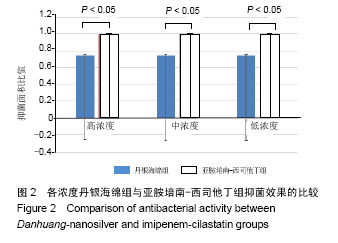
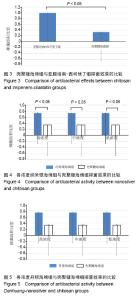
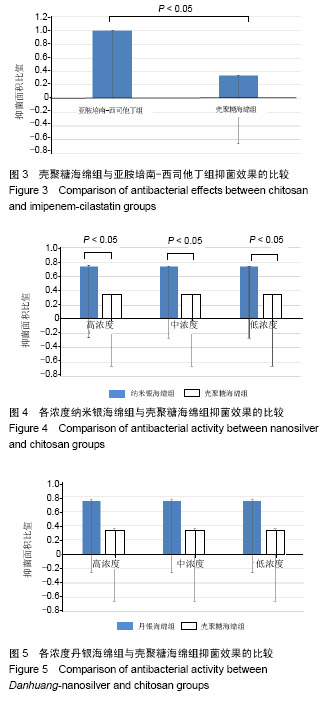
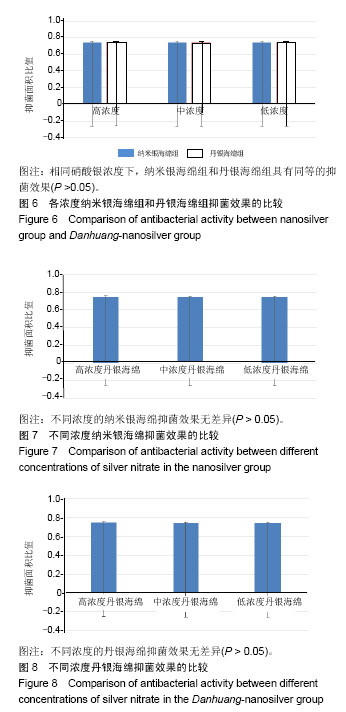
| [1]Zhang P,Lu J,Jing Y,et al.Global epidemiology of diabetic foot ulceration: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Med. 2016; 49(2):106-116.[2]He Y,Qian H,Xu L,et al.Association between estimated glomerular filtration rate and outcomes in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: a 3-year follow-up study. Eur J Endocrinol.2017;177(1):41-50.[3]罗伟,刘高熊,池卫东,等.不同致病菌感染对糖尿病足溃疡患者病情与预后影响分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2018,28(10):1511-1514.[4]项家丽,张杰,王淑敏,等.继发铜绿假单胞菌感染的糖尿病足溃疡患者病情特点及预后分析[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2018,34(5):371-376.[5]幸运,鲁卫平,喻华,等.中国西部地区耐亚胺培南-西司他丁铜绿假单胞菌的分布及耐药特点[J].中国抗生素杂志, 2018,43(9):1079-1082.[6]Subedi D,Vijay AK,Willcox M.Overview of mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa : an ocular perspective.Clin Exp Optom.2018;101(2):162-171.[7]Bowling FL,Rashid ST,Boulton AJ.Preventing and treating foot complicationsassociated with diabetes mellitus.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015;11(10):606-616.[8]中国医疗保健国际交流促进会糖尿病足病分会.中国糖尿病足诊治指南[J].中华医学杂志,2017,97(4):251-258.[9]Lim JZ,Ng NS,Thomas C.Prevention and treatment of diabetic foot ulcers.J R Soc Med. 2017;110(3):104-109.[10]Armstrong DG,Boulton AJM,Bus SA.Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Their Recurrence.N Engl J Med. 2017;376(24):2367-2375.[11]中国微循环学会周围血管疾病专业委员会糖尿病足学组.糖尿病足创面修复治疗专家共识[J].中华糖尿病杂志, 2018,10(5):305-309.[12]Armstrong DG,Boulton AJM,Bus SA.Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Their Recurrence.N Engl J Med.2017;376(24):2367-2375.[13]徐波,杨彩哲,刘朝阳,等.糖尿病足感染患者病原菌分布及其药物敏感试验[J].中华传染病杂志,2016,34(6):344-348.[14]王安宇,徐寒松,赵胜,等.基因表达谱差异分析丹黄散对糖尿病足创面修复的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(28): 5233-5236.[15]朱朝军,吕佳康,周贝,等.糖尿病足溃疡外用中药新药临床研究的思考[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2017,33(13):1257-1259.[16]张超.丹黄散促进糖尿病大鼠皮肤溃疡创面愈合的实验研究[D]. 贵阳:贵阳中医学院,2014:1-45.[17]张定安.丹黄散对糖尿病大鼠创面修复作用及CK14、CK15表达的研究[D]. 贵阳:贵阳中医学院,2014:1-57.[18]魏良纲.丹黄散对糖尿病足创面再上皮化能力的影响[D].贵阳:贵阳中医学院, 2013:1-39.[19]邸铁涛,张春玲,陈露,等.丹黄散促进糖尿病足溃疡大鼠创面毛细血管新生[J].糖尿病新世界,2017,20(16):165-166,189.[20]王安宇,乔艺杰,魏良纲.丹黄散外敷治疗糖尿病足的临床疗效观察[J].贵州医药,2011,35(6):505-507.[21]戴新新,宿树兰,郭盛,等.丹参酮类成分的生物活性与应用开发研究进展[J].中草药,2017,48(7):1442-1448.[22]高伟,胡添源,郭娟,等.丹参酮合成生物学研究进展[J].中国中药杂志, 2015,40(13):2486-2491.[23]梁伟雯,陈源,梁颖,等.丹参酮胶囊对临床细菌分离株的体外抑菌作用[J].广东医学,2017,38(24):3792-3795.[24]杨滢.大黄药效成分及其药理活性研究进展[J].中医临床研究, 2018, 10(5):142-144.[25]张斯琪,曾臣红,陈冲,等.如意金黄散的现代研究进展[J].中成药, 2018, 40(2):411-415.[26]张博,朱建光.浅析大黄在《伤寒杂病论》中的应用及其现代药理机制[J].中医学报,2017,32(5):766-769.[27]张来宾,吕洁丽,陈红丽,等.当归中苯酞类成分及其药理作用研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2016,41(2):167-176.[28]张炳厚.理气药的应用与鉴别(三)[J].中医杂志, 2016,57(18):1545-1548.[29]罗淑敏,蒋丽红,王亚明.松香活性基团的改性及应用研究进展[J].天然产物研究与开发,2015,27(4):737-741.[30]刘名倬,刘苗星,王小磊,等.纳米银的抗菌作用及其在烧伤治疗中应用的研究进展[J].中华烧伤杂志,2017,33(2):121-125.[31]Zapata PA,Larrea M,Tamayo L,et al. Polyethylene/ silver-nanofiber composites: A material for antibacterialfilms. Mat Sci Eng C. 2016; (69):1282-1289.[32]陈学情,蒋家璇,任志鸿,等.纳米银的抗菌特性及对多重耐药菌株的抗菌作用[J].微生物学报,2017,57(4):539-549.[33]于晓旭,鲍会静,徐晨,等.纳米银抗菌作用机制:剂量依赖性促进细菌凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(38):6173-6178.[34]Maryam A,Sakineh MS.Effects of silver nanoparticles on the thermal properties of polyethylene matrix nano-composites.Therm Anal Calori.2017;128(2):1117-1124.[35]王君君,薛玉英,唐萌.纳米银在医学领域中的抗菌应用及毒性[J].中华烧伤杂志,2016,32(10):631-634.[36]曹雪玲,陆书来,张东杰,等.纳米银作为抗菌剂的抗菌性能研究[J].吉林化工学院学报,2017,34(11):30-34. |