Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (8): 1222-1227.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1083
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment of finite element model of L4-5 and mechanical analysis of degenerative intervertebral discs
Wen Yi1, Su Feng2, Liu Su2, Zong Zhiguo2, Zhang Xin2, Ma Pengpeng2, Li Yuexuan1, Li Rui1, Zhang Zhimin3
- 1Graduate School, Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Spinal Surgery, 3Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China
-
Online:2019-03-18Published:2019-03-18 -
Contact:Su Feng, Master, Chief physician, Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Wen Yi, Master candidate, Attending physician, Graduate School, Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Major Medical Scientific Research Subject of Hebei Province, No. zd2013050 (to SF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wen Yi, Su Feng, Liu Su, Zong Zhiguo, Zhang Xin, Ma Pengpeng, Li Yuexuan, Li Rui, Zhang Zhimin. Establishment of finite element model of L4-5 and mechanical analysis of degenerative intervertebral discs
share this article
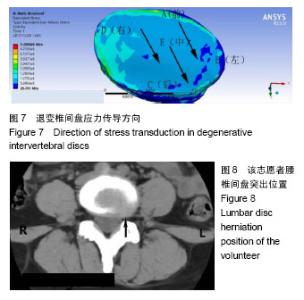
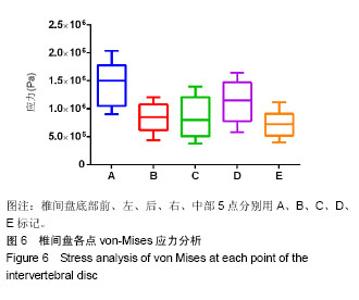
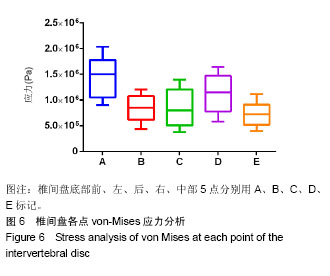
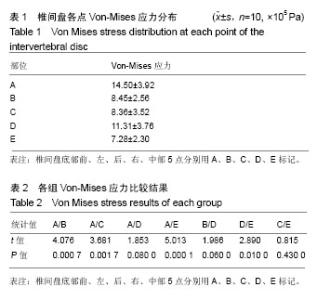
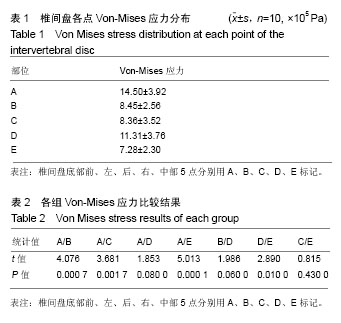
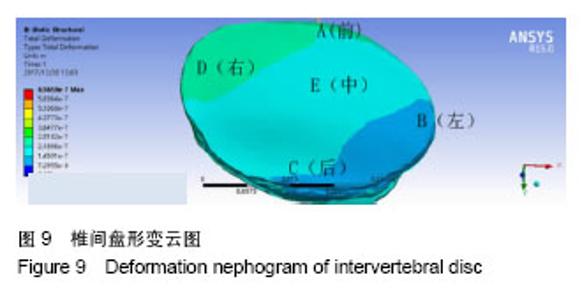
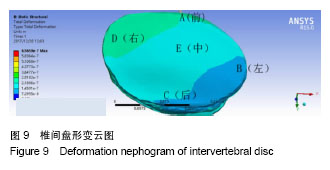
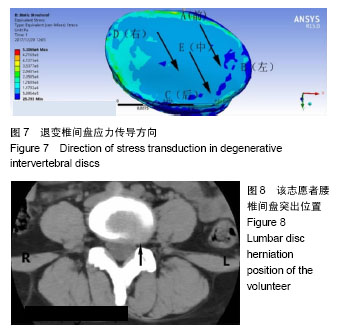
以椎间盘前部A点所受应力最大,椎间盘中部E点髓核所处的区域应力最小,以A组为对照组,5组间比较差异有显著性意义(F=7.995,P < 0.000 1),椎间盘前部所受应力明显大于中后部。5组间两两比较结果显示,椎间盘前部A点von-Mises应力大于中部E点(P < 0.000 1),A点应力大于椎间盘后部C点,差异有显著性意义(P=0.001 7)。E点与C点von-Mises应力差异无显著性意义(P=0.43),椎间盘左右两侧B点和D点应力差异无显著性意义(P=0.06)。D点应力明显大于髓核所在的E点,应力差异有显著性意义(P=0.01),A点应力明显大于B点应力,应力差异有显著性意义(P=0.000 7)。椎间盘A点和D点应力差异无显著性意义(P=0.08)。 故此次实验证实椎间盘von-Mises应力衰减的方向为从右前向左后方向,见图7;同椎间盘突出和形变的方向基本一致,见图8,9。"
| [1] 贾连顺. 现代脊柱外科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2007.[2] Schollum M, Wade K, Robertson P, et al. A Microstructural Investigation of Disc Disruption Induced by Low Frequency Cyclic Loading. Spine. 2018;43(3):E132-E142.[3] Chen W, Wang K, Yuan W, et al. [Relationship between lumbosacral multifidus muscle and lumbar disc herniation]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2016;29(6):581-584.[4] Zhou X, Cheung C, Karasugi T, et al. Trans-ethnic polygenic analysis supports genetic overlaps of lumbar disc degeneration with height, body mass index, and bone mineral density. Front Genet. 2018;9:267.[5] Chen L, Liu D, Zou L, et al. Efficacy of high intensity laser therapy in treatment of patients with lumbar disc protrusion: A randomized controlled trial. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2018;31(1): 191-196.[6] Ciesielska J, Lisiński P, Bandosz A, et al. Hip strategy alterations in patients with history of low disc herniation and non-specific low back pain measured by surface electromyography and balance platform. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2015;17(3):103-108.[7] Pereira P, Severo M, Monteiro P, et al. Results of Lumbar Endoscopic Adhesiolysis Using a Radiofrequency Catheter in Patients with Postoperative Fibrosis and Persistent or Recurrent Symptoms After Discectomy. Pain Pract. 2016;16(1):67-79.[8] 谢富荣,玉超杰. 腰椎间盘突出[J]. 医药前沿, 2018,8(16):9-10.[9] Wang C, Chi Q, Xu C, et al. Expression of LOXs and MMP-1, 2, 3 by ACL Fibroblasts and Synoviocytes Impact of Coculture and TNF-α. J Knee Surg. 2018.[10] Hu X, Liu L. [Progress on the cause and mechanism of a separation of clinical symptoms and signs and imaging features in lumbar disk herniation]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015;28(10): 970-975.[11] Chen S, Tai C, Lin C, et al. Biomechanical comparison of a new stand-alone anterior lumbar interbody fusion cage with established fixation techniques - a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2008;9:88.[12] Rohlmann A, Zander T, Rao M, et al. Applying a follower load delivers realistic results for simulating standing. J Biomech. 2009; 42(10):1520-1526.[13] 尹庆水,章莹,王成焘,等. 临床数字骨科学——创新理论体系与临床应用[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(7):649.[14] Meakin J, Smith F, Gilbert F, et al. The effect of axial load on the sagittal plane curvature of the upright human spine in vivo. J Biomech. 2008;41(13):2850-2854.[15] Rohlmann A, Zander T, Rao M, et al. Realistic loading conditions for upper body bending. J Biomech. 2009;42(7):884-890.[16] Yang L, Yang Y, Yang X, et al. [Design and clinical application of a three-dimensional biomechanical traction appliance for protrusion of intervertebral disc]. Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2002;26(3): 190-191.[17] Chen C, Shih S. Biomechanical analysis of a new lumbar interspinous device with optimized topology. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;56(8):1333-1341.[18] Li L, Shen T, Li Y. A Finite Element Analysis of Stress Distribution and Disk Displacement in Response to Lumbar Rotation Manipulation in the Sitting and Side-Lying Positions. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2017;40(8):580-586.[19] Coombs DJ, Rullkoetter PJ, Laz PJ. Efficient probabilistic finite element analysis of a lumbar motion segment. J Biomech. 2017;61:65-74.[20] Rho JY, Hobatho MC, Ashman RB. Relations of mechanical properties to density and CT numbers in human bone. Med Eng Phys. 1995;17(5):347-355.[21] Kopperdahl DL, Morgan EF, Keaveny TM. Quantitative computed tomography estimates of the mechanical properties of human vertebral trabecular bone. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(4):801-805.[22] Pyles C, Zhang J, Demetropoulos C, et al. Material Parameter Determination of an L4-L5 Motion Segment Finite Element Model Under High Loading Rates. Biomed Sci Instrum. 2015;51: 206-213.[23] Yang K, King A. Mechanism of facet load transmission as a hypothesis for low-back pain. Spine. 1984;9(6):557-565.[24] Guo L, Fan W. Impact of material properties of intervertebral disc on dynamic response of the human lumbar spine to vertical vibration: a finite element sensitivity study. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018.[25] Leite PMS, Mendonca ARC, Maciel LYS, et al. Does Electroacupuncture Treatment Reduce Pain and Change Quantitative Sensory Testing Responses in Patients with Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain? A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018;2018:8586746.[26] Li J, He J, Li H, et al. Proportion of neuropathic pain in the back region in chronic low back pain patients -a multicenter investigation. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16537.[27] Welch N, Moran K, Antony J, et al. The effects of a free-weight-based resistance training intervention on pain, squat biomechanics and MRI-defined lumbar fat infiltration and functional cross-sectional area in those with chronic low back. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2015;1(1):e000050.[28] Thiry P, Reumont F, Brismee JM, et al. Short-term increase in discs' apparent diffusion is associated with pain and mobility improvements after spinal mobilization for low back pain. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):8281.[29] Fongen C, Dagfinrud H, Berg IJ, et al. Frequency of Impaired Spinal Mobility in Patients with Chronic Back Pain Compared to Patients with Early Axial Spondyloarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2018.[30] Wagnac E, Aubin C, Chaumoître K, et al. Substantial vertebral body osteophytes protect against severe vertebral fractures in compression. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(10):e0186779.[31] Lee C, Landham P, Eastell R, et al. Development and validation of a subject-specific finite element model of the functional spinal unit to predict vertebral strength. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2017;231(9): 821-830.[32] Fan W, Guo L. Finite element investigation of the effect of nucleus removal on vibration characteristics of the lumbar spine under a compressive follower preload. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;78:342-351.[33] Paietta R, Burger E, Ferguson V. Mineralization and collagen orientation throughout aging at the vertebral endplate in the human lumbar spine. J Struct Biol. 2013;184(2):310-320.[34] Berg-Johansen B, Fields A, Liebenberg E, et al. Structure-function relationships at the human spinal disc-vertebra interface. J Orthop Res. 2017.[35] Lee C, Hsu C, Huang P. Biomechanical study of different fixation techniques for the treatment of sacroiliac joint injuries using finite element analyses and biomechanical tests. Comput Biol Med. 2017;87:250-257.[36] Wang K, Jiang C, Wang L, et al. The biomechanical influence of anterior vertebral body osteophytes on the lumbar spine: a finite element study. Spine J. 2018.[37] Wang Y, Yi X, Li C. The influence of artificial nucleus pulposus replacement on stress distribution in the cartilaginous endplate in a 3-dimensional finite element model of the lumbar intervertebral disc. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(50):e9149.[38] Barthelemy VM, van Rijsbergen MM, Wilson W, et al. A computational spinal motion segment model incorporating a matrix composition-based model of the intervertebral disc. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016;54:194-204.[39] Ghezelbash F, Eskandari AH, Shirazi-Adl A, et al. Effects of motion segment simulation and joint positioning on spinal loads in trunk musculoskeletal models. J Biomech. 2018;70:149-156.[40] Chik TK, Chooi WH, Li YY, et al. Bioengineering a multicomponent spinal motion segment construct--a 3D model for complex tissue engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(1):99-112.[41] Nagata K, Ando T, Nakamoto H, et al. Adaptation and limitation of anterior column reconstruction for pyogenic spondylitis in lower thoracic and lumbar spine. J Orthop Sci. 2018.[42] Uribe JS, Schwab F, Mundis GM, Jr., et al. The comprehensive anatomical spinal osteotomy and anterior column realignment classification. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018:1-11.[43] von Ruden C, Wenzel L, Becker J, et al. The pararectus approach for internal fixation of acetabular fractures involving the anterior column: evaluating the functional outcome. Int Orthop. 2018.[44] Khurana B, Prevedello LM, Bono CM, et al. CT for thoracic and lumbar spine fractures: Can CT findings accurately predict posterior ligament complex injury? Eur Spine J. 2018.[45] Mc AP, Cunningham B, Mullinex K, et al. Middle-Column Gap Balancing and Middle-Column Mismatch in Spinal Reconstructive Surgery. Int J Spine Surg. 2018;12(2):160-171.[46] McAfee PC, Eiserman L, Cunningham BW, et al. Middle Column Gap Balancing to Predict Optimal Anterior Structural Support and Spinal Height in Spinal Reconstructive Surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42 Suppl 7:S19-S20.[47] Sugaya T, Sakamoto M, Nakazawa R, et al. Relationship between spinal range of motion and trunk muscle activity during trunk rotation. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(2):589-595. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [4] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [5] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [6] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [7] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [8] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [9] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [10] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [11] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [12] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [13] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [14] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [15] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||