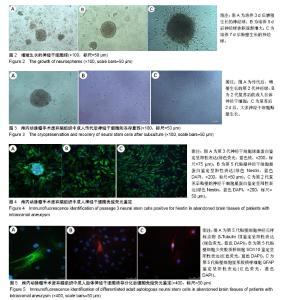
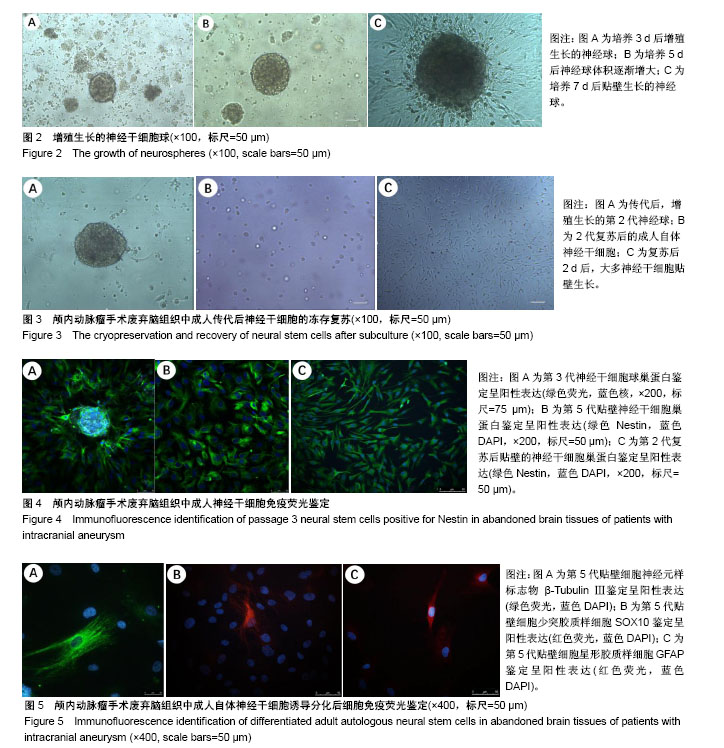
| [1] 李玲,李贵南.神经干细胞治疗新生儿胆红素脑病的进展[J].转化医学杂志, 2017,6(3):181-184. [2] 张涛,李文杰,王峰,等.小鼠室管膜下区神经干细胞增殖及分化研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(6):766-771.[3] Fu X, Li S, Zhou S, et al. Stimulatory effect of icariin on the proliferation of neural stem cells from rat hippocampus. BMC Complem Altern M. 2018;18(1):34. [4] 马浚宁,高俊玮,侯博儒,等.新生小鼠海马、嗅球及皮质神经干细胞的分离培养及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(45):7266-7272.[5] Roy NS, Wang S, Jiang L, et al. In vitro neurogenesis by progenitor cells isolated from the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med. 2000;6(3): 271-277. [6] Pagano SF, Impagnatiello F, Girelli M, et al. Isolation and Characterization of Neural Stem Cells from the Adult Human Olfactory Bulb. Stem Cells. 2000;18(4):295-300. [7] Belenguer G, Domingomuelas A, Ferrón SR, et al. Isolation, culture and analysis of adult subependymal neural stem cells. Differentiation. 2016;91(4-5):28-41. [8] Palmer TD, Schwartz PH, Taupin P, et al. Cell culture. Progenitor cells from human brain after death. Nature. 2001;411(6833):42-43.[9] Zheng W, Zhuge Q, Zhong M, et al. Neurogenesis in adult human brain after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotraum. 2013;30(22): 1872-1880. [10] Sgubin D, Aztiria E, Perin A, et al. Activation of endogenous neural stem cells in the adult human brain following subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85(8):1647-1655. [11] Zanni G, Martino ED, Omelyanenko A, et al. Lithium increases proliferation of hippocampal neural stem/progenitor cells and rescues irradiation-induced cell cycle arrest in vitro. Oncotarget. 2015;6(35): 37083-37097. [12] Giachino C, Basak O, Lugert S, et al. Molecular Diversity Subdivides the Adult Forebrain Neural Stem Cell Population. Stem Cells. 2014; 32(1):70-84.[13] 贺菊芳,余资江,朱晓瓞,等.SD大鼠胚胎神经干细胞悬浮培养与鉴定[J].贵阳医学院学报,2016,41(10):1128-1132. [14] Su P, Zhang J, Zhao F, et al. The interaction between microglia and neural stem/precursor cells. Brain Res Bull. 2014;109:32-38.[15] Drago D, Cossetti C, Iraci N, et al. The stem cell secretome and its role in brain repair. Biochimie. 2013;95(12):2271-2285. [16] Tomita T, Akimoto J, Haraoka J, et al. Clinicopathological significance of expression of nestin, a neural stem/progenitor cell marker, in human glioma tissue. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2014;31(3):162-171.[17] Fitzgerald DP, Cole SJ, Hammond A, et al. Characterization of neogenin-expressing neural progenitor populations and migrating neuroblasts in the embryonic mouse forebrain. Neuroscience. 2006; 142(3): 703-716.[18] Hegarty SV, Spitere K, Sullivan AM, et al. Ventral midbrain neural stem cells have delayed neurogenic potential in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 2014; 559(5):193-198. [19] Nguyen HX, Hooshmand MJ, Saiwai H, et al. Systemic neutrophil depletion modulates the migration and fate of transplanted human neural stem cells to rescue functional repair. J Neurosci. 2017;37(38): 2785-2716. [20] 王灿.神经干细胞及其在神经损伤中的应用进展[J].现代医药卫生,2014, 30(3):381-383. [21] Tønnesen J, Parish CL, Sørensen AT, et al. Functional Integration of Grafted Neural Stem Cell-Derived Dopaminergic Neurons Monitored by Optogenetics in an In Vitro Parkinson Model. PLoS One. 2011;6(3): e17560. [22] Ramos-Gómez M, Martínez-Serrano A.Tracking of iron-labeled human neural stem cells by magnetic resonance imaging in cell replacement therapy for Parkinson's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(1):49-52.[23] Becerra GD, Tatko LM, Pak ES, et al. Transplantation of GABAergic neurons but not astrocytes induces recovery of sensorimotor function in the traumatically injured brain. Behav Brain Res. 2007;179(1):118-125. [24] 吴惺,张冬,左传涛,等.自体神经干细胞移植后功能恢复的影像学评价[J].复旦学报(医学版),2005,25(6):46-48. [25] Blaya MO, Tsoulfas P, Bramlett HM, et al. Neural progenitor cell transplantation promotes neuroprotection, enhances hippocampal neurogenesis, and improves cognitive outcomes after traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2015;264:67-81. [26] Brewer GJ, Espinosa J, Mcilhaney MP, et al. Culture and regeneration of human neurons after brain surgery. J Neurosci Meth. 2001;107(1-2): 15-23. [27] Shevde N. Stem cells: flexible friends.Nature.2012;483(7387):S22-26.[28] Shetty AK.Hippocampal injury-induced cognitive and mood dysfunction, altered neurogenesis, and epilepsy:can early neural stem cell grafting intervention provide protection? Epilepsy Behav. 2014;38:117-124.[29] Butti E, Cusimano M, Bacigaluppi M, et al. Neurogenic and non-neurogenic functions of endogenous neural stem cells. Front Neurosci-Switz. 2014;8(8):92. [30] Cova L, Armentero MT, Zennaro E, et al. Multiple neuro-genic and neurorescue effects of human mesenchymal stem cell after transplantation in an experimental model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2010;1311:12-27. [31] Lee JS, Hong JM, Moon GJ, et al. A long-term follow-up study of intravenous autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with ischemic stroke. Stem Cells. 2010;28(6):1099-1106. |