Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (27): 4356-4362.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1385
Previous Articles Next Articles
Changes of kidney in rat models of type 2 diabetes mellitus after administering Lizhong Decoction
Liang Lichang1, 2, Fan Yawen1, 2, Mu Lei1, 2, Xie Tian1, 2, Jiang Xiaobing3, Ren Hui3, Zhang Tianfeng1
- (1Shenzhen Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Futian), Shenzhen 518034, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 3the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China)
-
Received:2019-03-30Online:2019-09-28Published:2019-09-28 -
Contact:Zhang Tianfeng, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Shenzhen Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Futian), Shenzhen 518034, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Liang Lichang, Doctoral candidate, Shenzhen Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Futian), Shenzhen 518034, Guangdong Province, China; Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81774338 (to JXB); the Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine Bureau of Guangdong Province, No. 20184018 (to ZTF); the Research Project of Shenzhen Health and Family Planning Commission, No. SZXJ2017071 (to ZTF); the Research Project of Futian District Science and Technology Bureau of Shenzhen, No. FTWS2017002 (to ZTF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Lichang, , Fan Yawen, , Mu Lei, , Xie Tian, , Jiang Xiaobing, Ren Hui, Zhang Tianfeng. Changes of kidney in rat models of type 2 diabetes mellitus after administering Lizhong Decoction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(27): 4356-4362.
share this article
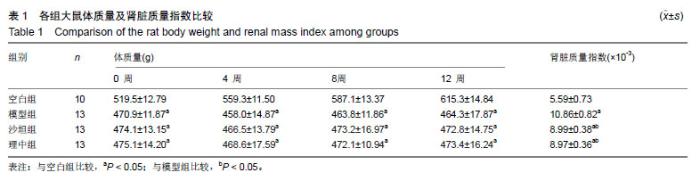
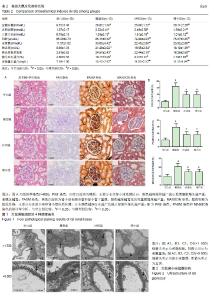
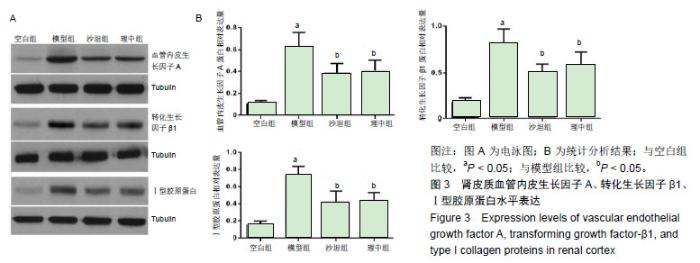
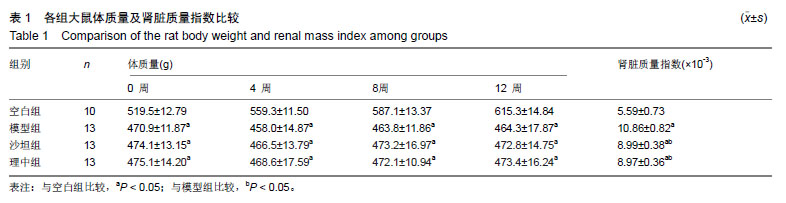
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验选用大鼠60只,分为空白组10只和造模组50只,剔除不符合食源性肥胖9只及不符合2型糖尿病模型的2只大鼠,其余49只大鼠(分为4组)进入结果分析。 2.2 大鼠一般情况、体质量和肾脏质量指数 正常组大鼠毛色洁白有光泽,活动状态良好,反应灵敏,饮食及尿便正常。造模组大鼠于注射链脲佐菌素后出现明显的多饮、多食、多尿,毛色泛黄无光泽、反应稍迟钝等症状。与空白组比较,给药0,4,8,12周时,各组大鼠的体质量均下降(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,在给药后各时间点理中组和沙坦组大鼠的体质量差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。给药12周后,与空白组比较,各组大鼠肾脏质量指数显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,理中组和沙坦组大鼠的肾脏质量指数均明显降低(P < 0.05),但2组间比较无明显差异(P > 0.05)。见表1。 2.3 各项肾脏相关的生化指标 给药12周后,与空白组相比,各组的空腹血糖、总胆固醇、三酰甘油、肌酐、尿素氮、胰岛素、胰岛素抵抗指数、糖化血红蛋白和尿微量白蛋白均显著升高(P < 0.05)。与模型组相比,理中组能降低血糖、总胆固醇、三酰甘油、胰岛素、胰岛素抵抗指数和糖化血红蛋白(P < 0.05),而沙坦组降低作用无显著性意义(P > 0.05);同时与模型组相比,理中组和沙坦组均可以明显降低肌酐、尿素氮和尿微量白蛋白(P < 0.05), 但2组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。见表2。 2.4 肾脏组织形态学变化 ①4种特殊染色综合分析见图1。空白组肾小球和肾小管形态基本正常,球内毛细血管腔清晰且无扩张,系膜细胞无增生,系膜基质分布正常,有完整的囊壁结构,肾小球和肾小管间隙有少量胶原纤维分布;模型组肾小球出现代偿性扩张或萎缩,系膜细胞明显增生,系膜区增宽,基底膜增厚,部分球囊壁出现粘连,肾小管上皮细胞出现空泡变性,肾小球和肾小管间隙胶原纤维明显增多,出现肾小球硬化;理中组和沙坦组肾脏的病理变化较模型组明显减轻,系膜细胞和系膜基质轻度增生,局部基底膜增厚,肾小管上皮细胞空泡变性减少,肾小球和肾小管间隙胶原纤维明显减少。3种染色阳性率分析:与模型组比较,理中组和沙坦组PAS、PASM、MASSON染色阳性率均显著降低(P < 0.05);②透射电镜观察见图2。与空白组比较,模型组可见肾小球内系膜细胞增生,系膜区基质增多变宽、基底膜明显增厚,足突排列紊乱,部分足突融合,足突间隙增宽。与模型组比较,理中组和沙坦组系膜细胞、系膜基质、基底膜和足突改变均有所减轻。 2.5 肾皮质血管内皮生长因子A、转化生长因子β1、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达 与空白组比较,糖尿病各组大鼠血管内皮生长因子A、转化生长因子β1、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05)。与模型组比较,理中组和沙坦组血管内皮生长因子A、转化生长因子β1、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达明显降低(P < 0.05),但理中组和沙坦组2组间比较无明显差异(P > 0.05)。见图3。 "
| [1]Patschan D,Muller GA.Acute Kidney Injury in Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Nephrol.2016;2016: 6232909.[2]Riddy DM,Delerive P, Summers RJ, et al. G Protein-Coupled Receptors Targeting Insulin Resistance, Obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Pharmacol Rev.2018;70(1): 39-67.[3]Maleckas A,Venclauskas L,Wallenius V,et al.Surgery in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Scand J Surg.2015;104(1): 40-47.[4]中华医学会糖尿病分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J].中国实用内科杂志,2018,38(4): 292-344.[5]中华医学会糖尿病分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2013年版) [J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2017, 7(3): 26-88.[6]Liang S,Cai GY,Chen XM.Clinical and pathological factors associated with progression of diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton).2017;22 Suppl 4:14-19.[7]Chen ZJ,Ma F,Sun XM,et al.Renoprotective Effect of a Chinese Herbal Formula, Qidan Dihuang Decoction, on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in Rat. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2018; 2018: 7321086.[8]Dong H, Zhou Y, Wang Y, et al. The protective role of intermedin in promoting angiogenesis during renal fibrosis.Gene.2018;688: 34-43.[9]Nguyen-Thanh T,Kim D,Lee S,et al.Inhibition of histone deacetylase 1 ameliorates renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis via modulation of inflammation and extracellular matrix gene transcription in mice.Int J Mol Med.2018;41(1):95-106.[10]Carranza K, Veron D, Cercado A, et al. Cellular and molecular aspects of diabetic nephropathy; the role of VEGF-A.Nefrologia. 2015;35(2): 131-138.[11]D'Arpino MC,Fuchs AG,Sanchez SS,et al.Extracellular matrix remodeling and TGF-beta1/Smad signaling in diabetic colon mucosa.Cell Biol Int.2018;42(4): 443-456.[12]Kanta J.Collagen matrix as a tool in studying fibroblastic cell behavior.Cell Adh Migr.2015; 9(4): 308-316.[13]Kawanami D,Matoba K,Takeda Y,et al.SGLT2 Inhibitors as a Therapeutic Option for Diabetic Nephropathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(5).[14]DeFronzo RA,Ferrannini E,Groop L, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers.2015; 1: 15019.[15]Kao KT,Sabin MA.Type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Aust Fam Physician.2016;45(6):401-406.[16]仝小林,倪青,魏军平,等.糖尿病中医诊疗标准[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2011,6(6)540-547.[17]朱章志,裴倩.扶阳法治疗糖尿病[J]. 药品评价,2009,6(12):471-472.[18]武文慧,裴香萍,门九章,等.门九章运用理中汤加味治疗放化疗后呕吐经验[J].湖北中医杂志,2018, 40(4): 18-20.[19]国家中医药管理局医政司. 24个专业92个病种中医诊疗方案[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2017:194.[20]张广梅,李杰,吴萍,等.血清D-木糖与太阴病(脾阳虚证)“欲解时”及理中汤干预的研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2018,33(10): 4685-4688.[21]吴水生,郭改革,李长伟,等.中药“疾病缩减效应”假说与理中丸抗消化性溃疡多成分多靶点整合协同作用的实验验证[J].世界科学技术(中医药现代化),2010,12(4): 580-584.[22]段永强,程卫东,李兰珍,等.四君子汤和理中汤对脾虚肠易激综合征大鼠一氧化氮信号通路及胃动素表达影响的差异[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,(18): 5148-5151.[23]周晓玲,唐农,余静芳,等.理中汤对肝硬化大鼠肠道微生态的影响[J].辽宁中医杂志,2018,45(7): 1521-1525.[24]陈丽艳,陈鹏,孙银玲,等.玉米须对2型糖尿病模型大鼠降糖机制研究[J].中华中医药杂志, 2016, 31(10): 4253-4255.[25]施红,金国琴,余文珍.诱导构建最佳类似人类2型糖尿病大鼠的造模方式[J].中国组织工程研究,2005, 9(39): 69-71.[26]桂莉, 郭家智, 曹梅,等.高脂?高胆固醇灌胃诱导2型糖尿病SD大鼠模型的实验研究.昆明医学院学报,2010, 31(10): 41-44.[27]张松筠,杨长春,郝咏梅,等. 食源性肥胖大鼠2型糖尿病模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究,2010, 14(28): 5212-5215.[28]Levin BE, Hogan S, Sullivan AC. Initiation and perpetuation of obesity and obesity resistance in rats. Am J Physiol.1989;256(3 Pt 2): R766-771.[29]Levin BE, Dunn-Meynell AA,Balkan B,et al.Selective breeding for diet-induced obesity and resistance in Sprague-Dawley rats. Am J Physiol.1997;273(2 Pt 2): R725-730.[30]陈凤丽,曹晨,孙亦农,等.高脂饲料诱发大鼠肥胖模型的实验研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2015,42(9):1792-1794.[31]Zhang S, Xu H, Yu X, et al. Metformin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in a rat model of low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes.Exp Ther Med.2017;14(1):383-390.[32]Chen P,Shi X, Xu X,et al.Liraglutide ameliorates early renal injury by the activation of renal FoxO1 in a type 2 diabetic kidney disease rat model.Diabetes Res Clin Pract.2018;137: 173-182.[33]Sugano M,Yamato H,Hayashi T,et al.High-fat diet in low-dose- streptozotocin-treated heminephrectomized rats induces all features of human type 2 diabetic nephropathy: a new rat model of diabetic nephropathy.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2006;16(7): 477-484.[34]Kim Y, Park CW. Adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2016;35(2): 69-77.[35]Dugbartey GJ.Diabetic nephropathy: A potential savior with 'rotten-egg' smell.Pharmacol Rep. 2017;69(2): 331-339.[36]Liu C,Feng X,Li Q,et al.Adiponectin, TNF-alpha and inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cytokine.2016;86: 100-109.[37]林子桐,张超,沈雪梅.糖尿病肾病发病机制研究进展[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2014,28(5): 765-773.[38]Almeida J, Mello V, Canani L, et al. Role of dietary lipids in diabetic nephropathy. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol.2009;53(5): 634-645.[39]Gin H, Rigalleau V, Aparicio M. Lipids, protein intake, and diabetic nephropathy.Diabetes Metab. 2000;26: 45-53.[40]Zhang L,Chen Z,Gong W,et al.Paeonol Ameliorates Diabetic Renal Fibrosis Through Promoting the Activation of the Nrf2/ARE Pathway via Up-Regulating Sirt1. Front Pharmacol.2018;9: 512.[41]Kinashi H, Ito Y, Sun T, et al. Roles of the TGF-beta(-)VEGF-C Pathway in Fibrosis-Related Lymphangiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(9). pii: E2487.[42]Tetiko?lu M, Yüksel Z, Aktas S, et al. VEGF-A gene polymorphisms and responses to intravitreal ranibizumab treatment in patients with diabetic macular edema. Int Ophthalmol. 2018;38(6):2381-2388. [43]Chellini F, Tani A, Vallone L, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Prevents In Vitro Transforming Growth Factor-beta1-Induced Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Transition: Involvement of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)-A/VEGF Receptor-1-Mediated Signaling (dagger). Cells. 2018;7(9). pii: E142.[44]Wei J, Jiang H, Gao H, et al. Blocking Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Attenuates HIF-1alpha Pathways Engaged-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in Diabetic Retinopathy.Cell Physiol Biochem.2016;40(6):1570-1577.[45]Mortuza R,Feng B,Chakrabarti S.SIRT1 reduction causes renal and retinal injury in diabetes through endothelin 1 and transforming growth factor β1. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(8): 1857-1867.[46]王劲松. TGF-β1?CTGF在增生性糖尿病视网膜病变患者血清中的表达及意义[J].临床眼科杂志,2014, 22(5): 464-466.[47]贾会玉,李中南,陈光亮.转化生长因子-β1介导的Smads和MAPKs信号通路在糖尿病肾病中的作用及其抑制剂研究进展[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2015,20(10):1171-1176.[48]Genovese F,Manresa AA,Leeming DJ,et al.The extracellular matrix in the kidney: a source of novel non-invasive biomarkers of kidney fibrosis?.Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair.2014;7(1): 1-12. |
| [1] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [2] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [3] | Zhang Hui, Wang Shaohua, Wang Qian, Wang Hui, Gan Hongquan, Cui Yishuang, Li Qijia, Wang Zhiqiang. Porous tantalum coated with RGD polypeptide can activate the integrin/focal adhesion kinase signaling pathway of MG63 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2535-2540. |
| [4] | Chen Qiang, Zhuo Hongwu, Xia Tian, Ye Zhewei . Toxic effects of different-concentration isoniazid on newborn rat osteoblasts in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1162-1167. |
| [5] |
Zhang Cong, Zhao Yan, Du Xiaoyu, Du Xinrui, Pang Tingjuan, Fu Yining, Zhang Hao, Zhang Buzhou, Li Xiaohe, Wang Lidong.
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine and pelvis in adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis with lumbar major curve |
| [6] | He Yujie, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Cai Yongqiang, Dai Lina, Xu Yangyang, Wang Yidan, Xu Xuebin. Digital measurements of the anatomical parameters of pedicle-rib unit screw fixation in thoracic vertebrae of preschoolers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 869-876. |
| [7] | Wu Qi, Liao Ying, Sun Guanghua, Zhou Guijuan, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Zhong Peirui, Cheng Guo, Deng Chengyuan, Wang Tiantian. Changes of subchondral bone in rat models of knee osteoarthritis treated by elcatonin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 709-715. |
| [8] | Sun Jian, Fang Chao, Gao Fei, Wei Laifu, Qian Jun. Clinical efficacy and complications of short versus long segments of internal fixation for the treatment of degenerative scoliosis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 438-445. |
| [9] | Yan Caiping, Chen Lu, Deng Changgong, Chen Qian, Jiang Ke, Yi Yuanyuan, Li Yuling. Beta-ecdysterone promotes in vitro proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4605-4612. |
| [10] | Li Xuewei, Hu Beibei, Zhang Dawei, Quan Lulu, Liang Yongqiang. Calcium hydrogen phosphate dehydrate combined with gelatin and recombinant human bone morphologic protein 2/7 for repair of bone defects in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4533-4539. |
| [11] |
Li Ying, Lin Wentao, Weng Xiquan.
Effects of different exercise intensities on visfatin level and glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4196-4200. |
| [12] | Xu Yangyang, Zhang Kai, Li Zhijun, Zhang Yunfeng, Su Baoke, Wang Xing, Wang Lidong, Wang Yidan, He Yujie, Li Kun, Wang Haiyan, Li Xiaohe. Morphological analysis of optimal selection of lumbar pedicle screws in adolescents aged 12-15 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3321-3328. |
| [13] | Jiang Han, Ding Jie, Chen Gen, Xie Qiang, Li Wei, Wang Zhibin, Zhu Lei. Hypoxia-mediated miRNAs affect glucose metabolism: new recognition of preventing and controlling glucose metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 303-311. |
| [14] | Liu Yuetong, Wang Qin, Yang Ye, Zhu Jun, Abulikemu•Tuerdi. Effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on microRNA-130b and transforming growth factor beta 1 in renal tissue of rat models of diabetic nephropathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 248-253. |
| [15] | Qin Haikuo, Luo Shixing. Correlation of cortical bone thickness and X-ray gray value in different planes of proximal femur with brittle fracture of female hip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2867-2872. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||