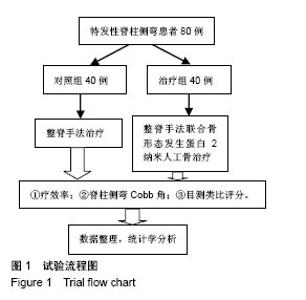
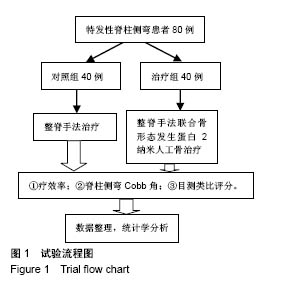
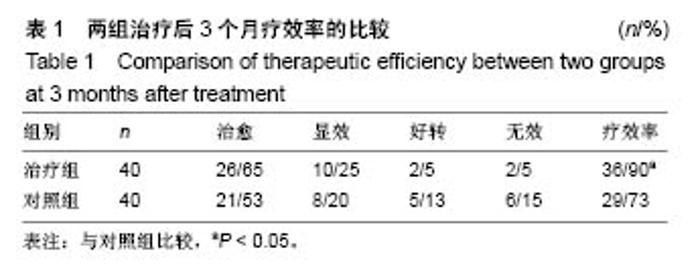
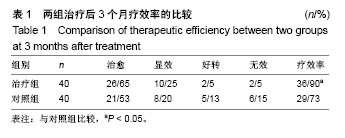
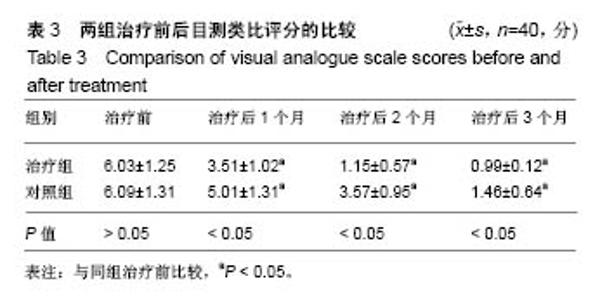
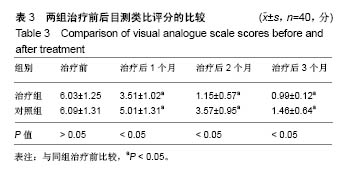
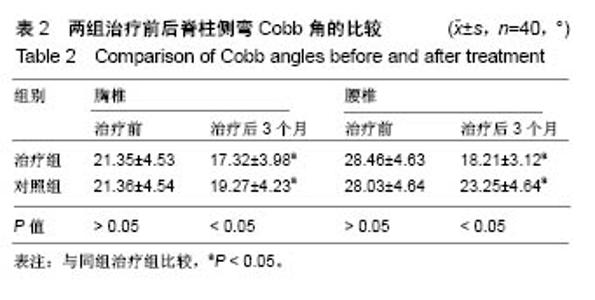
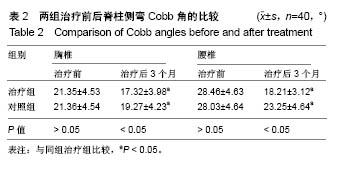
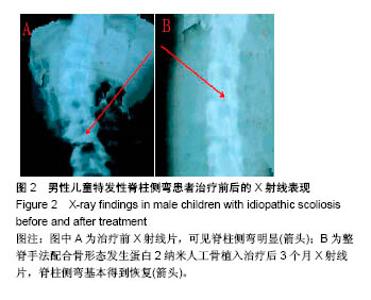
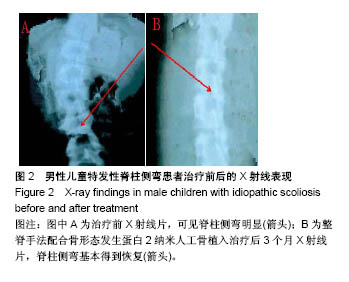
| [1] 张波波,陶惠人.青少年特发性脊柱侧弯与骨盆关系的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(13):1198-1201.[2] 王其飞,杨军林,范恒伟,等.Thrsp蛋白在青少年特发性脊柱侧弯患者MSCs成脂分化过程中的差异性表达和作用[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,23(3):263-269.[3] Hengwei F,Zifang H,Qifei W,et al.Prevalence of Idiopathic Scoliosis in Chinese Schoolchildren: A Large, Population- Based Study.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2016;41(3):259-264.[4] 刘海雁,朱泽章,史本龙,等.体感诱发电位联合运动诱发电位在Chiari畸形伴脊柱侧凸后路矫形手术中的应用价值[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(4):299-303.[5] 毛赛虎,史本龙,孙旭,等.支具治疗后初始Cobb角进展速率对青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者支具疗效的预测价值[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(4):333-337.[6] Grimes DT,Boswell CW,Morante NF,et al. Zebrafish models of idiopathic scoliosis link cerebrospinal fluid flow defects to spine curvature.Science.2016;352(6291):1341.[7] 司泽兵,吴继功,马华松,等.成人重度僵硬性脊柱侧后凸合并脊髓畸形的截骨手术治疗[J].颈腰痛杂志,2015,36(6):453-458.[8] 赵检,杨明园,李超,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的病因学研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(15):1383-1387.[9] 程剑洋,王策,马君,等.色努(Chêneau)支具在青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(9):794-799.[10] 管大凡,刘洪美,张聪,等.骨形态发生蛋白2/血管内皮生长因子165转染骨髓间充质干细胞复合多孔纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66修复兔桡骨缺损[J].中华创伤杂志,2015,31(4):353-359.[11] 何红晨,王谦,柳学明,等.三维超声用于青少年特发性脊柱侧凸评估的信度与效度研究[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2017,32(2): 146-150.[12] Charles YP,Sfeir G,Matterparrat V,et al.Cervical sagittal alignment in idiopathic scoliosis treated by posterior instrumentation and in situ bending.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2015; 40(7):419-27.[13] 张爱平,刘羲,刘志峰,等.基于3D打印的定制脊柱侧弯矫形器设计制造与舒适度评价[J].北京工业大学学报, 2017,43(4):518-525.[14] Xu JF,Yang GH,Pan XH,et al.Association of GPR126 gene polymorphism with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Chinese populations.Genomics.2015;105(2):101-107.[15] 叶晓愚,周忠亮,张全明.传统针法怪蟒翻身结合定向本体感觉神经肌肉促进疗法治疗脊柱侧弯三维矫形植骨融合内固定术后单侧梨状肌退变性疼痛一例并文献复习[J].中国全科医学, 2016, 19(36):4528-4532.[16] 陈强,张怡元,林妙阔,等.Iso-C臂三维导航系统指导下的脊柱侧弯椎弓根钉内固定:问题与优势[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(39): 6385-6389.[17] Kuru T,Yeldan I,Dereli EE,et al.The efficacy of three-dimensional Schroth exercises in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a randomised controlled clinical trial.Clin Rehabil. 2016;30(2):181-190. [18] 赵凤娜,秦柳花,彭虹菊,等.心理干预对特发性脊柱侧弯患者围手术期医学应对方式的影响分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016, 24(23):2203-2205.[19] 王宏伟,齐素青,张超,等.上颌快速扩弓联合前方牵引治疗骨性Ⅲ类错牙合畸形对上气道影响的锥形束CT分析[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2016,32(4):532-536.[20] Gozde G,Burcu D,Cigdem A,et al.Effect of a spinal brace on postural control in different sensory conditions in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A preliminary analysis.Gait Posture. 2015; 41(1):93-99.[21] 张波波,陶惠人.青少年特发性脊柱侧弯与骨盆关系的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(13):1198-1201.[22] 王英杰,贾连顺.人工椎间盘置换术与颈椎融合术治疗神经根型颈椎病手术疗效的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,23(19): 1734-1739.[23] Yang M,Li C,Li Y,et al.Application of 3D Rapid Prototyping Technology in Posterior Corrective Surgery for Lenke 1 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients.Medicine. 2015;94(8): e582.[24] 李忠海,侯树勋,吴闻文,等.单节段颈椎动态稳定器植入术对颈椎曲度和活动度的影响[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2013,(10):574-579.[25] 娄纪刚,刘浩,龚全,等.单节段PrestigeLP人工颈椎间盘置换术后置换节段活动度的影响因素分析[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2015,36(1): 20-24.[26] 栗向东,王臻,郭征,等.后路I期全脊椎整块切除治疗胸腰椎原发和转移性肿瘤的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2014,22(50): 336-340.[27] 楚戈,张宏其,唐明星,等.钛网及植骨融合修复中重度脊柱后凸畸形[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(22):4034-4041.[28] Bia&X M,ek.Mild Angle Early Onset Idiopathic Scoliosis Children Avoid Progression Under FITS Method(Functional Individual Therapy of Scoliosis).Medicine.2015;94(20):e863. |