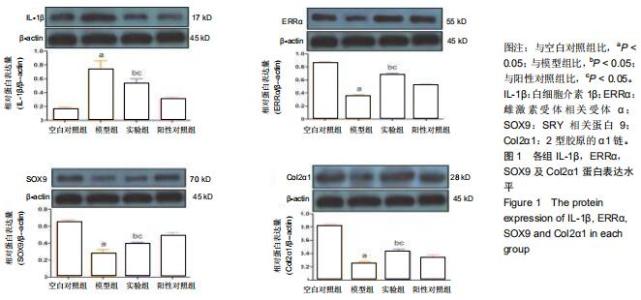
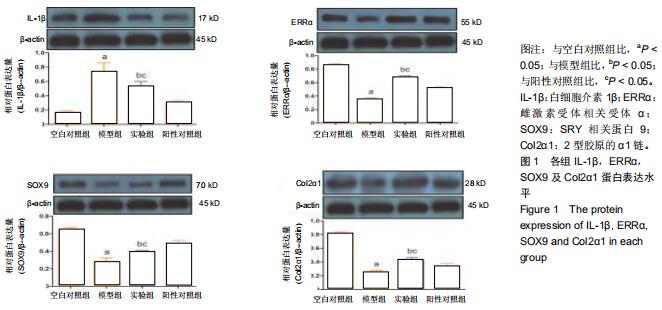
|
[1] CHEN D, SHEN J, ZHAO W, et al. Osteoarthritis: toward a comprehensive understanding of pathological mechanism. Bone Res. 2017;5:6044.
[2] SHARMA AR, JAGGA S, LEE SS, et al. Interplay between cartilage and subchondral bone contributing to pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(10):19805-19830.
[3] 黄枫,唐勇,郑晓辉,等.补肾强膝方对绝经后妇女膝骨性关节炎的影响[J].中医正骨,2002,14(4):12-13.
[4] 霍少川.脏腑辨证指导下绝经后妇女KOA经筋病变的治疗及经筋通方干预机制研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2017.
[5] 汤家铭.实验动物学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2016.
[6] 张晨,马骏,吕雷锋,等.盐酸氨基葡萄糖对膝骨关节炎膝关节软骨下骨Ⅰ型胶原及骨钙素表达的影响[J].郑州大学学报(医学版), 2017, 52(1):9-13.
[7] 王俊玲,黄思敏,梁启瑶,等.雌激素的来源及其在骨代谢中的作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):729-732.
[8] 黄捷,薄占东,刘刚,等.早期膝骨关节炎患者血清雌二醇和睾酮水平与病变程度的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(36):5760-5765.
[9] 马浩哲,黄奎.补肾活血方对肾虚血瘀证膝关节骨性关节炎患者的疗效及其对血清细胞因子的影响[J].世界中医药,2019,14(3):696-699.
[10] KIM YI, NO LJ, BHANDARI S, et al. Cartilage development requires the function of Estrogen-related receptor alpha that directly regulates sox9 expression in zebrafish. Sci Rep. 2015;5: 18011.
[11] BONNELYE E, REBOUL P, DUVAL N, et al. Estrogen receptor- related receptor alpha regulation by interleukin-1beta in prostaglandin E(2)- and cAMP-dependent pathways in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(8): 2374-2384.
[12] BONNELYE E, LAURIN N, JURDIC P, et al. Estrogen receptor- related receptor-alpha (ERR-alpha) is dysregulated in inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatol (Oxford). 2008;47(12): 1785-1791.
[13] 汤晓晨,俞峰,孙书龙,等.黄芪甲苷对人膝骨关节炎退变关节软骨IL-1β表达的影响[J].南京中医药大学学报,2013,29(1):48-52.
[14] 姚丽,赵婧,周强,等.祛痰化瘀利湿方对大鼠膝骨关节炎滑膜组织和血清IL-1β,MMP-1及COMP,CTX-Ⅱ的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(11):5-8.
[15] 贺牡丹,王小平,陈同生.白细胞介素-1β诱导关节软骨细胞凋亡的分子机理[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2011,33(1):49-54.
[16] GOLDRING MB, OTERO M, PLUMB DA, et al. Roles of inflammatory and anabolic cytokines in cartilage metabolism: signals and multiple effectors converge upon MMP-13 regulation in osteoarthritis. Eur Cell Mater. 2011;21:202-220.
[17] 季卫锋,童培建,袁小凤,等.补肾法与活血法对SD大鼠膝骨性关节炎滑膜IL-1β、TNF-α及软骨MMP-13、ADAMTS-5的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2012,20(2):1-5.
[18] ATTUR M, KRASNOKUTSKY S, STATNIKOV A, et al. Low-grade inflammation in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: prognostic value of inflammatory plasma lipids and peripheral blood leukocyte biomarkers. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(11):2905-2915.
[19] LEFEBVRE V, DE CROMBRUGGHE B. Toward understanding SOX9 function in chondrocyte differentiation. Matrix Biol. 1998; 16(9):529-540.
[20] 马春辉,蔡国平,阎作勤,等.Ⅱ型胶原在骨关节炎软骨细胞中的表达[J].复旦学报(医学版),2009,36(6):734-736.
[21] 崔英霞,夏欣一,杨滨,等.COL2A1基因突变致先天性脊柱骨骺发育不良的软骨组织超微结构观察[J].医学研究生学报,2009,22(4): 376-379.
|