Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (25): 4083-4088.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0964
Previous Articles Next Articles
Anti-tumor effects of mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes
Wu Xue, Qian Man-qing, Wu Dong-liang, Zhao Xiao-yin
- Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310014, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Revised:2018-05-17Online:2018-09-08Published:2018-09-08 -
Contact:Zhao Xiao-yin, M.D., Lecturer, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310014, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Wu Xue, Master candidate, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310014, Zhejiang Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31500739; Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, No. LQ15H160012, LY18B020020
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Xue, Qian Man-qing, Wu Dong-liang, Zhao Xiao-yin. Anti-tumor effects of mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(25): 4083-4088.
share this article
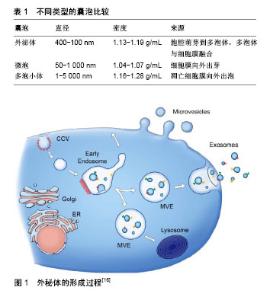
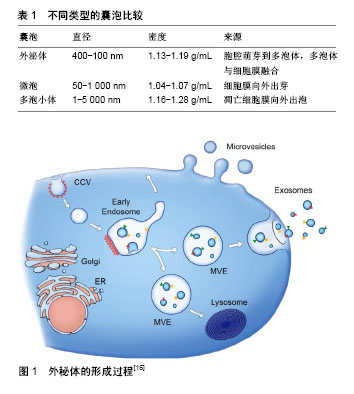
2.1 MSCs简介 MSCs是来源于中胚层的一类具有高度自我更新能力和多向分化潜能的成体干细胞;主要存在于结缔组织和器官间质中,如脂肪、骨髓、胎盘、脐血、黏膜、骨骼、羊水、羊膜、肌肉、肺、肝、胰腺等。2006年国际细胞治疗协会(ISCT)统一了MSCs的最低鉴定标准[9]:①贴壁生长;②细胞表面表达一些特异性抗原标记物(CD29、CD44、CD73、CD90、CD105、CD106等);③具有向脂肪细胞、成骨细胞、软骨细胞分化的能力[10-11]。MSCs由于其独特的低免疫原性及免疫调节能力,已被广泛应用于包括肿瘤在内的多种临床研究中。据公开的临床试验网公布,截至2018年2月16日正在进行或已完成的用MSCs治疗疾病的临床试验有804项(http://clinicaltrials.gov),其中有37项是与肿瘤相关的研究。对MSCs功能及作用机制的深入研究将促进MSCs在炎症、肿瘤等疾病临床治疗中的安全应用。 2.2 MSCs来源外泌体简介 细胞在静息或应激状态下都能够分泌大量囊泡,这些囊泡按照分泌途径及直径大小被划分为3类[12]:外泌体、微泡、凋亡小体(表1),虽然大小及生物合成方式不同,但它们都由脂类、蛋白质、mRNA及miRNA组成。近年来研究显示,MSCs能够通过分泌外泌体发挥对肿瘤细胞的调节作用[13]。外泌体(exosome)是细胞外纳米级的囊泡,直径介于30- 150 nm之间,密度在 1.13-1.19 g/mL 之间,由双层磷脂分子包围。外泌体的膜内富含脂质,如胆固醇、神经酰胺和鞘脂类[14],Tan等[15]通过检测脂质筏的成分进一步证实了MSCs产生的外泌体的核内体来源。外泌体的形成过程:首先,部分细胞膜向内凹陷形成早期核内体,早期核内体再形成晚期核内体或称多泡小体(multivesicular endosome,MVE),其实是管腔内的囊泡,这些囊泡会经由溶酶体途径降解或随多泡小体转运至细胞膜,紧接着多泡小体与细胞膜融合,释放出里面的小囊泡,即为外泌体(图1)[16]。"

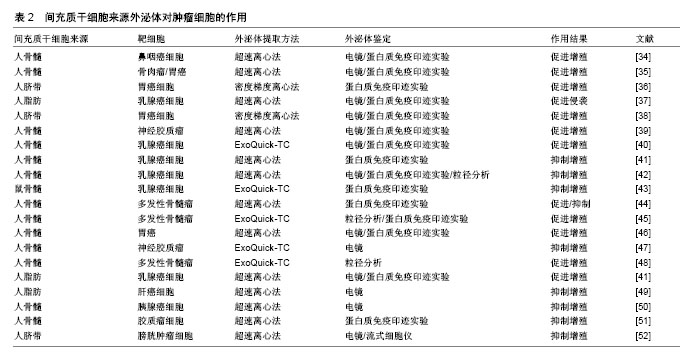
在开展外泌体相关研究时,可通过超速离心法[17-18]、膜过滤法、免疫磁珠分选法、聚乙二醇沉淀法或使用试剂盒分离提取细胞产生的外泌体[19],其中最为广泛使用的方法是超速离心法,这种方法得到的外泌体形态良好,杂质少而且成本低廉,但步骤繁琐,耗时且容易污染,因此常与密度梯度离心结合,例如可以选用蔗糖、Percoll或者Optiprep配制成密度梯度溶液[20-22],样本溶液中的外泌体会富集在1.13-1.19 g/mL范围内,也可以搭配0.2 μm过滤膜进行过滤,从而获得更干净的外泌体。 外泌体的鉴定方法有许多种,其中比较常用的有:①用透射电子显微镜或者扫描电子显微镜观察是否呈双层膜囊泡状或杯样形态[23];②采用纳米粒子分析仪检查径粒分布,一般直径范围为30-150 nm;③外泌体标志蛋白检测,包括流式法、ELISA、Western blot法。常见的外泌体标志性蛋白有四次跨膜蛋白家族CD9、CD63及CD81;热休克蛋白HSP90及HSP70等;多泡体相关蛋白,如凋亡转接基因互作蛋白X(ALIX),肿瘤易感基因101蛋白(TSG101)等[24-27]。Sokolova等[28]通过纳米粒子跟踪分析、动态光散射及扫描电子显微镜对人体细胞来源外泌体进行了表征分析,发现外泌体在-20 ℃条件下直径及生物形态都未发生明显变化,能够长期保存;在4 ℃下保存三四天,外泌体直径减小至原先的75%;在37 ℃下保存2 d后,外泌体直径下降60%左右;因此外泌体可以长期储存在-20 ℃或-80 ℃。 2.3 MSCs来源外泌体对肿瘤细胞的调控作用 外泌体中包含一系列生物活性分子,如蛋白质、mRNA、microRNA、多肽及脂类等,其所含组分与其分泌细胞密切相关;外泌体可运载细胞产生的多种重要生物活性分子穿梭于细胞器官之间,根据靶细胞表面的受体、配体,将其内含物靶向投递至特定的部位,并释放内含物发挥作用[7-8],是细胞间交流和信息传递的重要媒介。MSCs来源外泌体与MSCs具有类似的生物学活性,如低免疫原性、免疫调节能力、向炎症或肿瘤部位归巢的能力等[29-30]。因此,近年来MSCs来源外泌体被作为药物或生物活性分子的运输载体广泛应用于多种疾病的无细胞治疗相关研究[31-33]。目前,MSCs对肿瘤到底是促进作用还是抑制作用存在很大争议,许多研究呈现出不一致的结论。 2.3.1 MSCs来源外泌体对肿瘤的促进作用 Shi等[34]证实了MSCs来源外泌体通过FGF19介导的FGFR4信号级联的激活促进鼻咽癌细胞的发生、增殖和迁移;2017年,中国研究者发现人骨髓MSCs来源外泌体通过激活Hedgehog信号通路促进骨肉瘤细胞及胃癌细胞的生长[35]。人胎儿脐带MSCs来源外泌体通过激活Akt信号通路诱导胃癌细胞HGC-27发生上皮间质转化,增强其迁移和侵袭能力[36]。另外,MSCs来源外泌体不仅可以通过激活Wnt通路促进乳腺癌细胞系发生上皮间质转化[37],还可能会使得胃癌细胞产生抗药性[38]。2017年,Figueroa等[39]发现神经胶质瘤相关性MSCs能够通过其外泌体在细胞间运载miR-1587,下调肿瘤抑制核受体辅助抑制物NCOR1,增强胶质瘤母细胞的侵袭性,并促进其增殖与集落形成,从而降低宿主存活率。Bliss等[40]发现休眠的乳腺癌细胞能够启动MSCs释放含有不同miRNA的外泌体(如miR-222/223),这些外泌体在细胞间运载miR222/223促使肿瘤细胞休眠并产生耐药性。 2.3.2 MSCs来源外泌体对肿瘤的抑制作用 有研究者认为MSCs来源外泌体能够抑制肿瘤的生长。2014年,Ono等[41]发现人骨髓MSCs来源外泌体能够通过运载miR-23b至乳腺癌细胞(BM2),并被BM2获取,miR-23b通过抑制促细胞周期活动性蛋白MARCKS基因的表达,促使BM2细胞休眠,抑制了BM2细胞增殖及其对基质细胞的侵袭,同时还降低了其对多烯紫杉醇的敏感性。Lou等[4]研究指出人脂肪MSCs转染miR-122后,MSCs来源外泌体能够有效地将miR-122包裹入其中,参与到MSCs与肝癌细胞间的miR-122交流,通过改变肝癌细胞中miR-122靶基因的表达,提高癌细胞对化疗药物索拉非尼的敏感性,增强抗肿瘤效果,他们认为通过MSCs来源外泌体运载抗肿瘤活性因子至肿瘤部位会是一个肿瘤靶向治疗的新策略和方向。Pakravan等[42]认为骨髓MSCs来源外泌体能够显著且剂量依赖性地通过mTOR/HIF-1α信号轴降低乳腺癌细胞中血管内皮生长因子表达和分泌,从而抑制新生血管形成,抑制癌细胞的生长和增殖。MSCs来源外泌体能够抑制乳腺癌细胞表达血管内皮生长因子[43],从而抑制肿瘤生长。Roccaro等[44]发现多发性骨髓瘤患者的MSCs来源外泌体中肿瘤抑制因子miR-15a的含量比正常人低,而致瘤蛋白、细胞因子及黏附因子的含量较多。研究发现多发性骨髓瘤患者的MSCs来源外泌体会促进肿瘤生长,而正常人的MSCs来源外泌体则会抑制肿瘤生长。 表2汇总了近些年有关MSCs来源外泌体对肿瘤细胞调控作用的部分报道[34-52]。"
| [1] Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(1):11-30.[2] Bianco P, Cao X, Frenette PS, et al. The meaning, the sense and the significance: translating the science of mesenchymal stem cells into medicine. Nat Med. 2013;19(1):35-42.[3] 廖联明,韩钦,赵春华. 间充质干细胞在免疫治疗中的应用[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志, 2005, 13(1):158-163.[4] Lou G, Song X, Yang F, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-122-modified adipose tissue-derived MSCs increase chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:122.[5] Hong IS, Lee HY, Kang KS. Mesenchymal stem cells and cancer: friends or enemies. Mutat Res. 2014;768:98-106.[6] Pan BT, Johnstone RM. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell. 1983;33(3):967-978.[7] Fais S, O'Driscoll L, Borras FE, et al. Evidence-Based Clinical Use of Nanoscale Extracellular Vesicles in Nanomedicine. ACS Nano. 2016;10(4):3886-3899.[8] Nagata M, Muto S, Horie S. Molecular Biomarkers in Bladder Cancer: Novel Potential Indicators of Prognosis and Treatment Outcomes. Dis Markers. 2016;2016:8205836.[9] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[10] Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997;276(5309):71-74.[11] Tyndall A, Walker UA, Cope A, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells: a review based on an interdisciplinary meeting held at the Kennedy Institute of Rheumatology Division, London, UK, 31 October 2005. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(1):301.[12] Crescitelli R, Lässer C, Szabó TG, et al. Distinct RNA profiles in subpopulations of extracellular vesicles: apoptotic bodies, microvesicles and exosomes. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013;2.[13] Katsuda T, Tsuchiya R, Kosaka N, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells secrete functional neprilysin-bound exosomes. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1197.[14] Meckes DG Jr, Raab-Traub N. Microvesicles and viral infection. J Virol. 2011;85(24):12844-12854.[15] Tan SS, Yin Y, Lee T, et al. Therapeutic MSC exosomes are derived from lipid raft microdomains in the plasma membrane. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013;2.[16] Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373-383.[17] Lai RC, Yeo RW, Lim SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:82-88.[18] Ratajczak J, Wysoczynski M, Hayek F, et al. Membrane- derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia. 2006; 20(9):1487-1495.[19] Mathivanan S, Fahner CJ, Reid GE, et al. ExoCarta 2012: database of exosomal proteins, RNA and lipids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(Database issue):D1241-1244.[20] Welton JL, Khanna S, Giles PJ, et al. Proteomics analysis of bladder cancer exosomes. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010;9(6): 1324-1338.[21] Mathivanan S, Lim JW, Tauro BJ, et al. Proteomics analysis of A33 immunoaffinity-purified exosomes released from the human colon tumor cell line LIM1215 reveals a tissue-specific protein signature. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010;9(2):197-208.[22] Rider MA, Hurwitz SN, Meckes DG Jr. ExtraPEG: A Polyethylene Glycol-Based Method for Enrichment of Extracellular Vesicles. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23978.[23] Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S, et al. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science. 2008;319(5867):1244-1247.[24] Gutiérrez-Vázquez C, Villarroya-Beltri C, Mittelbrunn M, et al. Transfer of extracellular vesicles during immune cell-cell interactions. Immunol Rev. 2013;251(1):125-142.[25] Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;Chapter 3: Unit 3.22.[26] Melo SA, Luecke LB, Kahlert C, et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2015;523(7559):177-182.[27] Ti D, Hao H, Tong C, et al. LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J Transl Med. 2015;13:308.[28] Sokolova V, Ludwig AK, Hornung S, et al. Characterisation of exosomes derived from human cells by nanoparticle tracking analysis and scanning electron microscopy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011;87(1):146-150.[29] Tetta C, Bruno S, Fonsato V, et al. The role of microvesicles in tissue repair. Organogenesis. 2011;7(2):105-115.[30] Bruno S, Grange C, Deregibus MC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(5):1053-1067.[31] Phinney DG, Pittenger MF. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4): 851-858.[32] Rani S, Ryan AE, Griffin MD, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Extracellular Vesicles: Toward Cell-free Therapeutic Applications. Mol Ther. 2015;23(5):812-823.[33] Miranda KC, Bond DT, McKee M, et al. Nucleic acids within urinary exosomes/microvesicles are potential biomarkers for renal disease. Kidney Int. 2010;78(2):191-199.[34] Shi S, Zhang Q, Xia Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes facilitate nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression. Am J Cancer Res. 2016;6(2):459-472.[35] Qi J, Zhou Y, Jiao Z, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Tumor Growth Through Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(6):2242-2254.[36] Gu H, Ji R, Zhang X, et al. Exosomes derived from human mesenchymal stem cells promote gastric cancer cell growth and migration via the activation of the Akt pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(4):3452-3458.[37] Lin R, Wang S, Zhao RC. Exosomes from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote migration through Wnt signaling pathway in a breast cancer cell model. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;383(1-2):13-20.[38] Ji R, Zhang B, Zhang X, et al. Exosomes derived from human mesenchymal stem cells confer drug resistance in gastric cancer. Cell Cycle. 2015;14(15):2473-2483.[39] Figueroa J, Phillips LM, Shahar T, et al. Exosomes from Glioma-Associated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Increase the Tumorigenicity of Glioma Stem-like Cells via Transfer of miR-1587. Cancer Res. 2017;77(21):5808-5819.[40] Bliss SA, Sinha G, Sandiford OA, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Stimulate Cycling Quiescence and Early Breast Cancer Dormancy in Bone Marrow. Cancer Res. 2016;76(19):5832-5844.[41] Ono M, Kosaka N, Tominaga N, et al. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells contain a microRNA that promotes dormancy in metastatic breast cancer cells. Sci Signal. 2014;7(332):ra63.[42] Pakravan K, Babashah S, Sadeghizadeh M, et al. MicroRNA-100 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes suppresses in vitro angiogenesis through modulating the mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling axis in breast cancer cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017;40(5):457-470.[43] Lee JK, Park SR, Jung BK, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells suppress angiogenesis by down-regulating VEGF expression in breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e84256.[44] Roccaro AM, Sacco A, Maiso P, et al. BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(4):1542-1555.[45] Hendrix A. Bone Marrow Stromal Cell-Derived Exosomes Facilitate Multiple Myeloma Cell Survival Through Inhibition Of The JNK Pathway. Blood. 2013; 122(21):679.[46] Zhu W, Huang L, Li Y, et al. Exosomes derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2012;315(1):28-37.[47] Katakowski M, Buller B, Zheng X, et al. Exosomes from marrow stromal cells expressing miR-146b inhibit glioma growth. Cancer Lett. 2013;335(1):201-204.[48] Wang J, Hendrix A, Hernot S, et al. Bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomes as communicators in drug resistance in multiple myeloma cells. Blood. 2014;124(4):555-566.[49] Ko SF, Yip HK, Zhen YY, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Suppress Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth in a Rat Model: Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, Natural Killer T-Cell Responses, and Histopathological Features. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:853506.[50] Pascucci L, Coccè V, Bonomi A, et al. Paclitaxel is incorporated by mesenchymal stromal cells and released in exosomes that inhibit in vitro tumor growth: a new approach for drug delivery. J Control Release. 2014;192:262-270.[51] Munoz JL, Bliss SA, Greco SJ, et al. Delivery of Functional Anti-miR-9 by Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Exosomes to Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells Conferred Chemosensitivity. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013;2:e126.[52] Wu S, Ju GQ, Du T, et al. Microvesicles derived from human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells attenuate bladder tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e61366.[53] 庞一琳,张斌,陈虎. 间充质干细胞与肿瘤细胞相互作用:促进还是抑制[J]. 中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版, 2013,3(1):30-37.[54] 刘晗,陈军,徐祗顺. 间充质干细胞与肿瘤生长发展关系的研究现状[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2010,14(19):3565-3568.[55] 封冰,陈龙邦. 间充质干细胞与肿瘤:抑制或促进[J]. 中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志, 2009,16(5):532-536. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [14] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [15] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||