Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (22): 3500-3505.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1277
Previous Articles Next Articles
Osteogenic property of beta-tricalcium phosphate/alpha-calcium sulphate hemihydrate combined bone graft in multi-segment posterolateral arthrodesis of rabbit thoracic vertebrae
- 1Department of Traumatic Hand and Foot Surgery, Taian City Central Hospital, Taian 271000, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, General Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100853, China
-
Received:2019-03-13 -
About author:Liang Maohua, MD, Attending physician, Department of Traumatic Hand and Foot Surgery, Taian City Central Hospital, Taian 271000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51772328 (to MKY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Maohua, Mao Keya, Xia Bo, Liu Qiang,Tang Peifu, Wang Jifang. Osteogenic property of beta-tricalcium phosphate/alpha-calcium sulphate hemihydrate combined bone graft in multi-segment posterolateral arthrodesis of rabbit thoracic vertebrae[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(22): 3500-3505.
share this article
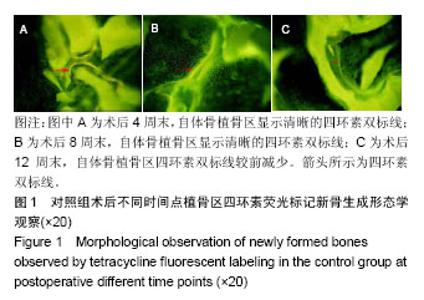
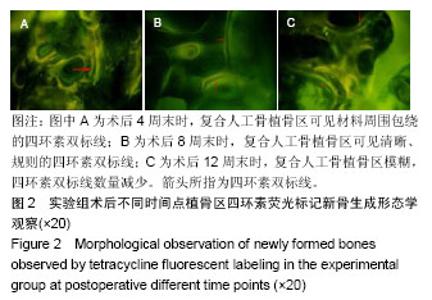
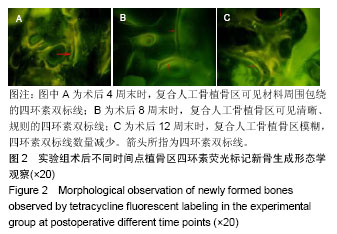
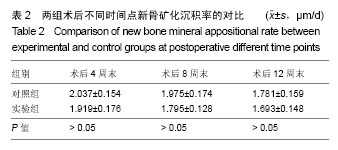
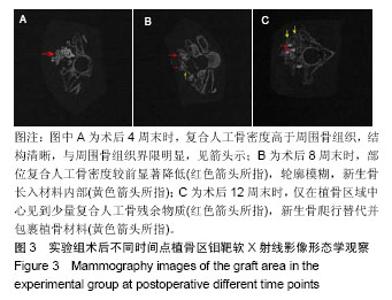
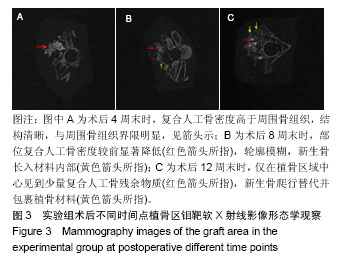
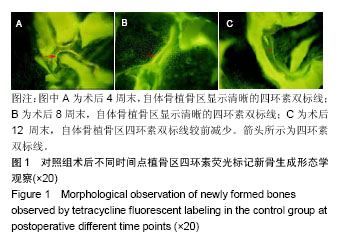
2.1 实验动物数量分析 36只新西兰大白兔均进入结果分析。 2.2 四环素荧光标记新骨生成形态学观察结果 对照组:实验全程皆可见植骨区内浓聚的荧光标记,术后4周末时,四环素荧光标记线主要位于自体骨植骨区域边缘;术后8周末时,荧光标记已出现在植骨块中央地区,说明在此时段新骨沉积到达自体植骨的内部,此时四环素双标线为实验全程最整齐清晰时段,说明此时新骨矿化沉积最活跃;至术后12周末时,自体骨植骨区中央及无缘地带的荧光标记已经显著减少,说明这时新骨矿化沉积速率显著减低,见图1。 实验组:同自体植骨区一致,实验全程皆可见复合人工骨植骨区中浓聚的四环素荧光标记,材料被荧光物质围绕,术后8周末时,复合人工骨区域四环素荧光标线最为整齐清晰,说明此时新骨生成沉积最活跃;术后4周末时,四环素荧光标线主要位于复合人工骨的边缘地带;术后8,12周末时,四环素荧光标记线已进入复合人工骨中央区域,说明新生骨已爬行长入复合人工骨中央区域,见图2。 新骨矿化沉积率:随时间的延长,两组植骨材料的新骨矿化沉积率逐渐下降,复合人工骨植骨区术后不同时间点的新骨矿化沉积率均较自体骨植骨区域稍慢,但组间差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表2。"
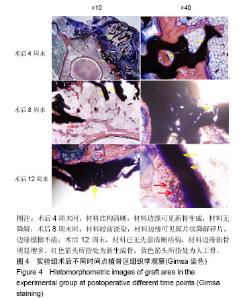
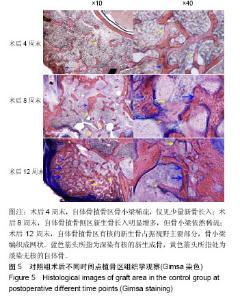
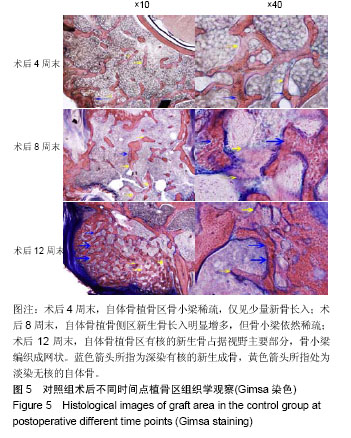
2.4 组织学Giemsa染色观察结果 实验组:术后4周末时,复合人工骨中的α-半水硫酸钙已被全部吸收降解,仅见到β-磷酸三钙,结构完整清晰,未见材料周边有降解痕迹,可见β-磷酸三钙周边区域有新骨生成包绕;至术后8周末时,β-磷酸三钙周边新生骨进一步增多并爬行入材料内部,已对材料形成包围,但新生骨骨小梁结构凌乱而不规则,边缘可见其少量降解碎片,材料染色较术后4周末时明显变淡;至术后12周末时,新生骨组织完全包围,可见增粗的骨小梁结构,β-磷酸三钙材料边缘可见大量降解而成的碎片状结构,β-磷酸三钙结构已不清晰,见图4。 对照组:术后4周末时,自体骨植骨区可见杂乱稀疏的骨小梁,有核的新生骨出现于自体植骨块周围,但占绝大多数的仍然是淡染的无核自体骨植骨块;术后8周末时,新生骨组织进一步增多,占据视野主导地位的已是有核的新生骨组织,但新生骨骨小梁排列杂乱、稀疏而无规则;术后12周末时,自体骨植骨区域已形成大量新生骨组织,自体骨植骨块被新生骨完全取代,骨小梁排列整齐、规则,局部仅可见少量无核的自体骨植骨块,见图5。"

| [1]Abdullah KG,Steinmetz MP,Benzel EC,et al.The state of lumbar fusion extenders. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2011;36(20):E1328-1334.[2]Buser Z,Brodke DS,Youssef JA,et al.Synthetic bone graft versus autograft or allograft for spinal fusion: a systematic review.J Neurosurg Spine. 2016; 25(4):509-516.[3]Mao K,Cui F,Li J,et al.Preparation of combined β-TCP/α-CSH artificial bone graft and its performance in a spinal fusion model.J Biomater Appl. 2012; 27(1):37-45.[4]毛克亚,李江涛,杨云,等.β-TCP/α-CSH复合植骨材料的制备与理化性能检测[J].生物医学工程与临床, 2011,15(3):205-209.[5]Parfitt AM.Bone histomorphometry: proposed system for standardization of nomenclature, symbols, and units.Calcif Tissue Int.1988;42(5):284-286.[6]Pierannunzii L,Zagra L.Bone grafts, bone graft extenders, substitutes and enhancers for acetabular reconstruction in revision total hip arthroplasty. EFORT Open Rev.2016;1(12):431-439.[7]Fillingham Y,Jacobs J.Bone grafts and their substitutes.Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(1 Suppl A):6-9.[8]Rh OG,Dard M,Larjava H.Hydoxyapatite/beta-tricalcium phosphate biphasic ceramics as regenerative material for the repair of complex bone defects.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2018;106(6): 2493-2512.[9]Barbanti BG,Griffoni C,Nataloni A,et al.Biomaterials as bone graft substitutes for spine surgery: from preclinical results to clinical study.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents.2017;31(4 suppl 1):167-181.[10]Pulyala P,Singh A,Dias-Netipanyj MF,et al.In-vitro cell adhesion and proliferation of adipose derived stem cell on hydroxyapatite composite surfaces.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;75: 1305-1316.[11]Oliveira HL,WLO DR,Cuevas-Suárez CE,et al.Histological Evaluation of Bone Repair with Hydroxyapatite: A Systematic Review.Calcif Tissue Int. 2017;101(4):341-354.[12]Li B,Liu Z,Yang J,et al.Preparation of bioactive β-tricalcium phosphate microspheres as bone graft substitute materials.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;70(Pt 2): 1200-1205.[13]Fathima H, Harish. Osteostimulatory effect of bone grafts on fibroblast cultures. J Nat Sci Biol Med.2015;6(2):291-294.[14]Dahabreh Z,Panteli M,Pountos I,et al.Ability of bone graft substitutes to support the osteoprogenitor cells: An in-vitro study.World J Stem Cells. 2014;6(4):497-504.[15]Barradas AM,Monticone V,Hulsman M,et al. Molecular mechanisms of biomaterial-driven osteogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stromal cells.Integr Biol (Camb).2013;5(7):920-931.[16]毛文文,茹江英.羟基磷灰石类陶瓷在骨组织工程中的研究与更广泛应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(30):4855-4863.[17]Rakhmatia YD,Ayukawa Y,Jinno Y,et al.Micro-computed tomography analysis of early stage bone healing using micro-porous titanium mesh for guided bone regeneration: preliminary experiment in a canine model. Odontology. 2017;105(4):408-417.[18]Demirel M,Aksakal B.Effect of porosity on the structure, mechanical properties and cell viability of new bioceramics as potential bone graft substitutes.Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2018;20(2):11-22.[19]Pihlman H,Keränen P,Paakinaho K,et al.Novel osteoconductive β-tricalcium phosphate/poly(L-lactide-co-e-caprolactone) scaffold for bone regeneration: a study in a rabbit calvarial defect.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018;29(10):156.[20]Okada T,Kanai T,Tachikawa N,et al.Histological and Histomorphometrical Determination of the Biogradation of β-Tricalcium Phosphate Granules in Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation: A Prospective Observational Study. Implant Dent.2017;26(2):275-283.[21]Tanaka T,Komaki H,Chazono M,et al.Basic research and clinical application of beta-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP).Morphologie.2017;101(334): 164-172.[22]Matsunaga A,Takami M,Irié T,et al.Microscopic study on resorption of β-tricalcium phosphate materials by osteoclasts.Cytotechnology. 2015 ; 67(4):727-732.[23]Jelusic D,Zirk ML,Fienitz T,et al.Monophasic ß-TCP vs. biphasic HA/ß-TCP in two-stage sinus floor augmentation procedures - a prospective randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res.2017;28(10):e175-e183.[24]Fouad H,AlFotawi R,Alothman OY,et al.Porous Polyethylene Coated with Functionalized Hydroxyapatite Particles as a Bone Reconstruction Material.Materials (Basel).2018;11(4). pii: E521. doi: 10.3390/ma11040521.[25]Leventis M,Fairbairn P,Mangham C,et al.Bone Healing in Rabbit Calvaria Defects Using a Synthetic Bone Substitute: A Histological and Micro-CT Comparative Study.Materials (Basel).2018;11(10). pii: E2004. doi: 10.3390/ma11102004.[26]Shih TC,Teng NC,Wang PD,et al.In vivo evaluation of resorbable bone graft substitutes in beagles: histological properties.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013; 101(8):2405-2411.[27]Pförringer D,Harrasser N,Mühlhofer H,et al.Osteoinduction and -conduction through absorbable bone substitute materials based on calcium sulfate: in vivo biological behavior in a rabbit model. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018; 29(2):17.[28]Tan V,Evaniew N,Finlay K,et al.Chronology of the Radiographic Appearances of the Calcium Sulfate-Calcium Phosphate Synthetic Bone Graft Composite Following Resection of Bone Tumors: A Follow-up Study of Postoperative Appearances.Can Assoc Radiol J.2016;67(1):21-27.[29]谭海涛,孟志斌,李俊,等.β磷酸三钙和α半水硫酸钙复合人工骨生物相容性及在脊柱融合模型中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(26):4119-4124.[30]Orellana BR,Hilt JZ,Puleo DA.Drug release from calcium sulfate-based composites. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2015;103(1):135-142.[31]Wu CC,Huang YK,Chang WJ,et al.Limitation of the antibiotic-eluting bone graft substitute: An example of gentamycin-impregnated calcium sulfate.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2018;106(1): 80-87.[32]王骞,耿广起,丛晓明,等.载三联抗痨药硫酸钙/聚氨基酸缓释材料在兔脊柱结核模型体内的缓释性能[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(10):1520-1526.[33]Civinini R,Capone A,Carulli C,et al.The kinetics of remodeling of a calcium sulfate/calcium phosphate bioceramic.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2017;28(9):137.[34]Sakata M,Tonomura H,Itsuji T,et al.Bone Regeneration of Osteoporotic Vertebral Body Defects Using Platelet-Rich Plasma and Gelatin β-Tricalcium Phosphate Sponges. Tissue Eng Part A.2018; 24(11-12): 1001-1010. |
| [1] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| [2] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [3] | Liu Lihua, Sun Wei, Wang Yunting, Gao Fuqiang, Cheng Liming, Li Zirong, Wang Jiangning. Type L1 steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head through femoral head and neck junction decompression by fenestration: a single-center prospective clinical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 906-911. |
| [4] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [5] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [6] | Zhang Qifu, Ma Yonghong, Wang Tao, Hu Yibo, Zhang Heling, Zong Qunchuan. Effects of anterior corpectomy and fusion versus posterior single open-door laminoplasty on cervical range of motion of patients with multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3870-3874. |
| [7] | Gao Kun, Chen Dayu, Zhang Yong, Liu Weidong, Sun Shufen, Lai Wenqiang, Ma Dujun, Wu Yihong, Lin Zhanpeng, Jiang Yinglu, Yu Weiji. Achyranthes bidentata alcohol extract inhibits extracellular matrix degradation of the cartilage by regulating synovial fibroblast exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3636-3640. |
| [8] | Zhou Anqi, Tang Yufei, Wu Bingfeng, Xiang Lin. Designing of periosteum tissue engineering: combination of generality and individuality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [9] | Lang Limin, He Sheng, Jiang Zengyu, Hu Yiyi, Zhang Zhixing, Liang Minqian. Application progress of conductive composite materials in the field of tissue engineering treatment of myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [10] | Liu Jun, Yang Long, Wang Weiyu, Zhou Yuhu, Wu Ying, Lu Tao, Shu Liping, Ma Minxian, Ye Chuan. Preparation and properties of poly3-hydroxybutyrate 4-hydroxybutyrate/polyethylene glycol/graphene oxide tissue-engineered scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3466-3472. |
| [11] | Li Yuefei, Li Rui, Ren Jiabin, Liu Xin, Sun Ning, Liu Weike, Bi Jingwei, Sun Zhaozhong. Three-dimensional CT analysis of the treatment of thoracic disc herniation by percutaneous endoscopic posterolateral approach: establishment of a good osseous channel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3354-3359. |
| [12] | Liu Xing, Wei Xiaohan, Deng Jie, Li Zhongming . Preparing a blunt contusion model of rabbit skeletal muscle under different blow strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 196-200. |
| [13] | Mu Yufeng, Wei Lina, Wu Yong, Shao Anliang, Chen Liang, Qu Shuxin, Xu Liming. Development and evaluation of alpha-galactosyl antigen-deficient rabbit model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 281-285. |
| [14] | Cao Yang, Zhang Junping, Peng Li, Ding Yi, Li Guanghui. Isolation and culture of rabbit aortic endothelial cells and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [15] | Chen Pu, Ruan Anmin, Zhou Jun, Zhang Xiaozhe, Ma Yufeng, Zong Chenzhong, Wang Qingpu. Effect of Tongluo Analgesic Gel on cartilage inflammation and degeneration in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2670-2675. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||