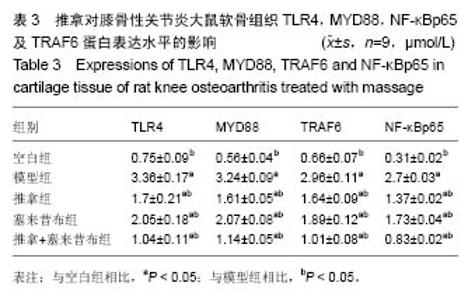
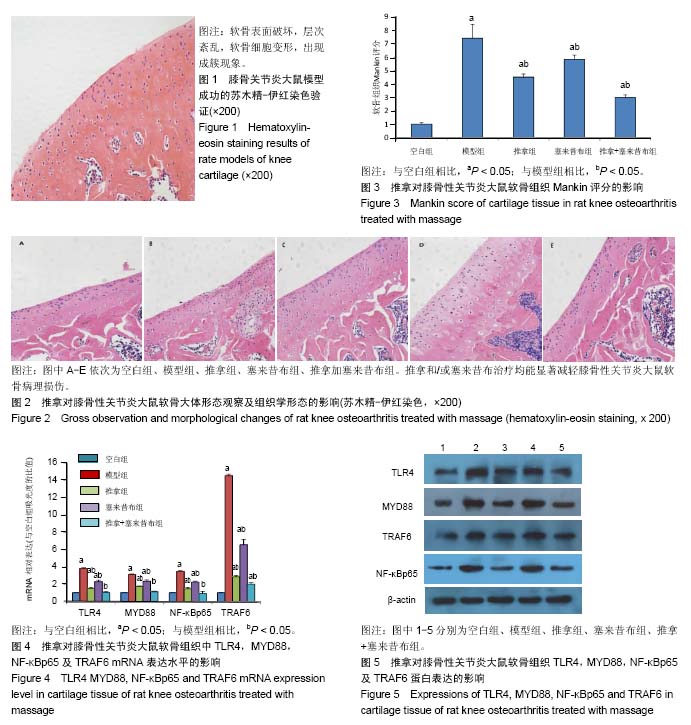
| [1] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印钦.实用骨科学[M].4版.北京:人民军医出版社,2012: 1676-1682.[2] 严隽陶.推拿学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2003:175-176.[3] 李建华,龚利,房敏,等.推拿对膝骨关节炎患者膝屈伸肌肌张力的影响[J].中国骨伤,2011,24(7):575-577.[4] 杜宁,陆勇,顾翔,等.手法促进膝关节炎软骨修复的核磁共振病例对照研究[J].中国骨伤,2008,21(11):824-827.[5] 方苏亭,王胜利.松凝分筋手法治疗兔膝骨性关节炎病的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2001,9(2):27.[6] Pat Archer.运动保健按摩疗法[M].李国惠,译.天津:天津科技翻译出版公司,2008:70.[7] 王春林,向勇,田启东,等.“拔伸松动手法”对膝骨性关节炎兔白细胞介素1β 和肿瘤坏死因子α的影响[J].环球中医药,2014,7(2):85-88.[8] 韦嵩,申茜茸,李晓昊,等.经筋微创松解术治疗膝骨关节炎对TLR4/ MyD88/ NF-κB信号转导通路的影响[J].中华中医药杂志, 2018,33(10): 4637-4641.[9] 郑洁,赵莉平,胡亚莉,等.青藤碱对兔膝骨关节炎模型软骨Toll样受体2、4及髓样分化因子88表达的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2018,25(9):49-51.[10] 李忠仁.实验针灸学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2008:33-35.[11] 魏伟,吴希美,李元建.药理实验方法学[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2010: 1698.[12] 王文胜,陈伟,沈堡垒,等.上、下坡跑台训练膝骨关节炎模型大鼠关节软骨及炎症因子的变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(2):197-200.[13] Mankin HJ. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in osteoarthritic human cartilage. Fed Proc. 1973;32(4):1478-1480.[14] 杨智,程春凤,黄昕艳,等.Trizol法提取新生小鼠脑组织总RNA优化比较[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2012,29(2):155-156.[15] Sofat N, Robertson SD, Wait R. Fibronectin III 13-14 domains induce joint damage via Toll-like receptor 4 activation and synergize with interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor. J Innate Immun. 2012;4(1):69-79. [16] 胡炳麟,龚利,李建华,等.一指禅推法治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床研究[J].中医药导报,2017,23(2):72-74.[17] 朱雪坤,杨日芳,孟艳秋.Toll样受体4配体的研究进展[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2016,30(4):389-396.[18] Temperley ND, Berlin S, Paton IR, et al. Evolution of the chicken Toll-like receptor gene family: a story of gene gain and gene loss. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:62. [19] Anwar MA, Basith S, Choi S. Negative regulatory approaches to the attenuation of Toll-like receptor signaling. Exp Mol Med. 2013;45:e11.[20] 钱臣,卞晓星.Toll 样受体4 表达与膝骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡的关系[J].江苏大学学报,2015,25(2):128-132.[21] Hua F, Ha T, Ma J, et al. Blocking the MyD88-dependent pathway protects the myocardium from ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat hearts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;338(2):1118-1125. [22] Spehlmann ME, Eckmann L. Nuclear factor-kappa B in intestinal protection and destruction. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2009;25(2):92-99.[23] Lim BJ, Lee D, Hong SW, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 signaling is involved in IgA-stimulated mesangial cell activation. Yonsei Med J. 2011;52(4): 610-615. [24] Ye H, Arron JR, Lamothe B, et al. Distinct molecular mechanism for initiating TRAF6 signalling. Nature. 2002;418(6896):443-447.[25] Walsh MC, Lee J, Choi Y. Tumor necrosis factor receptor- associated factor 6 (TRAF6) regulation of development, function, and homeostasis of the immune system. Immunol Rev. 2015;266(1): 72-92. [26] Sina C, Arlt A, Gavrilova O, et al. Ablation of gly96/immediate early gene-X1 (gly96/iex-1) aggravates DSS-induced colitis in mice: role for gly96/iex-1 in the regulation of NF-kappaB. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010; 16(2):320-331. [27] Ostuni R, Zanoni I, Granucci F. Deciphering the complexity of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010;67(24):4109-4134. [28] Yang J, Amiri KI, Burke JR, et al. BMS-345541 targets inhibitor of kappaB kinase and induces apoptosis in melanoma: involvement of nuclear factor kappaB and mitochondria pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(3 Pt 1):950-960.[29] 何璐,吴子建,胡玲,等.艾灸对膝骨性关节炎模型大鼠膝关节软组织中NF-kbp65蛋白和IKB-α蛋白的影响[J].中医药临床杂志,2017,29(6): 856-858.[30] 袁普卫,李小群,康武林,等.蠲痹胶囊对膝骨关节炎豚鼠关节软骨组织形态及滑膜中Toll 样受体4?NF-κB p65及肿瘤坏死因子-α表达的影响[J].中医正骨,2016,28(9):5-12. |