肪[45-48]。然而,这种方法仅限于平面细胞生长,软骨细胞所在的环境是更加立体的,因此很难应用于需要悬浮培养的软骨组织。具体来说,在软骨形成过程中,单层培养的软骨细胞表型不稳定,所以培养软骨时通常是在有空间结构的小球中培养[49]。因此促进软骨修复的材料通常都构筑成有空间结构的形态。 WANG等[50]研制的人骨髓间充质干细胞组装的石墨烯生物复合材料致力于更好、更快的促进人骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨谱系分化用于软骨修复。实验中,他们分别将石墨烯、氧化石墨烯、多孔氧化石墨烯与细胞组装,并研究3 d后细胞的活性与分化情况。结果显示,3者都可促进干细胞向软骨分化成熟,且均能在生物复合材料形成空间结构,不同的是氧化石墨烯分布于生物复合材料的外周表层,而石墨烯与多孔氧化石墨烯则分布于材料内层,见图1。另外由于氧化石墨烯存在,氧化石墨烯组与多孔氧化石墨烯组会增加材料的孔隙率,这利于蛋白质的装载和物质的交换,使得细胞存活率更高。 "
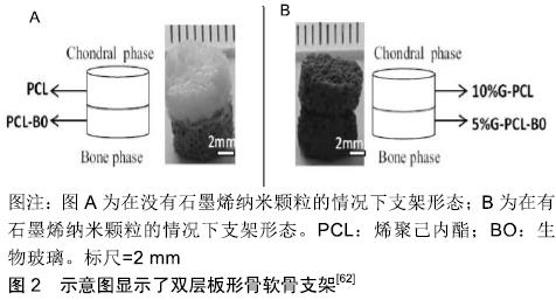
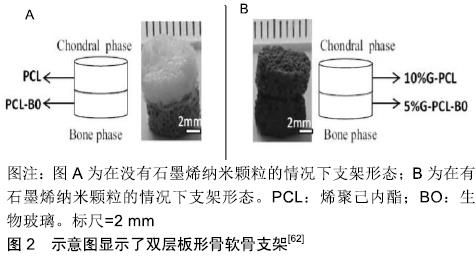
石墨烯相关的复合材料除了能促进干细胞分化成软骨,还能保护软骨组织,促进软骨细胞的增殖。有研究用氧化石墨烯纳米颗粒与水凝胶复合并通过3D打印制成支架,并移植入大鼠的双膝软骨组织中央位置,与软骨组织一起缝在骨膜上固定[51],4周后麻醉处死大鼠,对股骨远端软骨组织进行研究。研究发现氧化石墨烯纳米颗粒通过在细胞核中表达Rank来阻断Rank/Rankl/OPG的进程,并通过阻断Rank/Rankl/OPG通路来减少核因子kB释放,从而减轻组织损伤时而产生的炎症反应。SHAMEKHI等[52]通过包括交联和纳米颗粒掺入的方式制备了氧化石墨烯纳米颗粒/壳聚糖基支架,其物理力学性能得到了显著改善。在纳米复合材料支架上植入人关节软骨细胞后,随着氧化石墨烯百分比的增加,特别是在长时间的培养(14 d)中,细胞增殖增加。对人关节软骨细胞形态学的研究表明,在体外培养21 d后,交支架上的细胞呈球形。他们发现壳聚糖胺与氧化石墨烯羰基之间存在良好的相互作用,使材料交联密度增加,进而增加材料的孔隙度及机械强度增加,同时随着氧化石墨烯浓度从0增加到0.1%,0.2%和0.3%材料表面粗糙度与硬度也随之增加,增加了对细胞的黏附能力,这些都刺了激软骨细胞的增殖。 另外有人提出,虽然水凝胶或聚合物基材料能促进人骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化以及软骨细胞增殖,但新软骨常是纤维软骨样的,其力学性能不足以支撑膝关节的负荷。这使得软骨缺损的修复不够彻底,可能需要额外的手术[53]。有结果已经表明,相较于水凝胶或聚合物基材料,机械强度更高的支架材料可能能够促进关节软骨组织再生[54]。石墨烯泡沫也拥有三维结构,它是石墨烯的三维衍生物,由于其独特的力学、电学和热学性质,近年来在组织工程领域的应用受到广泛关注。YOCHAM等[55]测量了在应变值低于20%的准静态和动态载荷作用下,石墨烯泡沫/组织复合材料在无侧限压缩下的弹性和黏弹性性能。机械测试证明弹性模量增加了46%。另外,相较于氧化石墨烯,石墨烯泡沫复合材料更利于软骨细胞生长,这不仅是由于其高机械应力,还可能是由于氧化石墨烯是一种电绝缘体,其导电性远不如石墨烯泡沫[56],在电刺激下,细胞能产生更多的细胞外基质。另外导电性较高的支架不仅改善了细胞间的沟通交流,而且增加了细胞的附着和增殖能力[57-58],同时电刺激能选择性激活腺苷A2b受体,产生第二信使环磷酸腺苷,通过抗炎通路,降低一氧化氮的产生、金属蛋白酶的活性、软骨糖胺多糖的释放[59],起到保护软骨的作用。在导电性能方面,LIAO等[60]研制了硫酸软骨素/ PECA/氧化石墨烯支架却有意外的效果。该材料有具有良好的生物相容性和降解率,但令人惊讶的是他们发现,随着氧化石墨烯的浓度增加,该复合材料的导电性有了明显的提升,能直接或间接的促进细胞增殖,但这其中具体的机制不明。在兔软骨组织修复实验中,显微CT和组织学观察显示,细胞补充硫酸软骨素/PECA/氧化石墨烯支架组软骨细胞形态、软骨下骨连续性较好,新生软骨较支架组较对照组厚得多。钱志勇[61]制备的硫酸软骨素/PECA/石墨烯复合材料,其优势是降解率与软骨修复时间基本一致,这利于缺损新生软骨的长入,且它也表现出良好性能(高导电性、孔隙率、溶胀能力及弹性模量),在兔膝关节软骨缺损模型中,实验组在术后18个月,软骨的修复效果最好。 有研究研制了含石墨烯聚己内酯(PCL)/生物活性玻璃双层支架[62],一层为含10%石墨烯PCL支架用与软骨细胞ATDC5培养,另一层为含5%石墨烯PCL/生物玻璃支架用于成骨细胞MC3T3-E1培养,见图2。在单培养条件下,支架对成骨细胞和软骨细胞没有毒性反应,在共培养条件下则表现出更高的细胞存活率。同时结果还表明,含10%石墨烯PCL支架植入ATDC5细胞后有较高的矿化表现。这可能与软骨细胞向成熟软骨细胞的分化有关。促进软骨修复的石墨烯相关复合材料,见表1。 "

2.2.2 代替软骨的石墨烯相关复合材料 石雁[63]用纳米填充法制备了聚乙烯醇/石墨烯复合水凝胶。在使用氧化石墨烯复合时发现,氧化石墨烯使水凝胶的孔隙更加致密且分布更加均匀。同时适量的氧化石墨烯使复合水凝胶的拉伸强度与压缩强度都有所加强,在含量为0.15%时,拉伸强度最大,在含量为0.10%时,压缩强度最大。随着氧化石墨烯含量增加,复合材料的摩擦系数也降低了;而在与单层石墨烯或多层石墨烯复合时,材料表现出两相结构,这与天然软骨相似。适量的石墨烯也能增加材料的压缩与拉伸强度,然而随着石墨烯含量的增加复合材料的摩擦系数先降低后增高,在含量为0.10%(单层石墨烯)与0.15%(多层石墨烯)时,摩擦系数最小。而杜高来[64]制备的双乙硫醇交联氧化石墨烯(E-cGO)/聚乙烯醇水凝胶表现出良好的软骨细胞贴附及增殖效果,这证明石墨烯/聚乙烯醇复合材料不仅有优良的力学性能去代替缺损的软骨,且能促进软骨的修复。 此外,陈炯润[65]采用的β-环糊精二醛交联的氧化石墨烯与聚乙烯醇复合材料,并用多巴胺改性及阿仑膦酸钠共价结合聚乙烯醇,促进其矿化性能,模拟软骨钙化层,解决材料与软骨下骨结合不牢靠的问题。WU等[66]则通过与淀粉复合制备的纳米氧化石墨烯改性的淀粉材料促进矿化性能,他们发现在模拟体液环境中,纳米氧化石墨烯的浓度越高,钙磷沉积量越高,这是由于材料的纳米氧化石墨烯是钙磷有效的锚定点,从而促进矿化。 ZHANG等[67]通过水蒸发诱导自组装并在碱性溶液中进行物理交联方法,制备了壳聚糖/氧化石墨烯复合水凝胶膜。当氧化石墨烯含量为5%时,水凝胶膜的抗拉强度为5.35 MPa,断裂伸长率为193.5%,这与天然肋软骨相当,表现出良好的机械应力。此外,水凝胶膜表现出pH值驱动的形状记忆效应,即在酸性环境中将材料弯曲后置入碱性环境,发现水凝胶能恢复成原来的直条状,这种独特的现象主要归因于氢键的部分物理交联的可逆转变化,这项发现可为设计和研制生物仿生软骨材料提供了新的策略。 "

| [1] ALLEN MJ, TUNG VC, KANER RB. Honeycomb carbon: a review of graphene. Chem Rev. 2009;110(1):132. [2] NOVOSELOV KS, GEIM AK, MOROZOV SV, et al. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science. 2004;306(5696): 666-669. [3] GEIM AK. Graphene: status and prospects. Science. 2009;324 (5934):1530-1534. [4] EDA G, FANCHINI G, CHHOWALLA M. Large-area ultrathin films of reduced graphene oxide as a transparent and flexible electronic material. Nat Nanotechnol. 2008;3(5):270-274. [5] MERIC I, HAN MY, YOUNG AF, et al. Current saturation in zero-bandgap, top-gated graphene field-effect transistors. Nat Nanotechnol. 2008;3(11):654-659. [6] SAHOO S, BHATTACHARYA P, DHIBAR S, et al. Graphene/poly (aniline-co-pyrrole) nanocomposite: potential candidate for supercapacitor and microwave absorbing applications. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015;15(9):6931-6941. [7] DUFFICY MK, KHAN SA, FEDKIW PS. Hierarchical graphene- containing carbon nanofibers for lithium-ion battery anodes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;8(2):1327-1336. [8] ZHU C, HAN YJ, DUOSS EB, et al. Highly compressible 3D periodic graphene aerogel microlattices. Nat Commun. 2015;6: 6962. [9] SHAO Y, WANG J, HONG W, et al. Graphene based electrochemical sensors and biosensors: a review. Electroanalysis. 2010;22(10): 1027-1036. [10] YANG W, RATINAC KR, RINGER SP, et al. Carbon nanomaterials in biosensors: should you use nanotubes or graphene? Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010;49(12):2114-2138. [11] PUMERA M. Graphene-based nanomaterials for energy storage. Chem Soc Rev. 2010;39(11):4146-4157. [12] SHIN SR, AGHAEI-GHAREH-BOLAGH B, DANG TT, et al. Cell-laden Microengineered and Mechanically Tunable Hybrid Hydrogels of Gelatin and Graphene Oxide. Adv Mater. 2013; 25(44):6385-6391. [13] SU RS, LI YC, JANG HL, et al. Graphene-based materials for tissue engineering. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2016;105(Pt B):255-274. [14] CHUNG C, BURDICK JA. Engineering cartilage tissue. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60(2):243-262. [15] ZHANG W, CHEN J, TAO J, et al. The use of type 1 collagen scaffold containing stromal cell-derived factor-1 to create a matrix environment conducive to partial-thickness cartilage defects repair. Biomaterials. 2013;34(3):713-723. [16] BUCKWALTER JA, MANKIN HJ, GRODZINSKY AJ. Articular cartilage and osteoarthritis. Instr Course Lect. 2005;54:465-480. [17] KO CS, HUANG JP, HUANG CW, et al. Type II collagen-chondroitin sulfate-hyaluronan scaffold cross-linked by genipin for cartilage tissue engineering. J Biosci Bioeng. 2009;107(2):177-182. [18] STREHIN I, NAHAS Z, ARORA K, et al. A versatile ph sensitive chondroitin sulfate-peg tissue adhesive and hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2010;31(10):2788-2797. [19] KHADEMHOSSEINI A, VACANTI JP, LANGER R. Progress in tissue engineering. Sci Am. 2009;300(5):64-71. [20] TAMAYOL A, AKBARI M, ANNABI N, et al. Fiber-based tissue engineering: progress, challenges, and opportunities. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31(5):669-687. [21] TSAI WB, CHEN WT, CHIEN HW, et al. Poly (dopamine) coating of scaffolds for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomaterialia. 2011;7(12):4187-4194. [22] SHANG NG, PAPAKONSTANTINOU P, MCMULLAN M, et al. Catalyst-free efficient growth, orientation and biosensing properties of multilayer graphene nanoflake films with sharp edge planes. Adv Funct Mater. 2010;18(21):3506-3514. [23] LIU NA, FANG L, WU HX, et al. One-step ionic-liquid-assisted electrochemical synthesis of ionic-liquid-functionalized graphene sheets directly from graphite. Adv Funct Mater. 2010;18(10): 1518-1525. [24] GEIM AK, NOVOSELOV KS. The rise of graphene. Nat Mater. 2007; 6(3):183-191. [25] LEE C, WEI X, KYSAR JW, et al. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science. 2008;321(5887):385-388. [26] BALANDIN AA, GHOSH S, BAO W, et al. Superior thermal conductivity of single-layer graphene. Nano Lett. 2008;8(3):902. [27] GÓMEZ-NAVARRO C, WEITZ RT, BITTNER AM, et al. Electronic transport properties of individual chemically reduced graphene oxide sheets. Nano Lett. 2007;7(11):3499-3503. [28] HUMMERS WS, OFFEMAN RE. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc. 1958;80(6):1339. [29] ZHANG J, ZHANG F, YANG H, et al. Graphene oxide as a matrix for enzyme immobilization. Langmuir. 2010;26(9):6083-6085. [30] KIM J, COTE LJ, KIM F, et al. Graphene oxide sheets at interfaces. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132(23):8180-8186. [31] SPRINKLE M, RUAN M, HU Y, et al. Scalable templated growth of graphene nanoribbons on SiC. Nat Nanotechnol. 2010;5(10):727-731. [32] KARLICKÝ F, DATTA KKR, OTYEPKA M, et al. Halogenated graphenes: rapidly growing family of graphene derivatives. Acs Nano. 2013; 7(8):6434-6464. [33] PARK S, AN J, JUNG I, et al. Colloidal suspensions of highly reduced graphene oxide in a wide variety of organic solvents. Nano Lett. 2009;9(4):1593-1597. [34] LIU Q, ZHANG M, HUANG L, et al. High-quality graphene ribbons prepared from graphene oxide hydrogels and their application for strain sensors. Acs Nano. 2015;9(12):151021121926005. [35] SANGILIYANDI G, JIN-HOI K. Synthesis, toxicity, biocompatibility, and biomedical applications of graphene and graphene-related materials. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11(default):1927-1945. [36] PANDEY H, PARASHAR V, PARASHAR R, et al. Controlled drug release characteristics and enhanced antibacterial effect of graphene nanosheets containing gentamicin sulfate. Nanoscale. 2011; 3(10):4104-4108. [37] ROJASANDRADE MD, CHATA G, ROUHOLIMAN D, et al. Antibacterial mechanisms of graphene-based composite nanomaterials. Nanoscale. 2016;9(3):994-1006. [38] CHATTERJEE N, EOM HJ, CHOI J. A systems toxicology approach to the surface functionality control of graphene-cell interactions. Biomaterials. 2014;35(4):1109-1127. [39] LI X, HUANG X, LIU D, et al. Synthesis of 3D Hierarchical Fe3O4/graphene composites with high lithium storage capacity and for controlled drug delivery. J Phys Chem C. 2011;115(44): 21567-21573. [40] MISRA SK, KONDAIAH P, BHATTACHARYA S, et al. Graphene as a nanocarrier for tamoxifen induces apoptosis in transformed cancer cell lines of different origins. Small. 2012;8(1):131-143. [41] LIAO KH, LIN YS, MACOSKO CW, et al. Cytotoxicity of graphene oxide and graphene in human erythrocytes and skin fibroblasts. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces. 2011;3(7):2607-2615. [42] SASIDHARAN A, PANCHAKARLA LS, CHANDRAN P, et al. Differential nano-bio interactions and toxicity effects of pristine versus functionalized graphene. Nanoscale. 2011;3(6):2461-2464. [43] SYAMA S, MOHANAN PV. Safety and biocompatibility of Graphene: a new generation nanomaterial for biomedical application. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;86:546-555. [44] BING C, HU K, LI C, et al. Bovine serum albumin bioconjugated graphene oxide: red blood cell adhesion and hemolysis studied by QCM-D. App Surf Sci. 2015;356:844-851. [45] CROWDER SW, PRASAI D, RATH R, et al. Three-dimensional graphene foams promote osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Nanoscale. 2013;5(10):4171-4176. [46] KIM J, CHOI KS, KIM Y, et al. Bioactive effects of graphene oxide cell culture substratum on structure and function of human adipose- derived stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2013; 101(12): 3520-3530. [47] KU SH, PARK CB. Myoblast differentiation on graphene oxide. Biomaterials. 2013;34(8):2017-2023. [48] WANG Y, LEE WC, MANGA KK, et al. Fluorinated graphene for promoting neuro-induction of stem cells. Adv Mater. 2012;24(31): 4284-4284. [49] CHEN FH, ROUSCHE KT, TUAN RS. Technology Insight: adult stem cells in cartilage regeneration and tissue engineering. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006;2(7):373. [50] LEE WC, LIM CH, KENRY, et al. Cell-assembled graphene biocomposite for enhanced chondrogenic differentiation. Small. 2014;11(8):963-969. [51] CHENG Z, LANDISH B, CHI Z, et al. 3D printing hydrogel with graphene oxide is functional in cartilage protection by influencing the signal pathway of Rank/Rankl/OPG. Mater Sci Eng C. 2017: S0928493117321306. [52] SHAMEKHI MA, MIRZADEH H, MAHDAVI H, et al. Graphene oxide containing chitosan scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Biol Macromol. 2019;6(127):396-405. [53] TUAN RS. A second-generation autologous chondrocyte implantation approach to the treatment of focal articular cartilage defects. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(5):109-109. [54] LIAO J F, QU Y, CHU B Y, et al. Biodegradable CSMA/PECA/ graphene porous hybrid scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. Sci Rep. 2015;5(34):9879. [55] YOCHAM KM, SCOTT C, FUJIMOTO K, et al. Mechanical properties of graphene foam and graphene foam-tissue composites. Adv Eng Mater. 2018;20(9):pii:1800166. [56] SINGH V, JOUNG D, ZHAI L, et al. Graphene based materials: past, present and future. Prog Mater Sci. 2011;56(8):1178-1271. [57] ASIRI AM, MARWANI HM, KHAN SB, et al. Greater cardiomyocyte density on aligned compared with random carbon nanofibers in polymer composites. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;2014(Issue 1): 5533-5539. [58] MATTIOLIBELMONTE M, GIAVARESI G, BIAGINI G, et al. Tailoring biomaterial compatibility: in vivo tissue response versus in vitro cell behavior. Int J Artifi Organs. 2003;26(12):1077-1085. [59] YUAN X, ARKONAC DE, CHAO PH, et al. Electrical stimulation enhances cell migration and integrative repair in the meniscus. Sci Rep. 2014;4(4):3674. [60] LIAO JF, QU Y, CHU BY, et al. Biodegradable CSMA/PECA/ Graphene Porous Hybrid Scaffold for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9879. [61] 钱志勇.可降解硫酸软骨素/PECA/石墨烯复合支架用于软骨修复工程[C].2014中国功能材料科技与产业高层论坛摘要集.2014. [62] DELIORMANLI AM, HARIKA A. Biological Response of Osteoblastic and Chondrogenic Cells to Graphene-Containing PCL/Bioactive Glass Bilayered Scaffolds for Osteochondral Tissue Engineering Applications. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2018;186(4):972-989. [63] 石雁.PVA基水凝胶仿生关节软骨材料增强改性研究[D].南京:南京理工大学,2017. [64] 杜高来.高强韧功能水凝胶的制备及其应用[D].宁波:中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所,2016. [65] 陈炯润.用于骨软骨修复的仿生化高强度PVA水凝胶的研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2017. [66] WU DB, CKSTR ME, HAKKARAINEN M. Starch derived nanosized graphene oxide functionalized bioactive porous starch scaffolds. Macromol Biosci. 2017:1600397. [67] ZHANG Y, ZHANG M, JIANG H, et al. Bio-Inspired layered chitosan/ graphene oxide nanocomposite hydrogels with high strength and ph- driven shape memory effect. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;177:116-125. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [6] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [7] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [8] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [9] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [10] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [11] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [12] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [13] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [14] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [15] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

