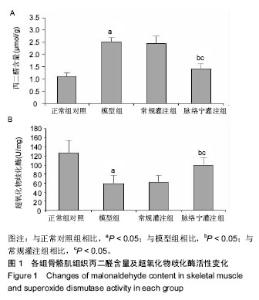
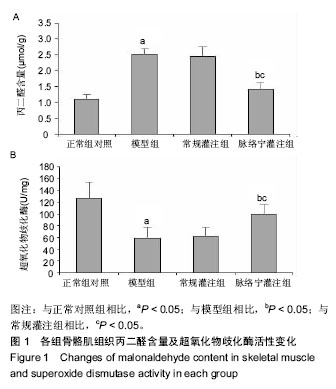
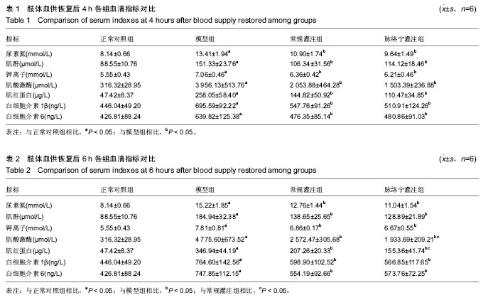
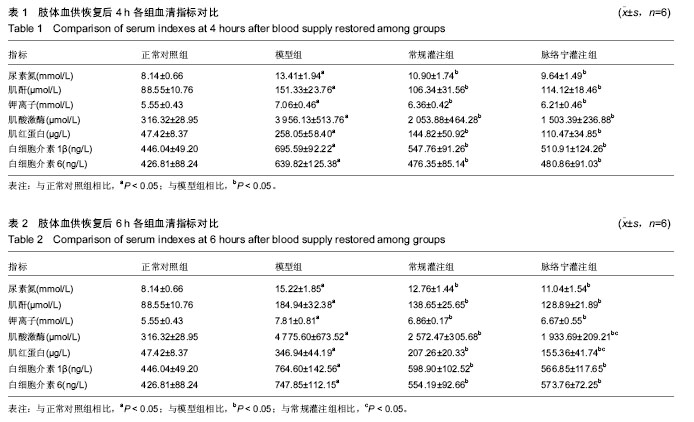
| [1] 王建柏,高劲谋,胡平,等.49例严重肢体挤压伤院前院内一体化救治[J].创伤外科杂志,2016,18(7):393-396.[2] 屈纪富,文亮,刘明华,等.58例严重挤压伤临床诊治分析[J].创伤外科杂志,2009,11(2):140-143. [3] 辛宇鹏,袁光亚,邵红刚,等.地震伤后154例挤压综合症的诊治体会[J].西部医学,2009,21(2):326-327. [4] Vanholder R, Van Biesen W, Lameire N, et al. The role of the international society of nephrology/renal disaster relief task force in the rescue of renal disaster victims. Contrib Nephrol. 2007;156:325-332. [5] 岳茂兴,王立祥,王东明,等.地震现场救援与卫生应急医疗处置专家共识(2017)[J].中华卫生应急电子杂志,2017,3(4):193-205. [6] 刘涛,白祥军.挤压伤和挤压综合征[J].创伤外科杂志, 2016, 18(7):447-449. [7] 邵景立,曹志强,高国梁,等.高海拔地区家兔挤压综合征模型的初步实验研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2018,18(8):1463-1468. [8] 陈怀祥,田海平,刘学军.51例挤压伤院前急救分析[J].华西医学, 2016,31(1):53-56. [9] 张伟,曹志强,高国梁,等.筋膜切开减压术治疗挤压综合征家兔模型的实验研究.现代生物医学进展,2018,18(9):1646-1653. [10] 王江宁,尹叶锋,高磊,等.不同氧体积分数气体对体外模拟体内生理环境寄养断肢系统血氧分压的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(5):855-858. [11] 尹叶锋,王江宁,高磊,等.不同温度对体外模拟体内生理环境寄养断肢系统的影响研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(1): 72-76. [12] 张绍春,秦新愿,左有为,等.脉络宁对体外模拟体内生理环境寄养断肢系统缺血/再灌注损伤模型的作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(36):5825-5829. [13] 李腾飞,王江宁,高磊,等.体外模拟体内生理环境寄养断肢系统采用远端缺血处理灌注方法对保存断肢的作用研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(1):91-94. [14] Duncan GW, Blalock A. The uniform production of experimental shock by crush injury: possible relationship to clinical crush syndrome. Ann Surg. 1942;115(4):684-697. [15] 梁培禾,靳凤烁.挤压综合征[J].中国医刊,2007,42(5):75-77. [16] 滕广宪.横纹肌溶解症的诊断和治疗[J].柳钢科技,2016,(4): 51-53.[17] 王德文,左红艳,李杨,等.模拟深埋条件下复合性挤压伤死亡大鼠的病理变化及其死亡原因[J].军事医学, 2014,38(6):424-432. [18] 王鑫,吕琪,侯世科.挤压伤-挤压综合征治疗的研究进展[J].中华灾害救援医学, 2016,4(8):466-470.[19] 王德文,左红艳,李杨,等.复合性挤压伤深埋条件下的特有伤类Ⅱ:“黄金抢救时间72h”解除挤压后的病理生理特点[J].军事医学,2014,38(6):401-406. [20] 潘鑫,邹圣强,苏兆亮,等.双下肢不同时间大鼠挤压伤-挤压综合征模型生化与病理观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,23(2): 156-159. [21] 孙震,张启福,王涛,等.挤压综合征家兔模型不同挤压时间后心、肾功能与病理观察[J].广东医学,2018,39(S2):36-39. [22] Zorova LD, Pevzner IB, Chupyrkina AA, et al. The role of myoglobin degradation in nephrotoxicity after rhabdomyolysis. Chem Biol Interact. 2016;256:64-70. [23] Shigemoto T, Rinka H, Matsuo Y, et al. Blood purification for crush syndrome. Ren Fail. 1997;19(5):711-719. [24] 白斌,樊毫军,丁辉,等.便携式连续性血液净化机在模拟地震环境中对挤压综合征犬的治疗效果及安全性[J].武警医学, 2014, 25(5):455-458. [25] 吴碧青,涂致远.地震后挤压综合征的肾脏替代治疗[J].中华灾害救援医学,2016,4(7):402-405.[26] 伏杭江,计婧,马元,等.连续性血液净化对严重挤压伤致急性肾功能衰竭的治疗作用[J].东南国防医药,2016,18(2):154-156. [27] 王蕾,刘真真,王淑歌.连续性血液净化治疗挤压综合征的临床观察[J].中国实用医药,2015,10(24):108-109. [28] Karvellas CJ, Farhat MR, Sajjad I, et al. A comparison of early versus late initiation of renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2011;15(1):R72. [29] Shiao CC, Wu VC, Li WY, et al. Late initiation of renal replacement therapy is associated with worse outcomes in acute kidney injury after major abdominal surgery. Crit Care. 2009;13(5):R171. [30] 刘涵,苟亚军,彭东,等.PE联合CVVH治疗挤压综合征患者临床疗效研究[J].临床急诊杂志,2015,16(8):585-587. [31] 邢兆国,常军英,贾东昭,等.亚硝酸盐对大鼠挤压综合征模型缺血/再灌注引起的肌肉损伤的影响[J].河北医科大学学报, 2015, 36(5):523-527. [32] Vanholder R, van der Tol A, De Smet M, et al. Earthquakes and crush syndrome casualties: lessons learned from the Kashmir disaster. Kidney Int. 2007;71(1):17-23. [33] 钟洲,刘熹,张晖,等.地震挤压综合征迟发性肌肉坏死的临床研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(10):1317-1319. [34] Zhao ZQ. Oxidative stress-elicited myocardial apoptosis during reperfusion. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004;4(2):159-165.[35] Van Wagoner DR, Bond M. Reperfusion arrhythmias: new insights into the role of the Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001;33(12):2071-2074.[36] Lin MT, Beal MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature. 2006;443 (7113):787-795. [37] Stowe DF, Camara AK. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in excitable cells: modulators of mitochondrial and cell function. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11(6):1373-1414. [38] Nunnari J, Suomalainen A. Mitochondria: in sickness and in health. Cell. 2012;148(6):1145-1159. [39] Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, et al. Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science. 1997;275(5303):1129-1132. [40] Candé C, Vahsen N, Kouranti I, et al. AIF and cyclophilin A cooperate in apoptosis-associated chromatinolysis. Oncogene. 2004;23(8):1514-1521. [41] 王岱君,鞠学红,田华.脉络宁对兔肢体缺血再灌注损伤的防护作用[J].中华创伤杂志,2004,20(4):46-49. [42] 梁倩倩,田华,庄宝祥,等.脉络宁对兔肢体缺血/再灌注损伤过程中SOD及MPO的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2012,28(6):885-886. [43] 李军凯,杨高潮,黄河.脉络宁对大鼠肢体缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2012,10(10):1232-1233. [44] 李娜,吴世政,张淑坤.脉络宁注射液对人血管内皮细胞缺氧损伤的保护作用[J].中国新药杂志,2012,21(11):1273-1277. |