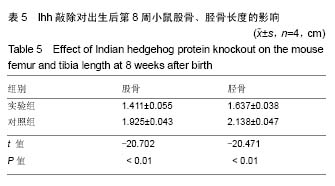
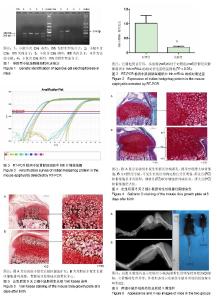
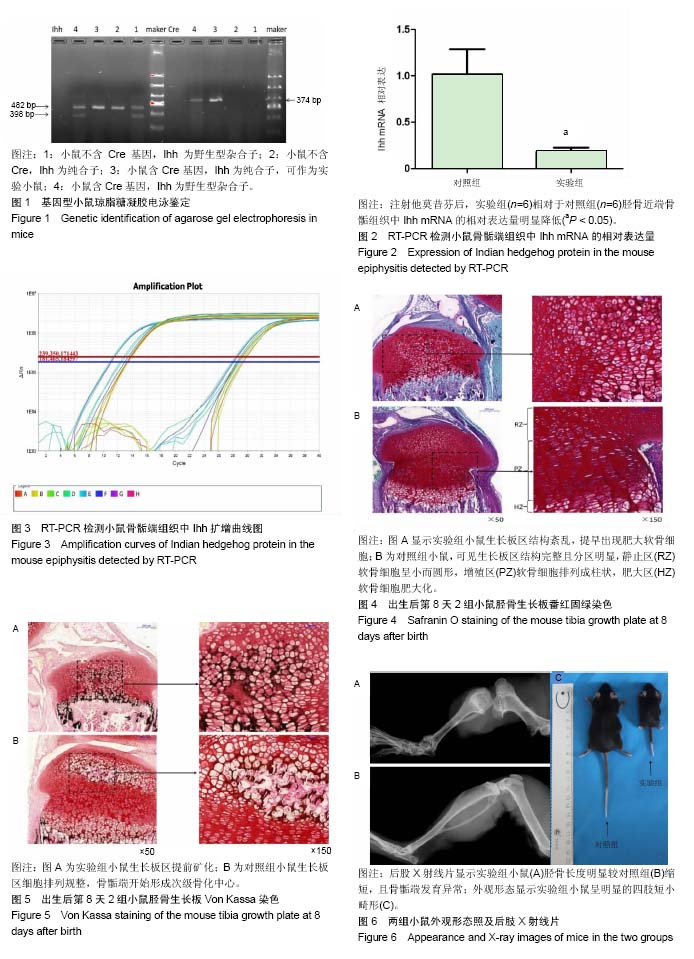
| [1] Amano K, Densmore M, Fan Y, et al. Ihh and PTH1R signaling in limb mesenchyme is required for proper segmentation and subsequent formation and growth of digit bones.Bone.2016; 83:256-266. [2] Pereira J, Johnson WE, O’Brien SJ, et al. Evolutionary Genomics and Adaptive Evolution of the Hedgehog Gene Family (Shh, Ihh and Dhh) in Vertebrates. Plos One.2014;9(12):e74132.[3] Samsa WE, Zhou X, Zhou G. Signaling pathways regulating cartilage growth plate formation and activity. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;62:3-15. [4] Haraguchi R, Kitazawa R, Imai Y, et al. Growth plate-derived hedgehog-signal-responsive cells provide skeletal tissue components in growing bone. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018; 149(4):365-373. [5] Wang W, Lian N, Ma Y, et al. Chondrocytic Atf4 regulates osteoblast differentiation and function via Ihh. Development. 2012;139(3):601-611.[6] Ohba S. Hedgehog Signaling in Endochondral Ossification. 2016;4(2):20.[7] Maeda Y, Nakamura E, Nguyen MT, et al. Indian Hedgehog produced by postnatal chondrocytes is essential for maintaining a growth plate and trabecular bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104(15):6382-6387.[8] Sternberg N, Hamilton D, Hoess R. Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination. II. Recombination between loxP and the bacterial chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1981;150(4):487-507.[9] Zhou J, Chen Q, Lanske B, et al. Disrupting the Indian hedgehog signaling pathway in vivo attenuates surgically induced osteoarthritis progression in Col2a1-CreER T2 ; Ihh fl /fl mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(1):R11.[10] Midic U, Oldfield C J, Dunker A K, et al. Unfoldomics of human genetic diseases: illustrative examples of ordered and intrinsically disordered members of the human diseasome.Protein Pept Lett. 2015;16(12):1533-1547.[11] Sandlesh P, Juang T, Safina A, et al. Uncovering the fine print of the CreERT2-LoxP system while generating a conditional knockout mouse model of Ssrp1 gene. Plos One.2018;13(6): e0199785.[12] Zhu M, Chen M, Lichtler A C, et al. Tamoxifen-Inducible Cre-Recombination in Articular Chondrocytes of Adult Col2a1-CreERT2 Transgenic Mice. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(1):129-130.[13] Tryfonidou MA, Hazewinkel HA, Riemers FM, et al. Intraspecies disparity in growth rate is associated with differences in expression of local growth plate regulators. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2010;299(6):E1044-1052.[14] Conover CA, Bale LK, Powell DR. Inducible knock out of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-a gene expression in the adult mouse: effect on vascular injury response.Endocrinology. 2013;154(8):2734.[15] Hilton M, Tu X, Long F. Tamoxifen-inducible gene deletion reveals a distinct cell type associated with trabecular bone, and direct regulation of PTHrP expression and chondrocyte morphology by Ihh in growth region cartilage. Dev Biol. 2007;308(1):93-105.[16] Kozhemyakina E, Lassar AB, Zelzer E. A pathway to bone: signaling molecules and transcription factors involved in chondrocyte development and maturation. Development.2015; 142(5):817-831.[17] Vortkamp A, Lee K, Lanske B, et al. Regulation of Rate of Cartilage Differentiation by Indian Hedgehog and PTH-Related Protein. Science.1996;273(5275):613-622.[18] Klingelhöffer C, Reck A, Ettl T, et al. The parathyroid hormone-related protein is secreted during the osteogenic differentiation of human dental follicle cells and inhibits the alkaline phosphatase activity and the expression of DLX3. Tissue Cell. 2016;48(4):334-339. [19] Wang Y, Yan Z, Fan W, et al. PTHrP/IHH Involvement in TGFβ and Bone Morphogenic Protein Cross-Talk in the Growth Plate and In Vitro Cartilage Development to Prevent Hypertrophy of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells. J Biomat Tissue Eng.2015; 5(5):120-126.[20] Hasegawa S, Kitoh H, Ohkawara B, et al. Tranilast stimulates endochondral ossification by upregulating SOX9 and RUNX2 promoters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;470(2): 356-361. [21] Yuan X, Liu H, Li L, et al. The roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the pathophysiological development of cartilage and chondrocytes. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(11):1693-1704. [22] Murgai A, Altmeyer S, Wiegand S, et al. Cooperation of BMP and IHH signaling in interdigital cell fate determination. Plos One.2018; 13(5):e0197535. [23] Zhou J, Wei X, Wei L. Indian Hedgehog, a critical modulator in osteoarthritis, could be a potential therapeutic target for attenuating cartilage degeneration disease. Connect Tissue Res. 2014;55(4):257-261. |