Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (25): 3937-3943.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0952
Apelin combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction
Hou Jing-ying, Long Hui-bao, Chen Xu-xiang, Wang Lei, Guo Tian-zhu, Zheng Shao-xin, Zhong Ting-ting, Wu Quan-hua, Wu Hao, Wang Tong
- Department of Emergency, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2018-03-22Online:2018-09-08Published:2018-09-08 -
Contact:Hou Jing-ying, Department of Emergency, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Hou Jing-ying, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Emergency, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81700242; the Science and Technology Research Project of Guangdong Province, No. 2017A020215176; the Medical Science Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. A2016264, A2017001
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hou Jing-ying, Long Hui-bao, Chen Xu-xiang, Wang Lei, Guo Tian-zhu, Zheng Shao-xin, Zhong Ting-ting, Wu Quan-hua, Wu Hao, Wang Tong. Apelin combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(25): 3937-3943.
share this article
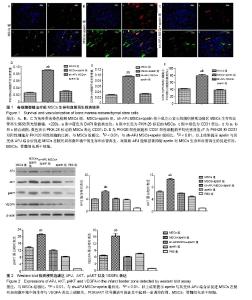
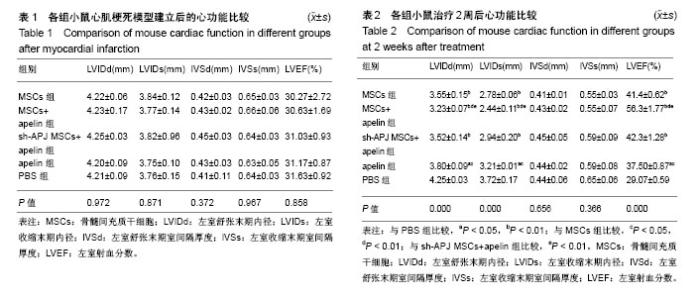
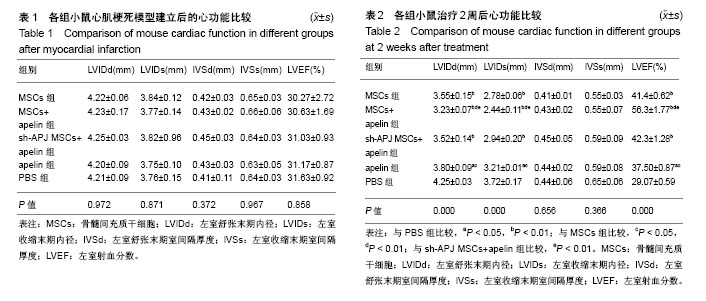
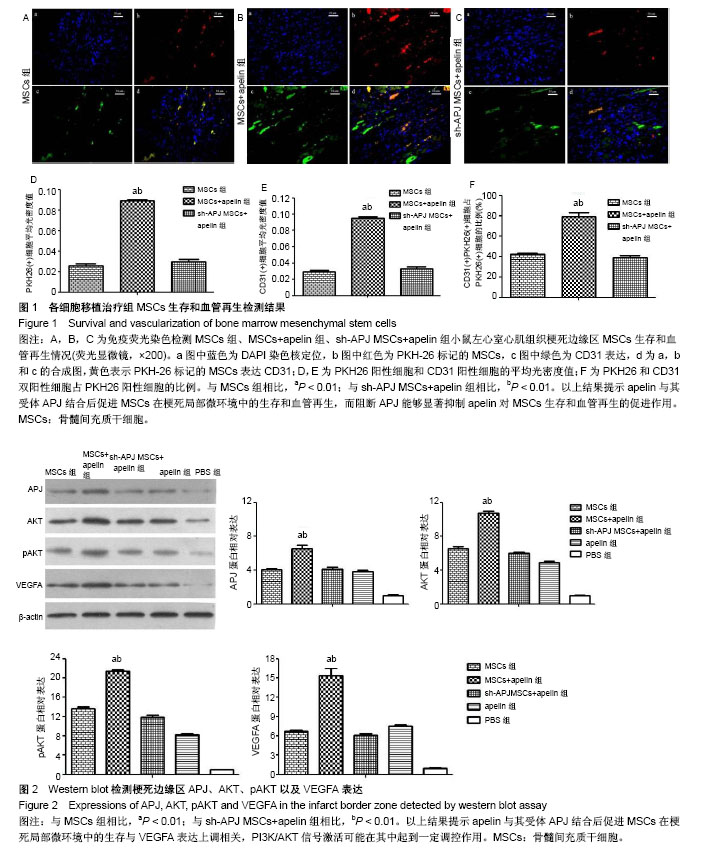
2.1 实验动物数量分析 50只C57BL/6小鼠全部存活,均进入结果分析。 2.2 各组心功能比较 小鼠心肌梗死模型建立后进行心脏超声检测,结果显示各组小鼠左室舒张末期内径、左室收缩末期内径、左室舒张末期室间隔厚度、左室收缩末期室间隔厚度、左室射血分数之间差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05,表1);在经过相关治疗后2周再次检测心功能,结果显示:与治疗前相比较,MSCs组、MSCs+apelin组、sh-APJ MSCs+apelin组以及apelin组左室舒张末期内径、左室收缩末期内径明显下降,左室射血分数明显增高(P < 0.01,表1和表2),而PBS组治疗前后相比各指标差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05,表1和表2)。与PBS组相比较,其余各组左室舒张末期内径、左室收缩末期内径明显下降,左室射血分数明显增高(P < 0.01,表2);与MSCs组、sh-APJ MSCs+apelin组及apelin组相比较,MSCs+apelin组左室舒张末期内径、左室收缩末期内径明显下降,左室射血分数明显增高(P < 0.01,表2);与MSCs组相比较,apelin组左室舒张末期内径、左室收缩末期内径增加,左室射血分数下降,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.3 MSCs生存和血管再生情况 与MSCs组、sh-APJ MSCs+apelin组相比较,MSCs+apelin组梗死边缘区PKH26(+)以及CD31(+)细胞的平均光密度值显著增高(P < 0.01,图1),PKH26和CD31双阳性细胞占PKH26(+)细胞的比例显著增多(P < 0.01,图1),差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01,图1),而sh-APJ MSCs+apelin组与MSCs组相比较,在上述指标方面差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.4 治疗后2周梗死边缘区APJ、AKT、pAKT以及VEGFA表达 与PBS组相比较,其他组APJ、AKT、pAKT以及VEGFA表达明显增高(P < 0.01,图2);与MSCs组和sh-APJ MSCs+apelin组相比,MSCs+apelin组APJ、AKT、pAKT以及VEGFA的蛋白表达水平明显增加(P < 0.01,图2),而MSCs组、sh-APJ MSCs+apelin组以及apelin组之间上述指标表达差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05,图2)。"
| [1] Hou J, Zhong T, Guo T, et al. Apelin promotes mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization under hypoxic-ischemic condition in vitro involving the upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor. Exp Mol Pathol. 2017;102(2):203-209.[2] Narita T, Suzuki K. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2015;20(1):53-68.[3] Hou J, Wang L, Hou J, et al. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Express Connexin43 via the Inhibition of TGF-β1/Smads Signaling in a Rat Model of Myocardial Infarction. Stem Cell Rev. 2015;11(6):885-899.[4] Karpov AA, Udalova DV, Pliss MG, et al. Can the outcomes of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for myocardial infarction be improved? Providing weapons and armour to cells. Cell Prolif. 2017; 50(2). doi: 10.1111/cpr.12316. [5] Lu L, Wu D, Li L, et al. Apelin/APJ system: A bifunctional target for cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Cardiol. 2017;230:164-170.[6] Liang D, Han D, Fan W, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of apelin on transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in hindlimb ischemic mice via regulation of autophagy. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21914.[7] Zeng X, Yu SP, Taylor T, et al. Protective effect of apelin on cultured rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells against apoptosis. Stem Cell Res. 2012;8(3):357-367.[8] Park JS, Yang HN, Yi SW, et al. Neoangiogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells transfected with peptide-loaded and gene-coated PLGA nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2016;76:226-237.[9] 侯婧瑛,汪蕾,钟婷婷,等, apelin干预骨髓间充质干细胞在缺血缺氧条件下的生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(1): 6-12.[10] Lv B, Hua T, Li F,et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 α protects mesenchymal stem cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury via autophagy induction and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(5):2492-2499.[11] Shi XF, Wang H, Xiao FJ, et al. MiRNA-486 regulates angiogenic activity and survival of mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxia through modulating Akt signal. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;470(3):670-677.[12] Zou Y, Wang B, Fu W, et al. Apelin-13 Protects PC12 Cells from Corticosterone-Induced Apoptosis Through PI3K and ERKs Activation. Neurochem Res. 2016;41(7):1635-1644.[13] Zhang J, Liu Q, Hu X, et al. Apelin/APJ signaling promotes hypoxia-induced proliferation of endothelial progenitor cells via phosphoinositide-3 kinase/Akt signaling. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(3): 3829-3834.[14] Dicarlo M, Bianchi N, Ferretti C, et al. Evidence Supporting a Paracrine Effect of IGF-1/VEGF on Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Commitment. Cells Tissues Organs. 2016;201(5):333-341.[15] Hou J, Long H, Zhou C, et al. Long noncoding RNA Braveheart promotes cardiogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):4.[16] 伍权华,侯婧瑛,郭天柱,等.吡格列酮联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗改善大鼠心肌梗死后的心功能[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(23):3698-3704.[17] 晏平,侯婧瑛,郑韶欣,等.过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ促进外源性骨髓间充质干细胞表达Cx43的作用及机制干细胞表达Cx43的作用及机制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(23):3357-3365.[18] Ji ST, Kim H, Yun J, et al. Promising Therapeutic Strategies for Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Cardiovascular Regeneration: From Cell Priming to Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:3945403.[19] Li L, Li L, Zhang Z, et al. Hypoxia promotes bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell proliferation through apelin/APJ/autophagy pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015;47(5):362-367.[20] Li L, Zeng H, Chen JX. Apelin-13 increases myocardial progenitor cells and improves repair postmyocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012;303(5):H605-618.[21] Tempel D, de Boer M, van Deel ED, et al. Apelin enhances cardiac neovascularization after myocardial infarction by recruiting aplnr+ circulating cells. Circ Res. 2012;111(5):585-598.[22] Kuchroo P, Dave V, Vijayan A, et al. Paracrine factors secreted by umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce angiogenesis in vitro by a VEGF-independent pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(4): 437-450.[23] Rud'ko AS, Efendieva MK, Budzinskaya MV, et al. Influence of vascular endothelial growth factor on angiogenesis and neurogenesis. Vestn Oftalmol. 2017;133(3):75-81.[24] Crafts TD, Jensen AR, Blocher-Smith EC, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor: therapeutic possibilities and challenges for the treatment of ischemia. Cytokine. 2015;71(2):385-393.[25] Pedersen TO, Blois AL, Xue Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells induce endothelial cell quiescence and promote capillary formation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(1):23.[26] Mykhaylichenko VY, Kubyshkin AV, Samarin SA, et al. Experimental induction of reparative morphogenesis and adaptive reserves in the ischemic myocardium using multipotent mesenchymal bone marrow-derived stem cells. Pathophysiology. 2016;23(2):95-104.[27] Tang Y, Gan X, Cheheltani R, et al. Targeted delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor improves stem cell therapy in a rat myocardial infarction model. Nanomedicine. 2014;10(8):1711-1718.[28] Liu G, Li L, Huo D, et al. A VEGF delivery system targeting MI improves angiogenesis and cardiac function based on the tropism of MSCs and layer-by-layer self-assembly. Biomaterials. 2017;127:117-131. [29] Ikhapoh IA, Pelham CJ, Agrawal DK. Atherogenic Cytokines Regulate VEGF-A-Induced Differentiation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Endothelial Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:498328.[30] Xing Y, Hou J, Guo T, et al. microRNA-378 promotes mesenchymal stem cell survival and vascularization under hypoxic-ischemic conditions in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(6):130.[31] Yu JS, Cui W. Proliferation, survival and metabolism: the role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development. 2016;143(17):3050-3060.[32] Bader AM, Klose K, Bieback K, et al. Hypoxic Preconditioning Increases Survival and Pro-Angiogenic Capacity of Human Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stromal Cells In Vitro. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138477.[33] Ma J, Zhao Y, Sun L, et al. Exosomes Derived from Akt-Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Cardiac Regeneration and Promote Angiogenesis via Activating Platelet-Derived Growth Factor D. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(1):51-59.[34] Jia X, Pan J, Li X, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate angiogenesis and renal damage via promoting PI3k-Akt signaling pathway activation in vivo. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(7):838-845.[35] Huang C, Dai C, Gong K, et al. Apelin-13 protects neurovascular unit against ischemic injuries through the effects of vascular endothelial growth factor. Neuropeptides. 2016;60:67-74. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [5] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [6] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [7] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [8] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [9] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [10] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [11] | Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun. The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 754-760. |
| [12] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [13] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [14] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [15] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||